Development of a thick-film conductive ink suitable for large-area, large-current printed electronics
2024-02-27
(Press-News.org) 1. NIMS, Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd. (based in Minato City, Tokyo), N.E. CHEMCAT CORPORATION (based in Minato City, Tokyo) and Priways Co., Ltd. (a NIMS-founded startup based in Tsukuba, Ibaraki) have jointly developed a thick-film, electrically conductive ink suitable for printing electronic circuits and sensors on the surfaces of films and other substrates to manufacture printed electronics. Sumitomo Metal Mining and Priways displayed the ink during the 38th Nepcon Japan exhibition to be held from January 24th to 26th, 2024.
2. Printed electronics are manufactured using additive methods (i.e., electronic circuits are directly printed on the surfaces of substrates) rather than conventional subtractive electronics manufacturing (i.e., metallic films are first deposited on substrate surfaces and unnecessary film regions are then removed to form circuits). The additive method uses less amount of metallic materials than the subtractive method, making it more environmentally friendly and inexpensive. In addition, the additive method can be used to print electronic circuits on the surfaces not only of rigid substrates but also flexible ones. Because of these advantages, the additive method is expected to serve as an effective wiring technique for use in next-generation device fabrication.
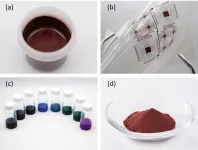
3. The new thick-film conductive ink was created using metal complex inks (i.e., inks consisting of a central metallic ion surrounded by charged molecular ligands) developed by NIMS and Priways and metallic powder synthesis and paste production technologies developed by Sumitomo Metal Mining. This ink is able to meet printed electronics requirements: its thickness is controllable and it is compatible with low-temperature sintering. These improvements were achieved by adding copper particles developed by Sumitomo Metal Mining to the ink, enabling it to form thick-film wiring at around 200°C on the surfaces of heat-resistant plastic films.
4. The newly developed ink is more inexpensive to synthesize and more oxidation-resistant than conventional conductive inks. In addition, the thickness of the ink film can be more than three times larger than that of conventional ink films, making it suitable for use in large-current, large-area electronic products. The research team is currently developing techniques for mass-producing this ink by leveraging N.E. CHEMCAT’s expertise in metal complex development and production. The team plans to further improve the performance of the ink and identify other applications for it.
***
5. This project was carried out by a research team consisting of Takeo Minari (Group Leader, Research Center for Macromolecules and Biomaterials (RCMB), NIMS), Wanli Li (Postdoctoral Researcher, RCMB, NIMS; currently Associate Professor, Jiangnan University), Lingying Li (Research Fellow, International Center for Young Scientists, NIMS), Shunto Arai (Independent Scientist, RCMB, NIMS), Chisato Niikura (Senior Researcher, RCMB, NIMS), Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd., N.E. CHEMCAT Corporation and Priways Co., Ltd.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-27
There’s a lot of research about moving away from carbon as an energy source, but what if instead the carbon that is being used is applied to its full capacity?
The importance of carbon as an energy source is not to be downplayed. Unfortunately, the reliance on these carbon-based materials has proven to be disastrous for the environment, especially in the quantities they are consumed on a global basis. Therefore, alternative means have to be researched. Superstructure carbons (SCC) are a possible way to use carbons in a more efficient and “green” way that can exceed the current performance and longevity ...
2024-02-27
The International Vaccine Institute (IVI), an international organization with a mission to discover, develop, and deliver safe, effective, and affordable vaccines for global health, and the Ministry of Health of Rwanda announced today that IVI will open its Africa Regional Office in Kigali this year. The IVI Board of Trustees (BOT) confirmed Rwanda as the location for IVI’s Africa Regional Office at a meeting in February, following a detailed evaluation of proposals from five countries to host the regional office.
Dr. Jerome Kim, Director General of IVI, said: “We are ...
2024-02-27
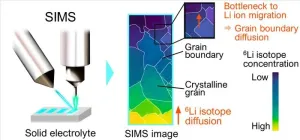
1. A NIMS research team has developed a new technique to image grain boundaries obstructing lithium-ion migration in solid-state batteries—a promising type of next-generation battery.
2. Solid-state batteries—next-generation rechargeable batteries—are intended to be safer and have higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion batteries by replacing liquid organic electrolytes with solid electrolytes. A major issue in current solid-state battery R&D is the obstruction of ...
2024-02-27
Digital Science is pleased to announce that ReadCube, an award-winning leader in literature management and full-text document delivery, has launched a new solution for research-driven organizations – known simply as Literature Review by ReadCube.
Literature Review seamlessly integrates with ReadCube's premier literature management platform, trusted by over 650 research organizations globally. Known for its best-in-class user experience and robust literature workflows, ReadCube's newest solution delivers a turnkey end-to-end workflow for teams tasked with monitoring and analyzing published literature related ...
2024-02-27
Every year, over 100 million people worldwide suffer a stroke. Ischemic strokes (cerebral infarction) are the most common, but they can also occur "silently" and therefore often go undetected. This can result in serious illnesses such as dementia, depression or even suicide. In order to determine the risk of stroke at an early stage, Prof. Dr. Olga Golubnitschaja, head of the research group for 3P (predictive, preventive and personalized) medicine at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB), together with the University of Bonn and other authors from 25 institutions from 11 countries, has developed a holistic approach to health ...
2024-02-27
OAK BROOK, Ill. – As artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used in radiology, researchers caution that it’s essential to consider the environmental impact of AI tools, according to a focus article published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Health care and medical imaging significantly contribute to the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions fueling global climate change. AI tools can improve both the practice of and sustainability in radiology through optimized imaging protocols resulting in shorter scan times, improved scheduling ...
2024-02-27
February 27 — Five of the world’s leading research and education (R&E) networking organizations have joined forces to form MetrANOVA, a consortium for Advancing Network Observation, Visualization, and Analysis. Together, founding members Energy Sciences Network (ESnet), GÉANT, GlobalNOC at Indiana University, Internet2, and Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) operate and connect a dizzying number of national, regional, and local R&E networks — yet representing a portion of the decentralized fabric linking scientific researchers in hundreds of countries ...
2024-02-27
Patients who have drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) have a similar microbiological response to bedaquiline-based second-line medications as patients with drug-sensitive TB taking first-line regimens, according to researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York and GHESKIO Centers in Haiti. Second-line medications are those that are given when one or more of the drugs given first for the disease are not effective. The research could have implications for shortening the duration of treatment for drug-resistant TB, which currently ...
2024-02-27
In an effort to expedite its life-saving work, the Colorectal Cancer Alliance (Alliance) Project Cure CRC initiative is excited to open its Request for Proposals (RFP). Tens of millions of dollars will be available to researchers from around the world whose work aims to expedite colorectal cancer (CRC) research to a curable science. Beginning March 1, the program is accepting applications for one to three-year projects from qualifying professionals at research-based institutions and private companies. Priority will be given to proposals that focus on high-risk/high-reward projects to accelerate new CRC therapies and technologies from bench to bedside.
The ...
2024-02-27
First-of-its-kind study suggests increasing the percentage of youth in the United States who participate in sports to meet a Healthy People 2030 goal could improve children’s physical and mental health and save $80 billion.
Achieving the Healthy People 2030 youth sports participation goal could save the United States $80 billion in direct medical costs and productivity losses and deliver over 1.8 million more quality years of life to Americans, according to a study that will be published on Feb. 27 in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Every decade since 1980, Healthy People has provided science-based, 10-year national objectives and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Development of a thick-film conductive ink suitable for large-area, large-current printed electronics