(Press-News.org) KANSAS CITY, MO—February 21, 2024—The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) has announced the awardees of their second cycle of Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Awards, part of the CZI Neurodegeneration Challenge Network (NDCN).
Scientific Director Kausik Si, Ph.D., from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research will receive an award for the project titled, “Tuning memory by altering amyloids,” which will be conducted alongside Investigator Lukasz Joachimiak, Ph.D., from the University of Texas Southwestern.
The Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Awards were launched in 2018 to investigate unsolved mysteries of neurodegenerative disease biology by aligning two scientists with diverse expertise. Thirty teams were chosen for the first cycle with more than half of these 18-month pilot projects receiving four-year acceleration phase funding, confirming that novel, bold, out-of-the-box based research is not only possible but can lead to transformative science.
Following the success of the first cycle, the NDCN expanded the research scope beyond neurodegenerative disease, seeking proposals covering broader neuroscience biology. While extensive research has focused on pathologic amyloids behind devastating diseases like Alzheimer’s, Si and Joachimiak are tackling a fundamentally different question: Can functional amyloids known to aid in memory formation be fine-tuned to enhance the acquisition and duration of long-term memories?
“This funding will allow us to explore a truly unorthodox idea-is it possible to expedite amyloid formation or increase the stability of amyloid to either reduce the threshold of memory formation or to make a memory more stable,” Si said. “Since this is an unorthodox idea, it is important to use a multifaceted approach. The collaboration between labs not only brings complementary experimental expertise, but also diverse ways of thinking about the problem,” he explained.
Neurodegeneration and amyloid have been virtually synonymous for over a century. For Si, whose research focuses on molecular mechanisms underlying memory, the discovery that certain amyloids are not only beneficial and functional but are also necessary for maintaining long-term memories was surprising. This radically challenged previous assumptions of amyloids as pathologic and required rethinking on how and why they form.
A certain class of protein common across species can form amyloid that aids in long-term memory. The amyloid form of this protein converts a memory from transient to persistent and in fruit flies, research from the Si Lab published in Science in 2020 resolved the structure of the first example of a memory boosting amyloid called Orb2.
Technological advances are now enabling scientists to manipulate the amyloid protein assembly process. The Joachimiak Lab, with expertise in protein engineering, and the Si Lab are joining forces to rationally design and test Orb2 variants as memory conduits. The team hypothesizes that enhancing the formation and stability of Orb2 will make memory formation easier and extend its duration, potentially uncovering fundamental insights into how amyloids can be beneficial.
“The award from CZI to Kausik and his collaborator is a nod to the Stowers Institute’s focus on spurring discovery and contributing scientific insight into some of the most difficult problems in the life sciences,” said Stowers Institute President and Chief Scientific Officer Alejandro Sánchez Alvarado, Ph.D.
About the Stowers Institute for Medical Research
Founded in 1994 through the generosity of Jim Stowers, founder of American Century Investments, and his wife, Virginia, the Stowers Institute for Medical Research is a non-profit, biomedical research organization with a focus on foundational research. Its mission is to expand our understanding of the secrets of life and improve life’s quality through innovative approaches to the causes, treatment, and prevention of diseases.
The Institute consists of 20 independent research programs. Of the approximately 500 members, over 370 are scientific staff that include principal investigators, technology center directors, postdoctoral scientists, graduate students, and technical support staff. Learn more about the Institute at www.stowers.org and about its graduate program at www.stowers.org/gradschool.
Media Contact:
Joe Chiodo, Head of Media Relations
724.462.8529
press@stowers.org
About the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative
The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative was founded in 2015 to help solve some of society’s toughest challenges — from eradicating disease and improving education to addressing the needs of our local communities. Our mission is to build a more inclusive, just, and healthy future for everyone. For more information, please visit chanzuckerberg.com
END
Stowers Institute Scientific Director Kausik Si receives coveted award from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative
Funding will allow the team to explore a “truly unorthodox” idea related to memory formation
2024-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
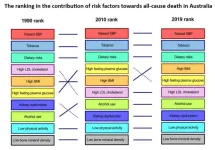
Raised blood pressure is the leading risk factor for death in Australia
2024-02-21
Raised blood pressure has been the leading risk factor for death in Australia for the past three decades, according to a study published February 21, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE led by Alta Schutte and Xiaoyue Xu from The George Institute for Global Health and UNSW, Sydney, with colleagues across Australia. It is also the main contributor to deaths from cardiovascular disease (CVD) specifically.
Raised blood pressure has long been recognized as a contributing factor to CVD and death, but is not always prioritized in national health plans. In this study, researchers focused on Australia, which lags ...
Biodiversity footprints for 151 dishes from around the world show that dishes with a larger impact on biodiversity tend to be meat, legume, or rice-based
2024-02-21
Dishes like Brazilian steak and Indian kidney bean curry have an especially large biodiversity footprint, or impact on biodiversity, according to a study published February 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Elissa Cheng from the National University of Singapore, Singapore, and colleagues.
Food choices can have significant environmental impacts. Previous research has begun to develop datasets that identify the encroachment of specific crops on the ranges of birds, mammals and amphibians. Based on these data, Cheng and colleagues estimated how 151 ...
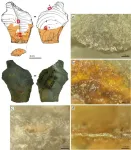
Did neanderthals use glue? Researchers find evidence that sticks
2024-02-21
Neanderthals created stone tools held together by a multi-component adhesive, a team of scientists has discovered. Its findings, which are the earliest evidence of a complex adhesive in Europe, suggest these predecessors to modern humans had a higher level of cognition and cultural development than previously thought.
The work, reported in the journal Science Advances, included researchers from New York University, the University of Tübingen, and the National Museums in Berlin.
“These ...
Severe maternal grief associated with increased risk of heart failure in child
2024-02-21
Prenatal stress is a potential risk factor for cardiovascular disease in offspring later in life. In a new study published today in JACC: Heart Failure, maternal loss of a partner or child shortly before or during pregnancy was found to be associated with increased risk of heart failure up to middle-age in the child.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the organs, causing a variety of symptoms. Heart failure cannot be cured but symptoms can be treated and managed to improve quality and length of life. According to the World Heart Federation, more than 64 million people worldwide have heart failure.
According ...
Increasingly similar or different? Centuries-long analysis suggests biodiversity is differentiating and homogenizing to a comparable extent
2024-02-21
The tendency of communities and the species within them to become more similar or more distinct across landscapes – biotic homogenisation and differentiation – are approximately balanced, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
Led by researchers at the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the researchers analysed 527 datasets collected from ecosystems like grasslands, shrublands, and coral reefs as far back as 500 years ago. The analysis is the first of its kind to provide ...
Long COVID linked to persistently high levels of inflammatory protein: a potential biomarker and target for treatments
2024-02-21
SARS-CoV-2 triggers the production of the antiviral protein IFN-γ, which is associated with fatigue, muscle ache and depression. New research shows that in Long COVID patients, IFN-y production persists until symptoms improve, highlighting a potential biomarker and a target for therapies.
A University of Cambridge-led study identifies the protein interferon gamma (IFN-γ) as a potential biomarker for Long COVID fatigue and highlights an immunological mechanism underlying the disease, which could pave the way for the development ...
Snaking toward a universal antivenom
2024-02-21
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research scientists have developed an antibody that can block the effects of lethal toxins in the venoms of a wide variety of snakes found throughout Africa, Asia and Australia.
The antibody, which protected mice from the normally deadly venom of snakes including black mambas and king cobras, is described on February 21, 2024, in Science Translational Medicine. The new research used forms of the toxins produced in the laboratory to screen billions of different human antibodies and identify one that can block the toxins’ activity. It represents a large step toward a universal ...
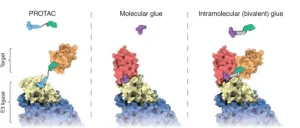
New system triggers cellular waste disposal
2024-02-21
Living cells resemble highly organized small towns - in addition to energy production, transportation systems, and construction, cells also require efficient waste disposal. Most proteins, which shape and sustain cellular function, have only a limited half-life and must eventually be disposed of, along with defective and unwanted proteins. This vital task falls upon specialized enzymes known as ubiquitin ligases, which tag obsolete proteins for degradation, guiding them to the cellular recycling center, ...
Possible trigger for autoimmune diseases discovered : B cells teach T cells which targets must not be attacked
2024-02-21
Immune cells must learn not to attack the body itself. A team of researchers from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU) has discovered a previously unknown mechanism behind this: other immune cells, the B cells, contribute to the "training" of the T cells in the thymus gland. If this process fails, autoimmune diseases can develop. The study confirms this for Neuromyelitis optica, a disease similar to Multiple Sclerosis. Other autoimmune diseases may be linked to the failure ...
Detecting pathogens faster and more accurately by melting DNA
2024-02-21
A new analysis method can detect pathogens in blood samples faster and more accurately than blood cultures, which are the current state of the art for infection diagnosis. The new method, called digital DNA melting analysis, can produce results in under six hours, whereas culture typically requires 15 hours to several days, depending on the pathogen.
Not only is this method faster than blood cultures, it’s also significantly less likely to generate false positives compared to other emerging DNA detection-based technologies such as Next Generation Sequencing.
Why ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
[Press-News.org] Stowers Institute Scientific Director Kausik Si receives coveted award from the Chan Zuckerberg InitiativeFunding will allow the team to explore a “truly unorthodox” idea related to memory formation