The mechanism of SlWRKY80 participating in salt alkali stress through its involvement in JA metabolic pathway
2024-02-27
(Press-News.org)
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is the most widely cultivated and consumed horticultural crop. At present, saline–alkali is an important abiotic stress source that affects tomato production. Exogenous methyl jasmonate (MeJA) can enhance the resistance of tomatoes to various stress, but its exact mechanism is still unclear.
In January 2024, Horticulture Research published a research entitled by “SlWRKY80-mediated jasmonic acid pathway positively regulates tomato resistance to saline-alkali stress by enhancing spermidine content and stabilizing Na+/K+ homeostasis”.
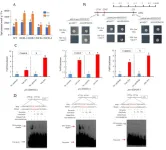
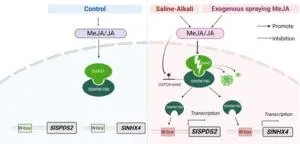
In this study we confirmed that 22.5 μmol/l MeJA could significantly improve the saline-alkali stress resistance of tomato. Saline–alkali stress increased the endogenous MeJA and jasmonic acid (JA) contents. Exogenous application of 22.5 μmol/l MeJA increased the endogenous MeJA and JA contents in tomato. Furthermore, an important transcription factor, SlWRKY80, which responded to MeJA, and actively regulated tomato resistance to saline–alkali stress. Spraying of exogenous MeJA (22.5 μmol/l) reduced the sensitivity of SlWRKY80 knockout lines to saline–alkali stress. The SlWRKY80 protein directly combines with the promoter of SlSPDS2 and SlNHX4 to positively regulate the transcription of SlSPDS2 and SlNHX4, thereby promoting the synthesis of spermidine and Na+/K+ homeostasis, actively regulating saline–alkali stress. The augmentation of JA content led to a notable reduction of 70.6% in the expression of SlJAZ1, and the release of the SlWRKY80 protein interacting with SlJAZ1. In conclusion, exogenous MeJA in tomato stress resistance through multiple metabolic pathways, elucidated that exogenous MeJA further promotes spermidine synthesis and Na+/K+ homeostasis by activating the expression of SlWRKY80)(Fig. 2), which provides a new theoretical basis for the study of the JA stress resistance mechanism and the actual production of tomato.
###
References
Authors
Chunyu Shang, Xiaoyan Liu, Guo Chen, Hao Zheng, Abid Khand, Guobin Li, Xiaohui Hu
Affiliations
College of Horticulture, Northwest A&F University
About Xiaohui Hu
College of Horticulture, Northwest A&F University, Professor/Doctoral Supervisor, Scientist of China Agriculture Research System (Vegetable), Shaanxi Vegetable Industry Technology System Scientist. She engaged in plant physiology of abiotic stress,technology of efficient production on protected vegetable, and automatic management of greenhouse, the main research crops are tomatoes and cucumbers.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-27
The impact of abdominal fat on brain health and cognition is generally more pronounced in middle-aged men at high risk of Alzheimer’s disease as opposed to women, according to researchers at Rutgers Health.
In middle-aged individuals with a family history of Alzheimer’s disease, the amount of fat in their abdominal organs (pancreas, liver, and belly fat) is related to their brain volumes and cognitive function, according to the study published in the journal Obesity. The study was written by Sapir Golan Shekhtman, a Ph.D. student at the Joseph Sagol Neuroscience Center at the Sheba Medical Center in Israel and led by ...
2024-02-27
ROCKVILLE, Md.— High-fat diets cause obesity in male mice. The underlying mechanism, however, remains controversial. After assessing three contrasting ideas, researchers have determined that the hedonic overdrive model provides the best fit, according to a new study published in the journal Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
“Our work provides some direction as to why high-fat/high-carb macronutrient combinations stimulate overconsumption. The study is in mice so we ...
2024-02-27
The tone and tuning of musical instruments has the power to manipulate our appreciation of harmony, new research shows. The findings challenge centuries of Western music theory and encourage greater experimentation with instruments from different cultures.
According to the Ancient Greek philosopher Pythagoras, ‘consonance’ – a pleasant-sounding combination of notes – is produced by special relationships between simple numbers such as 3 and 4. More recently, scholars have tried to find psychological explanations, but these ‘integer ratios’ are still credited with making a chord sound beautiful, and deviation from them ...
2024-02-27
A new paper in Genome Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, finds that the link between paternal age and rare congenital disorders is more complex than scientists had previously thought. While researchers have long realized that older fathers are more likely to have children with bone and heart malformations, such as Achondroplasia, Apert, or Noonan syndrome or neurodevelopmental disorders, schizophrenia, and autism, new examination indicates that while the link between some pathogenic mutations increases with paternal age, others do not and may even occur in the father’s testis before sexual maturity.
Delayed fatherhood results in a higher ...
2024-02-27
A study into parental smoking and childhood obesity has challenged previous notions by revealing that the links between the two are not confined to a specific socio-economic group.
The data shows a strong correlation between parents who smoke and their children’s consumption of high calorie unhealthy foods and drinks, across social classes.
Using longitudinal data on 5,000 Australian children collected over a 10-year period, the research found those living with parents who smoke, on average, eat less healthy, higher calorie food such as fruit juice, sausages, fries, snacks, full fat milk products, ...
2024-02-27
Professor Jian HE, from the Department of Chemistry at The University of Hong Kong (HKU), has spearheaded a research endeavour aimed at revolutionising organic synthesis. His research team has successfully developed a novel heterogeneous copper photocatalyst that enables the efficient formation of cyclobutane rings, a crucial structural element in a vast array of bioactive molecules. Cyclobutane rings are prominently featured in pharmaceuticals, natural products, and various biologically active compounds. By enabling researchers to construct these rings easily and selectively, ...
2024-02-27
The success of a deep learning-based network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) relies on large-scale, labeled, realistic traffic. However, automated labeling of realistic traffic, such as by sand-box and rule-based approaches, is prone to errors, which in turn affects deep learning-based NIDS.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Yuefei ZHU published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team ...
2024-02-27
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) reveal that the Snhg11 gene is critical for the function and formation of neurons in the hippocampus. Experiments with mice and human tissues revealed the gene is less active in brains with Down syndrome, potentially contributing to the memory deficits observed in people living with the condition. The findings are published today in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Traditionally, much of the focus in genomics has been on protein-coding genes, which in humans constitutes around just 2% of the entire genome. The rest is "dark ...
2024-02-27
In The BMJ today, Keisha Bentley-Edwards at Duke University, North Carolina, and colleagues argue that systemic racism and economic inequality are at the root of disparity in covid-19 outcomes and suggest how to distribute resources more equitably.
The article is part of a series that highlights the lessons that can be learned from the US’s covid-19 experience and the actions that are needed to prevent the loss of another million citizens in the next pandemic and improve and protect population health.
"Rather than waiting for the next pandemic to address systemic failures, the ...
2024-02-27
A group led by researchers at Nagoya University and Meijo University in Japan has developed a disinfection technology that uses low-temperature plasma generated by electricity to cultivate environmentally friendly hydroponically grown crops. This innovative technology sterilizes the crops, promoting plant growth without the use of chemical fertilizers. Their findings appeared in Environmental Technology & Innovations.
In hydroponic agriculture, farmers cultivate plants by providing their roots with a nutrient solution. However, the nutrient solution can become infected with pathogenic E. coli strains, contaminating the crop and leading to foodborne illnesses.
To avoid ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The mechanism of SlWRKY80 participating in salt alkali stress through its involvement in JA metabolic pathway