(Press-News.org) Dishes like Brazilian steak and Indian kidney bean curry have an especially large biodiversity footprint, or impact on biodiversity, according to a study published February 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Elissa Cheng from the National University of Singapore, Singapore, and colleagues.
Food choices can have significant environmental impacts. Previous research has begun to develop datasets that identify the encroachment of specific crops on the ranges of birds, mammals and amphibians. Based on these data, Cheng and colleagues estimated how 151 different popular dishes from around the world impact biodiversity.
The authors used lists of popular dishes taken from CNN.com and TasteAtlas.com, standardizing each dish to be 825 kCal. They calculated the biodiversity footprint of each dish’s ingredient by looking at the richness, conservation status, and range of wild mammals, birds, and amphibians within the agricultural land used for the specific product, and added each ingredient’s footprint together to generate an overall biodiversity footprint for every dish. Footprint scores shifted depending on whether the ingredient was locally or globally sourced, and industrially or small-scale farmed.
The top twenty dishes with the largest biodiversity footprints included several Brazilian steak dishes (picanha, churrasco, fraldinha) and other meat dishes like salsa verde pork, yukgaejang (a Korean spicy beef and vegetable stew), and caldo de pollo (chicken soup)—but also vegan dishes like dal (lentil soup), rajma (a kidney bean curry), chana masala (chickpea curry) and idli (a fermented savory rice cake). Overall, these tended to be dishes made with beef and chicken, as well as legumes and rice. For vegan and vegetarian dishes of the Indian subcontinent, rice and legumes grown industrially tended to have especially high impacts on threatened species and range biodiversity indicators. Brazilian beef and lamb dishes also had high biodiversity impacts due to the conversion of Amazon rainforest and other diverse ecosystems to pasture. The twenty dishes with the smallest biodiversity footprints tended to be vegetarian/vegan, starchy, and grain or potato-based—French fry-style recipes like pommes frites and triple cooked chips, kartoffelpuffer (a German potato pancake), and baguettes, for instance.
The authors note they didn’t differentiate between wildlife able to survive in cultivated habitats, versus wildlife with specific natural habitat requirements—and looked specifically at mammals, birds, and amphibians. They also note the dishes examined here are not necessarily representative and focus on dishes from countries with a high GDP, and that recipe variation might lead to different results. Regardless, this study underscores the importance of specific ingredients and areas of production in terms of biodiversity impact.
The authors add: “Small changes in the dish we choose to eat and where we get the ingredients from can go a long way in preventing species extinctions. In addition to the large footprint of beef and lamb dishes from countries containing biodiversity hotspots, vegetarian dishes from highly biodiverse and under strong human pressure countries like India, can be also very detrimental for biodiversity.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0296492
Citation: Cheng EMY, Cheng CML, Choo J, Yan Y, Carrasco LR (2024) Biodiversity footprints of 151 popular dishes from around the world. PLoS ONE 19(2): e0296492. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0296492
Author Countries: Singapore
Funding: L.R.C. and Y.Y. received funds from the Ministry of Education of Singapore. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Biodiversity footprints for 151 dishes from around the world show that dishes with a larger impact on biodiversity tend to be meat, legume, or rice-based
And come from countries with high biodiversity plus high agricultural pressure
2024-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Did neanderthals use glue? Researchers find evidence that sticks
2024-02-21
Neanderthals created stone tools held together by a multi-component adhesive, a team of scientists has discovered. Its findings, which are the earliest evidence of a complex adhesive in Europe, suggest these predecessors to modern humans had a higher level of cognition and cultural development than previously thought.
The work, reported in the journal Science Advances, included researchers from New York University, the University of Tübingen, and the National Museums in Berlin.
“These ...
Severe maternal grief associated with increased risk of heart failure in child
2024-02-21
Prenatal stress is a potential risk factor for cardiovascular disease in offspring later in life. In a new study published today in JACC: Heart Failure, maternal loss of a partner or child shortly before or during pregnancy was found to be associated with increased risk of heart failure up to middle-age in the child.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the organs, causing a variety of symptoms. Heart failure cannot be cured but symptoms can be treated and managed to improve quality and length of life. According to the World Heart Federation, more than 64 million people worldwide have heart failure.
According ...
Increasingly similar or different? Centuries-long analysis suggests biodiversity is differentiating and homogenizing to a comparable extent
2024-02-21
The tendency of communities and the species within them to become more similar or more distinct across landscapes – biotic homogenisation and differentiation – are approximately balanced, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
Led by researchers at the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the researchers analysed 527 datasets collected from ecosystems like grasslands, shrublands, and coral reefs as far back as 500 years ago. The analysis is the first of its kind to provide ...
Long COVID linked to persistently high levels of inflammatory protein: a potential biomarker and target for treatments
2024-02-21
SARS-CoV-2 triggers the production of the antiviral protein IFN-γ, which is associated with fatigue, muscle ache and depression. New research shows that in Long COVID patients, IFN-y production persists until symptoms improve, highlighting a potential biomarker and a target for therapies.
A University of Cambridge-led study identifies the protein interferon gamma (IFN-γ) as a potential biomarker for Long COVID fatigue and highlights an immunological mechanism underlying the disease, which could pave the way for the development ...
Snaking toward a universal antivenom
2024-02-21
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research scientists have developed an antibody that can block the effects of lethal toxins in the venoms of a wide variety of snakes found throughout Africa, Asia and Australia.
The antibody, which protected mice from the normally deadly venom of snakes including black mambas and king cobras, is described on February 21, 2024, in Science Translational Medicine. The new research used forms of the toxins produced in the laboratory to screen billions of different human antibodies and identify one that can block the toxins’ activity. It represents a large step toward a universal ...
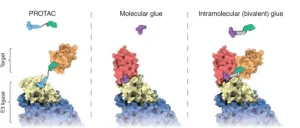
New system triggers cellular waste disposal
2024-02-21
Living cells resemble highly organized small towns - in addition to energy production, transportation systems, and construction, cells also require efficient waste disposal. Most proteins, which shape and sustain cellular function, have only a limited half-life and must eventually be disposed of, along with defective and unwanted proteins. This vital task falls upon specialized enzymes known as ubiquitin ligases, which tag obsolete proteins for degradation, guiding them to the cellular recycling center, ...
Possible trigger for autoimmune diseases discovered : B cells teach T cells which targets must not be attacked
2024-02-21
Immune cells must learn not to attack the body itself. A team of researchers from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU) has discovered a previously unknown mechanism behind this: other immune cells, the B cells, contribute to the "training" of the T cells in the thymus gland. If this process fails, autoimmune diseases can develop. The study confirms this for Neuromyelitis optica, a disease similar to Multiple Sclerosis. Other autoimmune diseases may be linked to the failure ...
Detecting pathogens faster and more accurately by melting DNA
2024-02-21
A new analysis method can detect pathogens in blood samples faster and more accurately than blood cultures, which are the current state of the art for infection diagnosis. The new method, called digital DNA melting analysis, can produce results in under six hours, whereas culture typically requires 15 hours to several days, depending on the pathogen.
Not only is this method faster than blood cultures, it’s also significantly less likely to generate false positives compared to other emerging DNA detection-based technologies such as Next Generation Sequencing.
Why ...
MD Anderson research highlights for February 21, 2024
2024-02-21
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson offer insights into drug-drug interactions for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes; patient-derived xenograft models as a viable translational ...
Engineers use AI to wrangle fusion power for the grid
2024-02-21
In the blink of an eye, the unruly, superheated plasma that drives a fusion reaction can lose its stability and escape the strong magnetic fields confining it within the donut-shaped fusion reactor. These getaways frequently spell the end of the reaction, posing a core challenge to developing fusion as a non-polluting, virtually limitless energy source.
But a Princeton-led team composed of engineers, physicists, and data scientists from the University and the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have harnessed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
[Press-News.org] Biodiversity footprints for 151 dishes from around the world show that dishes with a larger impact on biodiversity tend to be meat, legume, or rice-basedAnd come from countries with high biodiversity plus high agricultural pressure