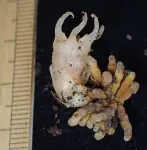
(Press-News.org) A new species and genus of fairy lantern, tiny glass-like white plants that feed on fungi, has been discovered in Japan. In the country renowned for its extensive flora research, the discovery of a new plant genus is extremely rare and has not occurred in almost 100 years.
Fairy lanterns, or Thismiaceae as they are known to botany, are very unusual plants found mainly in tropical but also in subtropical and temperate regions. First of all, they are not green and do not engage in photosynthesis, but rather feed on fungal mycelia in the ground. As a consequence, they are often hidden under fallen leaves and only for a brief period produce above-ground flowers that look like glasswork. The Japanese name for Thismia, one of the major groups within this family, is “Tanuki-no-shokudai,” which means “raccoon dog’s candleholder” and refers both to their shape and their underground lifestyle. However, they are also extremely rare and difficult to find. “At present, approximately 100 species within the family have been identified, nearly half of which are known only from their first discovery, sometimes from a single specimen,” explains Kobe University botanist SUETSUGU Kenji, who is an internationally renowned expert on non-photosynthetic plants.
Suetsugu has long-standing collaborations with local botanists who have access to secluded areas all over Japan. He says, “The dedication of Japanese amateur researchers to revealing the hidden flora of these regions has been crucial in identifying species unknown to science.” And so, when he was sent a specimen of a fairy lantern that a hobby botanist had found and that a local expert thought represented a new species of the genus of Tanuki-no-shokudai, he knew he had to investigate. However, it soon became clear “that this plant was not included in any of the existing genera (such as Thismia) because of its unique features, and it became necessary to obtain additional individuals for further examination.” So, he went to Kimotsuki in Kagoshima Prefecture, where the discovery had been made, but could not find any other samples. However, a year later he tried again and got lucky: They found four more plants, all in the same narrow area.
The Kobe University expert now published his analysis in the scientific Journal of Plant Research. Based both on morphological and genetic analysis, the team concluded that the plant is not only a new species, but in fact different enough from Tanuki-no-shokudai to be a different genus — the next level of relationship above species. The researchers think the plant probably diverged at an early stage in the evolution of the whole Thismiaceae family and retains characteristics that are common to the family but have been lost in the Thismia genus. This is the reason Suetsugu chose the name “Mujina-no-shokudai,” or “badger’s candleholder”: “Mujina” is an old Japanese word for a badger, but sometimes has also been used for the raccoon dog which it resembles but is different from. Thus, the name reflects the plant’s relationship with Thismia. The Latin name Relictithismia kimotsukiensis is similar, as it can be translated as “Thismia relict of Kimotsuki.”
“Japan is one of the regions in the world where botanical surveys are most advanced, making the discovery of new plant species extremely rare, and the discovery of a new genus even more so,” says Suetsugu. In fact, the last discovery of a new vascular plant concurrently identified as a separate genus was the discovery of Japonolirion in 1930, almost 100 years ago. Suetsugu explains, “This research might suggest that many other new species may be hiding in regions previously thought to be well-studied and underscores the critical need for ongoing exploration and investigation of the planet’s flora both abroad and at home.”
A plant that feeds on fungi and is so limited in its local spread is also exceptionally vulnerable to environmental change. This motivates Suetsugu to deepen his research, saying, “A segment of our future research will be dedicated to ecological studies aimed at deciphering the interactions between Relictithismia and its fungal hosts, in addition to assessing the impact of environmental alterations on these associations.”
This study was supported by the PRESTO program (grant JPMJPR21D6) of the Japan Science and Technology Agency, the JSPS KAKENHI (grant 21K06307) and the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (grant JPMEERF20204001) of the Ministry of the Environment, Japan. It was conducted in collaboration with an independent researcher and researchers from Kyoto University and the Kagoshima University Museum.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
A new plant’s name that tells a story
2024-02-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Noteworthy studies to be presented at the 2024 Multidisciplinary Head & Neck Cancers Symposium
2024-02-29
PHOENIX, February 29, 2024 — Research on patient-centered treatment of head and neck cancers will be presented at the 2024 Multidisciplinary Head and Neck Cancers Symposium, which takes place in Phoenix and online today through March 2. Media registration is available via our press kit, and general registration is available via the meeting website.
Seven high-impact studies recommended by symposium leadership for media are noted below. All abstracts are available online. Experts are available to provide outside commentary and perspective on research at the meeting; ...
Turbocharging CRISPR to understand how the immune system fights cancer
2024-02-29
Over the past two decades, the immune system has attracted increasing attention for its role in fighting cancer. As researchers have learned more and more about the cancer-immune system interplay, several antitumor immunotherapies have become FDA-approved and are now regularly used to treat multiple cancer types.
Yet despite these advances, much remains unknown about how the immune system fights cancer — and about immunity in general, said Martin LaFleur, a postdoctoral fellow in the laboratory of Arlene ...
UBC Okanagan researchers create new compound to build space-age antennas
2024-02-29
In a first-of-its-kind development, UBC Okanagan researchers, in collaboration with Drexel University, have created a new compound that can be used to 3D print telecommunication antennas and other connectivity devices.
These 3D printed products, created by combining a two-dimensional compound called MXenes with a polymer, can be used as an alternative for metallic counterparts and can make a vast improvement in communication technology including elements such as antennas, waveguides and filters.
Waveguides are everywhere, yet most people don’t know what they are, says Dr. Mohammad Zarifi, a researcher in UBC Okanagan’s Microelectronics and Gigahertz ...
Study detects cognitive changes in older drivers using in-vehicle sensors
2024-02-29
An estimated 4 to 8 million older adults with mild cognitive impairment are currently driving in the United States, and one-third of them will develop dementia within five years. Individuals with progressive dementias are eventually unable to drive safely, yet many remain unaware of their cognitive decline.
Currently, screening and evaluation services for driving can only test a small number of individuals with cognitive concerns, missing many who need to know if they require treatment.
Nursing, engineering and neuropsychology researchers at Florida Atlantic University are testing and evaluating a readily and rapidly available, unobtrusive in-vehicle sensing ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces 2024 Paul Terasaki Award recipient
2024-02-29
(LOS ANGELES) – February 29, 2024 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is pleased to announce their selection of Professor Nicholas A. Peppas of The University of Texas at Austin as the recipient of the 2024 Paul Terasaki Distinguished Scientist Innovation Award. The award will be presented at TIBI’s 2nd annual Terasaki Innovation Summit, to be held March 27-29, 2024, at the UCLA Meyer & Renee Luskin Conference Center.
The award was created in memory of Dr. Paul I. Terasaki, a pioneer in organ transplant research and innovation. It recognizes outstanding achievement in the field of biomedical ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces 2024 Hisako Terasaki Award recipients
2024-02-29
(LOS ANGELES) – February 29, 2024 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is pleased to announce their selections of Assistant Professors Amir Manbachi of Johns Hopkins University and Ritu Raman of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as the recipients of the 2024 Hisako Terasaki Young Innovator Awards. The awards will be presented at TIBI’s 2nd annual Terasaki Innovation Summit, to be held March 27-29, 2024, at the UCLA Meyer & Renee Luskin Conference Center.
The award was created in memory of Hisako Terasaki, philanthropist, accomplished artist, and wife ...
Small dietary changes can cut your carbon footprint by 25%
2024-02-29
The latest Canada’s Food Guide presents a paradigm shift in nutrition advice, nixing traditional food groups, including meat and dairy, and stressing the importance of plant-based proteins. Yet, the full implications of replacing animal with plant protein foods in Canadians’ diets are unknown.
New research at McGill University in collaboration with the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine provides compelling evidence that partially substituting animal with plant protein foods can increase life expectancy and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Importantly, ...
Uncertainty in measuring biodiversity change could hinder progress towards global targets for nature
2024-02-29
More than ever before, there is a growing interest in dedicating resources to stop the loss of biodiversity, as recently exemplified by the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) decided at COP15 in December 2022. The GBF focuses on understanding why biodiversity is declining and what actions are needed to reverse this trend. However, according to researchers at McGill University, implementing the plan is challenging because information about biodiversity changes is not evenly available everywhere, and is uncertain in many places.
With the available data, can the ...
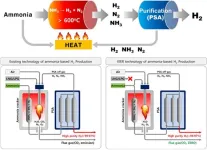
Zero emissions of carbon dioxide! Successful production of ammonia-based clean hydrogen
2024-02-29
Dr. Jung Unho's research team at the Hydrogen Research Department of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has developed Korea's first clean hydrogen production technology. This technology is based on ammonia decomposition and does not use fossil fuels. The team's breakthrough could pave the way for a more sustainable and eco-friendly energy source. This allows for the production of high-purity hydrogen that meets international standards for hydrogen-powered vehicles, without the carbon dioxide emissions produced by using fossil fuels.
Ammonia, a compound of hydrogen and nitrogen, has a hydrogen storage density 1.7 times ...
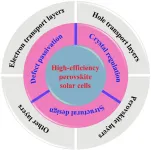
Guiding future research on ‘extraordinary potential’ of next-generation solar cells
2024-02-29
Today’s commercial solar panels can convert about 15% to 20% of the sunlight they absorb into electrical energy — but they could be much more efficient, according to researchers at Soochow University. The next generation of solar cells has already demonstrated 26.1% efficiency, they said, but more specific research directions are needed to make such efficiency the standard and expand beyond it.
They published their review of the current state of research on high-efficiency perovskite solar cells and their recommendations for future work in Energy Materials and Devices on February 4.
“Metal halide perovskite ...