(Press-News.org) A study quantifies the emission of extremely tiny particles by gas stoves and finds that the particles could harm human health. Airborne nanoparticles between 1–3 nm, referred to as nanocluster aerosol or NCA, are known to be bioactive and toxic, but measuring such minute particles has been a challenge. Brandon E. Boor and colleagues measured indoor NCA during propane gas cooking in the Purdue zero Energy Design Guidance for Engineers (zEDGE) test house using a novel instrument. Combining measurement data with the general dynamic equation for aerosols, the authors were able to characterize the production and behavior of the extremely tiny particles during cooking operations such as boiling water and cooking grilled cheese sandwiches. These activities emitted as much as ~1016 NCA/kg of cooking fuel, which is as much as or more NCA than produced by vehicles with internal combustion engines. The air around the stove often had higher concentrations of NCA than urban outdoor air. NCA formed during cooking is inhaled by humans and is delivered to the head airways and tracheobronchial region in large amounts, which is concerning, as flame-generated NCA is known to be toxic. According to the authors, indoor NCA should be considered a distinct air pollution category and should be routinely monitored.
END
Nano-sized particles emitted from gas stoves
2024-02-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reproducing the Moon's surface environment on Earth
2024-02-27
Continuous research is being conducted globally on using the Moon as an advanced base for deep space exploration, and Korea is no exception in these efforts. The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim, Byung-suk) successfully implemented an electrostatic environment that simulates the Moon's surface conditions, not in space but on Earth. The researchers also assessed its performance and effectiveness.
Among the most serious threats in executing lunar missions is the Moon's surface environment, which is electrostatically charged. Due to its extremely thin atmosphere, the Moon is directly exposed to solar ultraviolet rays, X-rays, ...
Social media and adolescent mental health
2024-02-27
In an editorial, Sandro Galea and Gillian Buckley summarize the findings of a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine consensus study report on social media and adolescent mental health. Social media has to some extent been treated as a monolith, but the report finds that different types of engagements with different digital platforms may have very different effects on mental health. In some situations, social media may benefit adolescent mental health, as when LGBTQ+ adolescents in isolating circumstances are able to form supportive ...
How decades of expertise with the fourth state of matter could bring satellites closer to Earth
2024-02-27
Thousands of satellites take pictures, gather information and relay internet traffic from high above the Earth. Now, the challenge is making satellites that operate closer to home, in what is called a very low earth orbit (VLEO), where there is ample space for additional satellites, and the pictures taken would be clearer.
Working at an altitude with air would mean more force would be needed to propel the satellite forward, but many scientists believe there is also an advantage: the air could be used as the propellant. They say charged particles of air-breathing plasma – the fourth state of matter – could be used to propel the thrusters, potentially ...
Living near pubs, bars and fast-food restaurants could be bad for heart health
2024-02-27
Research Highlights
Closer proximity to and a higher number of ready-to-eat food outlets — particularly pubs, bars and fast-food restaurants — may be associated with a greater risk of developing heart failure, according to a study of half a million adults in the UK Biobank.
The association between food environments and increased heart failure risk was stronger among people who did not have a college degree and those living in urban areas without access to facilities for physical activity such as gyms or fitness centers.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024
DALLAS, Feb. 27, 2024 — Living close to pubs, bars and fast-food restaurats may ...
Research adds to knowledge about heart disease and stroke in women of all ages
2024-02-27
Research Highlights:
Women’s heart disease and stroke risks and outcomes differ throughout life in comparison to men.
A special Journal of the American Heart Association “spotlight” issue features a collection of the latest research about sex differences in cardiovascular disease and their implications for gender-specific care.
Among the topics in this issue: the impact of sedentary behavior on heart disease risk in older women; sex differences in the relationship between schizophrenia and the development ...
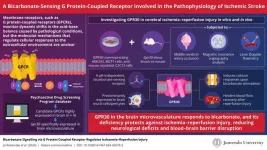
Innovative therapies for ischemic stroke: Novel bicarbonate-sensing G protein-coupled receptor shows promise
2024-02-27
Cells actively rely on maintaining an appropriate acid-base balance to support optimal function. Under normal physiological settings, the pH inside cells remains within a controlled range. However, disruptions in this equilibrium have been linked to a wide range of health conditions, both minor and catastrophic. Changes in the extracellular environment are monitored by “membrane receptors,” of which the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of membrane proteins that mediate multiple cellular responses. However, the role of GPR30, also known as G protein-coupled estrogen ...
AI-driven lab speeds catalysis research
2024-02-27
Researchers have developed a “self-driving” lab that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and automated systems to provide in-depth analyses of catalytic reactions used in chemical research and manufacturing. The new tool, called Fast-Cat, can provide more information in five days than is possible in six months of conventional testing.
At issue are the yield and selectivity of chemical reactions in the presence of molecules called ligands.
Yield refers to how efficiently a chemical reaction produces a desired product from the chemicals you started with. Selectivity refers ...
Unveiling the sustainability landscape in cultural organizations: A global benchmark
2024-02-27
Are museums, theaters, and opera houses truly walking the talk when it comes to social and environmental sustainability? The University of Lausanne (UNIL) delved into this pressing question, conducting an international survey with over 200 major cultural organizations. The verdict? While there's significant room for improvement across the spectrum, Anglophone countries lead the charge.
Cultural organizations, with their wide-reaching influence and power to shape narratives and imaginations, are poised to ...
The mechanism of SlWRKY80 participating in salt alkali stress through its involvement in JA metabolic pathway
2024-02-27
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is the most widely cultivated and consumed horticultural crop. At present, saline–alkali is an important abiotic stress source that affects tomato production. Exogenous methyl jasmonate (MeJA) can enhance the resistance of tomatoes to various stress, but its exact mechanism is still unclear.
In January 2024, Horticulture Research published a research entitled by “SlWRKY80-mediated jasmonic acid pathway positively regulates tomato resistance to saline-alkali stress by enhancing spermidine content and stabilizing ...
Abdominal fat can impact brain health and cognition in high Alzheimer’s risk individuals
2024-02-27
The impact of abdominal fat on brain health and cognition is generally more pronounced in middle-aged men at high risk of Alzheimer’s disease as opposed to women, according to researchers at Rutgers Health.
In middle-aged individuals with a family history of Alzheimer’s disease, the amount of fat in their abdominal organs (pancreas, liver, and belly fat) is related to their brain volumes and cognitive function, according to the study published in the journal Obesity. The study was written by Sapir Golan Shekhtman, a Ph.D. student at the Joseph Sagol Neuroscience Center at the Sheba Medical Center in Israel and led by ...