(Press-News.org)
“The present studies were performed to extend our knowledge of GZ17-6.02 biology from that known in solid tumor cell types such as prostate cancer cells to liquid tumor cell types, for example, mycosis fungoides.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 26, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on February 8, 2024, entitled, “GZ17-6.02 interacts with bexarotene to kill mycosis fungoides cells.”
In this new study, researchers Michael R. Booth, Laurence Booth, Jane L. Roberts, Cameron West, and Paul Dent from Virginia Commonwealth University and Genzada Pharmaceuticals investigated the therapeutic agent GZ17-6.02, composed of curcumin, harmine and isovanillin.
“Combined with our curcumin findings, we believe that isovanillin can complex with curcumin and harmine to create an entity with unique biology when compared to the three individual agents.”
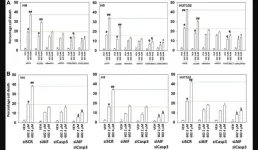
GZ17-6.02 has undergone phase I evaluation in patients with solid tumors (NCT03775525) with an RP2D of 375 mg PO BID. The biology of GZ17-6.02 in malignant T cells and in particular those derived from mycosis fungoides (MF) patients, has not previously been studied. The researchers found that GZ17-6.02 alone and in combination with standard-of-care agents was effective in killing MF cells.
“All three components are necessary for optimal killing of MF cells.”
GZ17-6.02 activated ATM, the AMPK, NFκB and PERK and inactivated ERK1/2, AKT, ULK1, mTORC1, eIF2α, and reduced the expression of BCL-XL and MCL1. GZ17-6.02 increased ATG13 S318 phosphorylation and the expression of Beclin1, ATG5, BAK and BIM. GZ17-6.02 in a dose-dependent fashion enhanced autophagosome formation and autophagic flux, and tumor cell killing.
Signaling by ATM and AMPK were both required for efficient killing but not for the dose-response effect whereas ER stress (eIF2α) and macroautophagy (Beclin1, ATG5) were required for both efficient killing and the dose-response. Knock down of the death receptor CD95 reduced killing by ~20% and interacted with autophagy inhibition to further reduce killing, collectively, by ~70%. Inhibition of autophagy and knock down of death-mediators downstream of the mitochondrion, AIF and caspase 3, almost abolished tumor cell killing. Hence in MF cells, the team wrote that GZ17-6.02 is a multi-factorial killer, utilizing ER stress, macroautophagy, death receptor signaling and directly causing mitochondrial dysfunction.”
“We discovered that GZ17-6.02 containing harmine, isovanillin and curcumin caused more tumor cell killing than any of the agents individually or in pairs, and that it could interact in an additive fashion with standard of care MF drugs such as bexarotene and vorinostat to cause additional tumor cell death.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28557
Correspondence to: Paul Dent
Email: paul.dent@vcuhealth.org
Keywords: autophagy, ER stress, GZ17-6.02, bexarotene, vorinostat
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Reddit
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
Memphis, Tenn. (February 26, 2024) – Shelley White-Means, PhD, a professor of Health Economics in the Department of Interprofessional Education and the director of the Consortium for Health Education, Economic Empowerment and Research (CHEER) at UT Health Science Center, recently received a $1.5 million, four-year grant from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities to explore the root causes of the disparity in breast cancer survival of Black women compared to white women.
Dr. White-Means and a team will look beyond the social determinants of health to explore what she terms “the intersectionality of race, ...
Stanford researchers are getting closer to building a tiny electron accelerator based on “accelerator-on-a-chip” technology with broad potential applications in studying physics as well as medical and industrial uses.
The researchers have demonstrated that a silicon dielectric laser accelerator, or DLA, can now both speed up and confine electrons, creating a focused beam of high-energy electrons. “If the electrons were microscopic cars, it’s as if, for the first time, we’re steering and we have our foot on the gas,” said Payton Broaddus, PhD ’23 in electrical engineering and the lead author on a paper published on ...
FINDINGS
Scientists at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, have devised an innovative approach to target and destroy hard-to-kill leukemia stem cells. The journal Blood published the preclinical findings today.
By overcoming challenges, such as drug resistance and treatment relapse common to patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the therapy method could provide a less toxic and more effective approach for older and sicker patients who don’t quality for stem cell transplants — currently the only cure for AML available.
Type II interferon (IFNy), a substance produced by immune cells, disrupts ...
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Scientists are getting a more detailed look than ever before at the electrons they use in precision experiments.
Nuclear physicists with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility have shattered a nearly 30-year-old record for the measurement of parallel spin within an electron beam – or electron beam polarimetry, for short. The achievement sets the stage for high-profile experiments at Jefferson Lab that could open the door to new physics discoveries.
In a peer-reviewed ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, February 26, 2024
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
BU Researchers Identify Potential New Subtype of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
One in six cases have a distinct distribution of disease, clinical profile
(Boston)—Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease defined by abnormal tau protein accumulating in a particular pattern in specific regions of the brain.
Studies to-date suggest CTE begins in the outermost layer of the frontal lobe, the neocortex, where it then spreads to connected brain regions. Later, in high-stage disease, ...
EMBARGOED by Cell until 11 am ET Feb. 26, 2024
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
BU Researchers Describe New Technological Platform to
Accelerate Drug Development
(Boston)— Drug development is currently an extremely long, expensive and inefficient process. Findings generated in a lab are often very hard to replicate once translated into animal models or in humans.
A family of pharmacological targets, on which approximately 35% of FDA-approved drugs work, consists of receptors at the surface ...
One of the most striking examples of gut plasticity can be observed in animals that are exposed to prolonged periods of fasting, such as hibernating animals or phyton snakes that goes for months without eating, where the gut shrinks with as much as 50%, but recovers in size following a few days of re-feeding. Importantly, the capacity of the gut to undergo resizing is broadly conserved. Hence, in humans, an increase in gut size is observed during pregnancy, which facilitates the uptake of nutrients to support the growth of the fetus.
The Colombani Andersen ...
What if it were possible to use a scientific model to predict hate crimes, protests, or conflict? Researchers at McGill University and University of Toronto have begun the groundwork to develop a formal predictive model of prejudice, similar to meteorological weather predictions.
The model can be explained by the equation: Prejudice = Threat – Contact + Identification, “with some numbers involved,” says lead author Eric Hehman, Associate Professor in the Department of Psychology and lead author of a new study published in Psychological ...
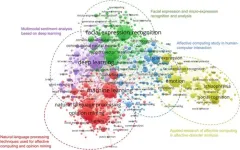
Imagine a world where your smartphone can detect your mood just by the way you type a message or the tone of your voice. Picture a car that adjusts its music playlist based on your stress levels during rush hour traffic. These scenarios are not just futuristic fantasies. They are glimpses into the rapidly evolving field of affective computing. Affective computing is a multidisciplinary field integrating computer science, engineering, psychology, neuroscience and other related disciplines. A new and comprehensive review on affective computing was published Jan. 5 in Intelligent ...
AI decision-making is now common in self-driving cars, patient diagnosis and legal consultation, and it needs to be safe and trustworthy. Researchers have been trying to demystify complex AI models by developing interpretable and transparent models, collectively known as explainable AI methods or XAI methods. A research team offered their insight specifically into audio XAI models in a review article published Jan. 23 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Although audio tasks are less researched than visual tasks, their expressive power is not less important. Audio signals are easy to understand and communicate, as they typically depend less on expert explanations ...