(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study of 536 participants identified changes in patient portal use over time and highlighted populations that had lower access to health information. The COVID-19 pandemic was associated with an increase in portal use. Sociodemographic disparities by sex and age were reduced, although disparities by health literacy widened. A brief validated health literacy measure may serve as a useful digital literacy screening tool to identify patients who need further support.
Authors: Esther Yoon, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.S., of Northwestern University in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0680)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0680?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=022924
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Disparities in patient portal use among adults with chronic conditions
JAMA Network Open
2024-02-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Factors associated with racial and ethnic disparities in locally advanced rectal cancer outcomes
2024-02-29
About The Study: The findings of this study of 34,500 patients suggest that racial and ethnic disparities in locally advanced rectal cancer treatment outcomes may be multifactorial, with an independent association with non-Hispanic Black race, suggesting unidentified biological variables or social determinants of health that warrant exploration.
Authors: Sanjeevani Arora, Ph.D., and Shannon M. Lynch, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0044)
Editor’s ...
CZI announces multi-institutional collaborations for tech to better understand cells
2024-02-29
Today, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) announced four multi-year grants that will bring together regional labs in California, the Mid-Atlantic, and the Research Triangle in North Carolina to explore the frontiers of genomics, cell biology, and synthetic biology by developing new measurement technologies. These projects will focus on developing technologies to engineer cell and tissue models, exploring cellular responses to genetic and environmental stressors, understanding RNA's role in metabolism, and more.
“To unravel the mysteries of the cell, we need new technologies, and the Exploratory Cell Networks grants support early-stage ...
Researchers uncover key therapeutic target involved in diabetic atherosclerosis
2024-02-29
Diabetes accelerates the development of atherosclerosis, increasing the incidence of cardiovascular events. In atherosclerosis, immune cells called macrophages release molecules such as chemokines and cytokines, causing inflammation and leading to arterial plaque formation. However, significant gaps persist in understanding the exact molecular mechanisms controlling this increased inflammatory response in individuals with diabetes. In a new, preclinical study, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, identified a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) sequence that could help them unravel the ...
Scripps Research scientists reveal how first cells could have formed on Earth
2024-02-29
LA JOLLA, CA—Roughly 4 billion years ago, Earth was developing conditions suitable for life. Origin-of-life scientists often wonder if the type of chemistry found on the early Earth was similar to what life requires today. They know that spherical collections of fats, called protocells, were the precursor to cells during this emergence of life. But how did simple protocells first arise and diversify to eventually lead to life on Earth?
Now, Scripps Research scientists have discovered one plausible pathway for how protocells may have first formed and chemically ...
EcoFABs could lead to better bioenergy crops
2024-02-29
– By Will Ferguson
A greater understanding of how plants and microbes work together to store vast amounts of atmospheric carbon in the soil will help in the design of better bioenergy crops for the fight against climate change.
Deciphering the mechanics of this mutually beneficial relationship is challenging, however, as conditions in nature are extremely difficult for scientists to replicate in the laboratory. To address this challenge, researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) created fabricated ecosystems or EcoFABs.
In a new paper in Science Advances, they ...
Digital Science announces Catalyst Grant winners, supporting AI-based innovations to benefit research
2024-02-29
Digital Science has awarded two new Catalyst Grants of £25,000 each to innovative AI-based technology ideas aimed at advancing global research.
The winners will use the funding to develop their ideas, which include using AI to alleviate the burden on researchers of applying for research funding, and to predict research impact.
The winning applications from Digital Science’s 2023 Catalyst Grant round announced today are:
Atom – Tomer du Sautoy (co-founder and CEO) and Hamilton Evans (co-founder and ...
Targeting seed microbes to improve seed resilience
2024-02-29
Fonio (Digitaria exilis), a type of millet, is the oldest indigenous crop in West Africa and one of the fastest maturing cereals. Despite its low yield, the combination of quick maturation and drought tolerance and its ability to thrive in poor soils make it a useful model for understanding how cereals can adapt to future climate change conditions.
Nutritionally, fonio is comparable to other millets, says KAUST researcher Naheed Tabassum, but yields are much lower than the major cereal crops rice, maize and wheat. Tabassum believes fonio could complement staple crops amid climate change and desertification ...
Astronomers discover heavy elements after bright gamma-ray burst from neutron star merger
2024-02-29
An international team of astronomers — including Clemson University astrophysicist Dieter Hartmann — obtained observational evidence for the creation of rare heavy elements in the aftermath of a cataclysmic explosion triggered by the merger of two neutron stars.
The massive explosion unleashed a gamma-ray burst, GRB230307A, the second brightest in 50 years of observations and about 1,000 times brighter than a typical gamma-ray burst. GRB230307A was first detected by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope on March 7, 2023.
Using multiple space- and ground-based ...
USTC reveals molecular mechanism of transmembrane bilirubin transport by human ABCC2 transporter
2024-02-29
The metabolic process of bilirubin has been a focus in medical research since the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin has been found to be associated with a variety of diseases. Bilirubin is a substance produced by the breakdown of aging or damaged red blood cells, and its effective removal is essential for human health.
A research team led by Prof. CHEN Yuxing and Prof. ZHOU Congzhao from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed the three-dimensional structure and working mechanism of the human bilirubin transporter ABCC2. The study was published ...
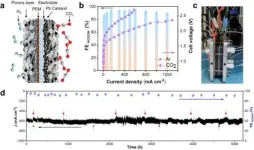
USTC realizes durable CO2 conversion in proton-exchange membrane system
2024-02-29
The metabolic process of bilirubin has been a focus in medical research since the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin has been found to be associated with a variety of diseases. Bilirubin is a substance produced by the breakdown of aging or damaged red blood cells, and its effective removal is essential for human health.
A research team led by Prof. CHEN Yuxing and Prof. ZHOU Congzhao from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
[Press-News.org] Disparities in patient portal use among adults with chronic conditionsJAMA Network Open