(Press-News.org) Memphis, Tenn. (February 26, 2024) – Shelley White-Means, PhD, a professor of Health Economics in the Department of Interprofessional Education and the director of the Consortium for Health Education, Economic Empowerment and Research (CHEER) at UT Health Science Center, recently received a $1.5 million, four-year grant from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities to explore the root causes of the disparity in breast cancer survival of Black women compared to white women.
Dr. White-Means and a team will look beyond the social determinants of health to explore what she terms “the intersectionality of race, residential segregation, and poverty as a driver of health disparities in breast cancer.” The goal is to identify effective public policy interventions and strategies to change the picture for Black women diagnosed with breast cancer.
The team includes Sam Li, PhD, assistant professor, Clinical Pharmacy and Translational Science, and Arash Shaban-Nejad, PhD, MPH, associate professor of Pediatrics, both from UT Health Science Center. Also on the team are University of Memphis faculty, Jill Dapremont, professor and division director of Family, Community, Health System Science; Daphene McFerrin, executive director of the Benjamin L. Hooks Institute for Social Change; and Elana Delavega, PhD, MSW, professor in the School of Social Work.
Using unique quantitative and qualitative methods the team will identify modifiable pathways to breast health, such as disadvantaged racially segregated neighborhoods, that are the “root causes” of social determinants of health.
“We’re adding a different look. We say that limited social determinants of health are just symptoms of disparities in breast cancer outcomes,” Dr. White-Means explained.
“We're calling the factors that we want to consider the root causes,” she continued. “What causes a neighborhood to lack social determinants of health resources? What policies and practices have created neighborhoods that have food insecurity, limited access to health care providers, and limited jobs and economic stability?”
The long-term goal is to identify interventions and policy solutions that transform disparities that are rooted in seemingly unalterable place-related community factors.
Dr. White-Means has spent her career exploring the racial disparity in outcomes for breast cancer survival. While the overall incidence of breast cancer is lower in Black women, they are 1.4 times more likely to die of breast cancer than white women.
She has looked at the perspectives of breast cancer survivors, attitudes and practices of the health care community, cultural and genetic issues, geographic location, and other factors that contribute to this disparity in breast cancer survival of Black women compared to white women in Memphis and elsewhere.
“I want to know why,” she says. “Why is it that we have this higher death rate among Black women compared to white women? What is going on in Memphis? We have a high-quality medical system, we have a high-quality cancer center, we have all this phenomenal care system. Why is it that Black women are dying more than white women?”
The mission of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center is transforming lives through collaborative and inclusive education, research, scholarship, clinical care, and public service. With six colleges – Dentistry, Graduate Health Sciences, Health Professions, Medicine, Nursing, and Pharmacy – at its main campus in Memphis, in addition to educational and clinical campuses at major hospitals in Memphis, Knoxville, Chattanooga, and Nashville, and sites across the state, UTHSC strives to fulfill its vision: Healthy Tennesseans. Thriving Communities. For more information, visit www.uthsc.edu. You can find the University of Tennessee Health Science Center on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, X, and YouTube.
END
University of Tennessee Health Science Center professor awarded $1.5m to study 'root causes' of disparity in breast cancer survival of Black women and white women
2024-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Steering and accelerating electrons at the microchip scale
2024-02-26
Stanford researchers are getting closer to building a tiny electron accelerator based on “accelerator-on-a-chip” technology with broad potential applications in studying physics as well as medical and industrial uses.
The researchers have demonstrated that a silicon dielectric laser accelerator, or DLA, can now both speed up and confine electrons, creating a focused beam of high-energy electrons. “If the electrons were microscopic cars, it’s as if, for the first time, we’re steering and we have our foot on the gas,” said Payton Broaddus, PhD ’23 in electrical engineering and the lead author on a paper published on ...
City of Hope scientists devise novel strategy to seek and destroy leukemia stem cells
2024-02-26
FINDINGS
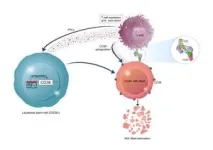
Scientists at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, have devised an innovative approach to target and destroy hard-to-kill leukemia stem cells. The journal Blood published the preclinical findings today.
By overcoming challenges, such as drug resistance and treatment relapse common to patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the therapy method could provide a less toxic and more effective approach for older and sicker patients who don’t quality for stem cell transplants — currently the only cure for AML available.
Type II interferon (IFNy), a substance produced by immune cells, disrupts ...
Laser-focused look at spinning electrons shatters world record for precision
2024-02-26
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Scientists are getting a more detailed look than ever before at the electrons they use in precision experiments.
Nuclear physicists with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility have shattered a nearly 30-year-old record for the measurement of parallel spin within an electron beam – or electron beam polarimetry, for short. The achievement sets the stage for high-profile experiments at Jefferson Lab that could open the door to new physics discoveries.
In a peer-reviewed ...
BU researchers identify potential new subtype of chronic traumatic encephalopathy
2024-02-26
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, February 26, 2024
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
BU Researchers Identify Potential New Subtype of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
One in six cases have a distinct distribution of disease, clinical profile
(Boston)—Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease defined by abnormal tau protein accumulating in a particular pattern in specific regions of the brain.
Studies to-date suggest CTE begins in the outermost layer of the frontal lobe, the neocortex, where it then spreads to connected brain regions. Later, in high-stage disease, ...
BU researchers describe new technological platform to accelerate drug development
2024-02-26
EMBARGOED by Cell until 11 am ET Feb. 26, 2024
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
BU Researchers Describe New Technological Platform to
Accelerate Drug Development
(Boston)— Drug development is currently an extremely long, expensive and inefficient process. Findings generated in a lab are often very hard to replicate once translated into animal models or in humans.
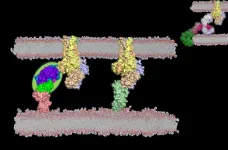
A family of pharmacological targets, on which approximately 35% of FDA-approved drugs work, consists of receptors at the surface ...
The small intestine adapt its size according to nutrient intake
2024-02-26
One of the most striking examples of gut plasticity can be observed in animals that are exposed to prolonged periods of fasting, such as hibernating animals or phyton snakes that goes for months without eating, where the gut shrinks with as much as 50%, but recovers in size following a few days of re-feeding. Importantly, the capacity of the gut to undergo resizing is broadly conserved. Hence, in humans, an increase in gut size is observed during pregnancy, which facilitates the uptake of nutrients to support the growth of the fetus.
The Colombani Andersen ...
Is it possible to predict when prejudice will occur?
2024-02-26
What if it were possible to use a scientific model to predict hate crimes, protests, or conflict? Researchers at McGill University and University of Toronto have begun the groundwork to develop a formal predictive model of prejudice, similar to meteorological weather predictions.
The model can be explained by the equation: Prejudice = Threat – Contact + Identification, “with some numbers involved,” says lead author Eric Hehman, Associate Professor in the Department of Psychology and lead author of a new study published in Psychological ...
Affective computing: Connecting computing with human emotions for empathetic AI
2024-02-26
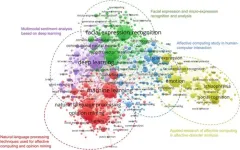
Imagine a world where your smartphone can detect your mood just by the way you type a message or the tone of your voice. Picture a car that adjusts its music playlist based on your stress levels during rush hour traffic. These scenarios are not just futuristic fantasies. They are glimpses into the rapidly evolving field of affective computing. Affective computing is a multidisciplinary field integrating computer science, engineering, psychology, neuroscience and other related disciplines. A new and comprehensive review on affective computing was published Jan. 5 in Intelligent ...
Demystifying “black box” audio models
2024-02-26
AI decision-making is now common in self-driving cars, patient diagnosis and legal consultation, and it needs to be safe and trustworthy. Researchers have been trying to demystify complex AI models by developing interpretable and transparent models, collectively known as explainable AI methods or XAI methods. A research team offered their insight specifically into audio XAI models in a review article published Jan. 23 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Although audio tasks are less researched than visual tasks, their expressive power is not less important. Audio signals are easy to understand and communicate, as they typically depend less on expert explanations ...
JMIR Neurotechnology invites submissions on brain-computer interfaces (BCIs)
2024-02-26
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue in JMIR Neurotechnology exploring brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) that represent the transformative convergence of neuroscience, engineering, and technology. The peer-reviewed journal aims to bridge the gap between clinical neuroscience and information technology by providing a platform for applied human research in the field of neurology.
JMIR Neurotechnology welcomes submissions from scientists, clinicians, and technologists. PhD students and early career researchers are ...