(Press-News.org) Fonio (Digitaria exilis), a type of millet, is the oldest indigenous crop in West Africa and one of the fastest maturing cereals. Despite its low yield, the combination of quick maturation and drought tolerance and its ability to thrive in poor soils make it a useful model for understanding how cereals can adapt to future climate change conditions.
Nutritionally, fonio is comparable to other millets, says KAUST researcher Naheed Tabassum, but yields are much lower than the major cereal crops rice, maize and wheat. Tabassum believes fonio could complement staple crops amid climate change and desertification challenges.
Tabassum and colleagues, led by Heribert Hirt and Simon Krattinger, have investigated the potential to improve fonio by manipulating its association with soil microbes.[1]
Plants grown in arid conditions associate and interact with bacteria that help them combat abiotic challenges. Hirt and his group are experts on plant-microbe interactions and their role in plant growth and development, nutrient uptake and protection against biotic stress.
“Plants evolve in close interaction with microbial partners, which is crucial for their survival and fitness,” says Hirt. “As seeds are the bottleneck for vertical transmission (from the mother plant) of potentially beneficial microbial communities, we tried to unravel the role of the fonio seed microbiome in various abiotic conditions.”
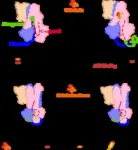
Their study investigated the bacterial seed endophyte diversity in 126 fully sequenced genetic groups of fonio accessions from distinct locations in West Africa.
The role of endophytic bacteria in seeds has been linked to plant growth and protection, yet the specific mechanisms remain to be explained in detail. The results of this study suggest that seed-associated endophytes support plant growth promotion through nutrient availability and assimilation. Previous studies have shown that seed endophytes produce biocontrol inhibitors to protect from pathogens.
When they analyzed the seed microbiomes, the researchers found that fonio millet has diverse heritable seed endophytic taxa. “Despite finding diverse microbiomes in fonio from distinct geographical locations, all fonio plants share a set of microbes, a so-called core microbiome, which probably plays important functions in the general metabolism of this cereal,” says Hirt.
To test whether environmental factors influenced the composition of the seed microbiomes, the researchers gathered meteorological and soil data (precipitation, temperature, pH and soil structure) at the collection sites. They found a correlation between several of these parameters and microbial diversity, indicating that environmental factors may affect microbial composition and transgenerational transmission.
“The seed coat and storage tissue represent distinct microhabitats,” explains Tabassum. “The vertical transmission of microbiota to fortify the progeny of a plant species opens a new technological application in crop breeding.”
“Seed microbe engineering could be used for targeted metabolites or to produce antimicrobial compounds to improve plant biomass and yield under stresses,” she says.
The recently published study provides a proof of concept to explain the composition and diversity of the seed-associated microbiomes of fonio from a number of locations.
In what they believe is a world first, the team performed genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of the 126 fonio accessions to identify genetic loci associated with seed endophyte diversity. This led to the identification of a number of known and novel genes that appear to influence the diversity of the microbial communities in different fonio accessions, suggesting that different fonio groups also genetically regulate the composition of their seed microbiomes.
“Although seed microbiome research is in its infancy, our work shows that it has great potential to advance our understanding of the plant-microbiome-environment interaction and in seed microbiome engineering of crops,” says Hirt.
“This study identified the seed microbiome as a potential target for enhancing crop resilience to climate stress in a sustainable way,” he concludes.
REFERENCE
Tabassum, N., Ahmed, I.A., Parween, S., Sheikh, A.H., Saad, M.M., Krattinger, S.G. & Hirt, H. Host genotype, soil composition and geo-climatic factors shape the fonio seed microbiome. Microbiome 12, 11 (2024).| article
END
Targeting seed microbes to improve seed resilience
2024-02-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Astronomers discover heavy elements after bright gamma-ray burst from neutron star merger
2024-02-29
An international team of astronomers — including Clemson University astrophysicist Dieter Hartmann — obtained observational evidence for the creation of rare heavy elements in the aftermath of a cataclysmic explosion triggered by the merger of two neutron stars.
The massive explosion unleashed a gamma-ray burst, GRB230307A, the second brightest in 50 years of observations and about 1,000 times brighter than a typical gamma-ray burst. GRB230307A was first detected by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope on March 7, 2023.
Using multiple space- and ground-based ...
USTC reveals molecular mechanism of transmembrane bilirubin transport by human ABCC2 transporter
2024-02-29
The metabolic process of bilirubin has been a focus in medical research since the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin has been found to be associated with a variety of diseases. Bilirubin is a substance produced by the breakdown of aging or damaged red blood cells, and its effective removal is essential for human health.
A research team led by Prof. CHEN Yuxing and Prof. ZHOU Congzhao from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed the three-dimensional structure and working mechanism of the human bilirubin transporter ABCC2. The study was published ...
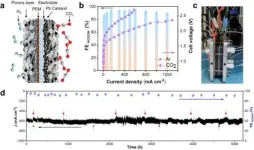
USTC realizes durable CO2 conversion in proton-exchange membrane system
2024-02-29
The metabolic process of bilirubin has been a focus in medical research since the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin has been found to be associated with a variety of diseases. Bilirubin is a substance produced by the breakdown of aging or damaged red blood cells, and its effective removal is essential for human health.
A research team led by Prof. CHEN Yuxing and Prof. ZHOU Congzhao from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed ...
A new plant’s name that tells a story
2024-02-29
A new species and genus of fairy lantern, tiny glass-like white plants that feed on fungi, has been discovered in Japan. In the country renowned for its extensive flora research, the discovery of a new plant genus is extremely rare and has not occurred in almost 100 years.
Fairy lanterns, or Thismiaceae as they are known to botany, are very unusual plants found mainly in tropical but also in subtropical and temperate regions. First of all, they are not green and do not engage in photosynthesis, but rather feed on fungal mycelia in the ground. As a consequence, they are often hidden under fallen leaves and only for a brief period produce above-ground flowers that look like glasswork. The ...
Noteworthy studies to be presented at the 2024 Multidisciplinary Head & Neck Cancers Symposium
2024-02-29
PHOENIX, February 29, 2024 — Research on patient-centered treatment of head and neck cancers will be presented at the 2024 Multidisciplinary Head and Neck Cancers Symposium, which takes place in Phoenix and online today through March 2. Media registration is available via our press kit, and general registration is available via the meeting website.
Seven high-impact studies recommended by symposium leadership for media are noted below. All abstracts are available online. Experts are available to provide outside commentary and perspective on research at the meeting; ...
Turbocharging CRISPR to understand how the immune system fights cancer
2024-02-29
Over the past two decades, the immune system has attracted increasing attention for its role in fighting cancer. As researchers have learned more and more about the cancer-immune system interplay, several antitumor immunotherapies have become FDA-approved and are now regularly used to treat multiple cancer types.
Yet despite these advances, much remains unknown about how the immune system fights cancer — and about immunity in general, said Martin LaFleur, a postdoctoral fellow in the laboratory of Arlene ...
UBC Okanagan researchers create new compound to build space-age antennas
2024-02-29
In a first-of-its-kind development, UBC Okanagan researchers, in collaboration with Drexel University, have created a new compound that can be used to 3D print telecommunication antennas and other connectivity devices.
These 3D printed products, created by combining a two-dimensional compound called MXenes with a polymer, can be used as an alternative for metallic counterparts and can make a vast improvement in communication technology including elements such as antennas, waveguides and filters.
Waveguides are everywhere, yet most people don’t know what they are, says Dr. Mohammad Zarifi, a researcher in UBC Okanagan’s Microelectronics and Gigahertz ...
Study detects cognitive changes in older drivers using in-vehicle sensors
2024-02-29
An estimated 4 to 8 million older adults with mild cognitive impairment are currently driving in the United States, and one-third of them will develop dementia within five years. Individuals with progressive dementias are eventually unable to drive safely, yet many remain unaware of their cognitive decline.
Currently, screening and evaluation services for driving can only test a small number of individuals with cognitive concerns, missing many who need to know if they require treatment.
Nursing, engineering and neuropsychology researchers at Florida Atlantic University are testing and evaluating a readily and rapidly available, unobtrusive in-vehicle sensing ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces 2024 Paul Terasaki Award recipient
2024-02-29
(LOS ANGELES) – February 29, 2024 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is pleased to announce their selection of Professor Nicholas A. Peppas of The University of Texas at Austin as the recipient of the 2024 Paul Terasaki Distinguished Scientist Innovation Award. The award will be presented at TIBI’s 2nd annual Terasaki Innovation Summit, to be held March 27-29, 2024, at the UCLA Meyer & Renee Luskin Conference Center.
The award was created in memory of Dr. Paul I. Terasaki, a pioneer in organ transplant research and innovation. It recognizes outstanding achievement in the field of biomedical ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces 2024 Hisako Terasaki Award recipients
2024-02-29
(LOS ANGELES) – February 29, 2024 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is pleased to announce their selections of Assistant Professors Amir Manbachi of Johns Hopkins University and Ritu Raman of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as the recipients of the 2024 Hisako Terasaki Young Innovator Awards. The awards will be presented at TIBI’s 2nd annual Terasaki Innovation Summit, to be held March 27-29, 2024, at the UCLA Meyer & Renee Luskin Conference Center.
The award was created in memory of Hisako Terasaki, philanthropist, accomplished artist, and wife ...