(Press-News.org) The University of Notre Dame has received a Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Award from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative to study genes that affect neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
This is Notre Dame’s first award from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative.
The award will fund a partnership between Cody Smith, the Elizabeth and Michael Gallagher Associate Professor of Biological Sciences at Notre Dame and a 2017 Alfred P. Sloan Fellow, and Beth Stevens, member of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and a 2015 MacArthur Fellow. With their combined expertise in neurological development, they will explore how gene expression and function changes with aging, allowing neurodegenerative diseases to occur.
“Instead of looking at an individual gene, our approach is to look at a suite of genes that work individually or together and decipher what their core function is,” Smith said. “By understanding their combined function we can get a better picture of what is happening in the brain and, eventually, why they enter disease states.”
Stevens’ team uses cutting-edge sequencing to identify multiple genes and how they are expressed at different ages. Her team will provide a list of genes to the Smith Lab, which will use advanced imaging approaches on a zebrafish model to analyze which genes are important for modifying microglia, or the cells that are responsible for regulating brain development and healing injured tissue. Stevens’ team will simultaneously analyze the genes in human microglia.
Together, the researchers will look at how those microglia shift into disease states and therefore may not work properly in defending the brain against neurodegenerative diseases.
“We don’t really know how specific risk genes change microglia function in disease. This collaborative project will allow us to develop new tools to track and manipulate microglia to better understand how genes relate to function and to identify conserved mechanistic pathways,” Stevens said.
The award will provide $200,000 over an 18-month period, and Smith and Stevens will also gain long-term access to the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative Neurodegeneration Challenge Network. The network offers support, mentoring and collaborative interactions with researchers across a broad range of fields to foster collaboration for tackling neurodegenerative disease.
Contact: Brandi Wampler, associate director of media relations, 574-631-2632, brandiwampler@nd.edu
END
Notre Dame receives Chan Zuckerberg Initiative award for neurodegenerative disease research
2024-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Shaping the Future of Skin Aging: 15th International Conference on Skin Challenges, November 2024
2024-02-21
Following the huge success of the previous edition, the 15th edition of the Skin Ageing & Challenges International Conference is set to take place on November 7-8, 2024, at Corinthia Palace in Malta. The conference will provide attendees with a comprehensive overview of the current landscape and future prospects in skin aging research.
Professor Jean Krutmann, conference president, is just as excited as we are: “Skin aging is complex, but by working together across different fields, we’re making incredible strides. This conference is where all that collaboration shines, helping us find new ways to keep our skin healthy and vibrant.”
Skin ...
Black hole at center of the Milky Way resembles a football
2024-02-21
BERKS, Pa. — The supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way is spinning so quickly it is warping the spacetime surrounding it into a shape that can look like a football, according to a new study using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the U.S. National Science Foundation’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA). That football shape suggests the black hole is spinning at a substantial speed, which researchers estimated to be about 60% of its potential limit.
The work, led by Penn State Berks Professor of Physics Ruth Daly, was published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Astronomers call this giant ...
Stowers Institute Scientific Director Kausik Si receives coveted award from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative
2024-02-21
KANSAS CITY, MO—February 21, 2024—The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) has announced the awardees of their second cycle of Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Awards, part of the CZI Neurodegeneration Challenge Network (NDCN).
Scientific Director Kausik Si, Ph.D., from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research will receive an award for the project titled, “Tuning memory by altering amyloids,” which will be conducted alongside Investigator Lukasz Joachimiak, Ph.D., from the University of Texas Southwestern.
The Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Awards were launched in 2018 to investigate unsolved mysteries ...
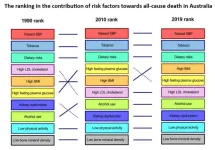
Raised blood pressure is the leading risk factor for death in Australia
2024-02-21
Raised blood pressure has been the leading risk factor for death in Australia for the past three decades, according to a study published February 21, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE led by Alta Schutte and Xiaoyue Xu from The George Institute for Global Health and UNSW, Sydney, with colleagues across Australia. It is also the main contributor to deaths from cardiovascular disease (CVD) specifically.
Raised blood pressure has long been recognized as a contributing factor to CVD and death, but is not always prioritized in national health plans. In this study, researchers focused on Australia, which lags ...
Biodiversity footprints for 151 dishes from around the world show that dishes with a larger impact on biodiversity tend to be meat, legume, or rice-based
2024-02-21
Dishes like Brazilian steak and Indian kidney bean curry have an especially large biodiversity footprint, or impact on biodiversity, according to a study published February 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Elissa Cheng from the National University of Singapore, Singapore, and colleagues.
Food choices can have significant environmental impacts. Previous research has begun to develop datasets that identify the encroachment of specific crops on the ranges of birds, mammals and amphibians. Based on these data, Cheng and colleagues estimated how 151 ...
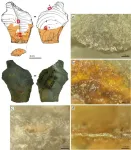
Did neanderthals use glue? Researchers find evidence that sticks
2024-02-21
Neanderthals created stone tools held together by a multi-component adhesive, a team of scientists has discovered. Its findings, which are the earliest evidence of a complex adhesive in Europe, suggest these predecessors to modern humans had a higher level of cognition and cultural development than previously thought.
The work, reported in the journal Science Advances, included researchers from New York University, the University of Tübingen, and the National Museums in Berlin.
“These ...
Severe maternal grief associated with increased risk of heart failure in child
2024-02-21
Prenatal stress is a potential risk factor for cardiovascular disease in offspring later in life. In a new study published today in JACC: Heart Failure, maternal loss of a partner or child shortly before or during pregnancy was found to be associated with increased risk of heart failure up to middle-age in the child.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the organs, causing a variety of symptoms. Heart failure cannot be cured but symptoms can be treated and managed to improve quality and length of life. According to the World Heart Federation, more than 64 million people worldwide have heart failure.
According ...
Increasingly similar or different? Centuries-long analysis suggests biodiversity is differentiating and homogenizing to a comparable extent
2024-02-21
The tendency of communities and the species within them to become more similar or more distinct across landscapes – biotic homogenisation and differentiation – are approximately balanced, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
Led by researchers at the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the researchers analysed 527 datasets collected from ecosystems like grasslands, shrublands, and coral reefs as far back as 500 years ago. The analysis is the first of its kind to provide ...
Long COVID linked to persistently high levels of inflammatory protein: a potential biomarker and target for treatments
2024-02-21
SARS-CoV-2 triggers the production of the antiviral protein IFN-γ, which is associated with fatigue, muscle ache and depression. New research shows that in Long COVID patients, IFN-y production persists until symptoms improve, highlighting a potential biomarker and a target for therapies.
A University of Cambridge-led study identifies the protein interferon gamma (IFN-γ) as a potential biomarker for Long COVID fatigue and highlights an immunological mechanism underlying the disease, which could pave the way for the development ...
Snaking toward a universal antivenom
2024-02-21
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research scientists have developed an antibody that can block the effects of lethal toxins in the venoms of a wide variety of snakes found throughout Africa, Asia and Australia.
The antibody, which protected mice from the normally deadly venom of snakes including black mambas and king cobras, is described on February 21, 2024, in Science Translational Medicine. The new research used forms of the toxins produced in the laboratory to screen billions of different human antibodies and identify one that can block the toxins’ activity. It represents a large step toward a universal ...