(Press-News.org) Obesity is a risk factor for stillbirth, and the risk increases as pregnancy advances to term, according to a large study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221450.
The overall risk of stillbirth in pregnancy is approximately 0.4% in Canada. "Our findings suggest that an earlier delivery date may help reduce the risk of stillbirth for pregnant people with obesity," says lead author Dr. Naila Ramji, a high-risk pregnancy specialist in Fredericton, New Brunswick, and assistant professor at Dalhousie University, with coauthors at The Ottawa Hospital and senior author Dr. Laura Gaudet, a high-risk pregnancy specialist and associate professor at Queen's University.
Although the link between obesity and stillbirth is well-known, there was little research on the association between obesity and stillbirth risk by gestational age, or on the impact of higher classes of obesity.
To address this gap, the researchers analyzed data from the Better Outcomes Registry and Network on 681 178 singleton births, 1956 of which were stillbirths, in Ontario between 2012 and 2018. After adjusting for other stillbirth risk factors like diabetes and high blood pressure, the researchers found that people with class I obesity (BMI 30–34.9 kg/m2) had double the risk of stillbirth at 39 weeks' gestation compared to those with normal BMI (18.5–24.9 kg/m2). For those in obesity classes II and III (BMI 35–39.9 kg/m2 and BMI 40 kg/m2 and higher, respectively), stillbirth risk at 36 weeks was 2 to 2.5 times that of people with normal BMI. This risk further increased with gestational age, with a more than fourfold risk at 40 weeks.
"For other medical conditions that increase the risk of stillbirth, there are guidelines that recommend delivery at 38 or 39 weeks. Interestingly, the risk thresholds for those conditions are lower than the risks we found associated with obesity. We worry that implicit biases against people with obesity may be causing the medical community to take the risks they face less seriously," says Dr. Ramji.
The authors also looked at whether stillbirths occurred before or during delivery and found a higher risk of stillbirths occurring before delivery in people with class I and II obesity.
They hope that these findings will improve care for this at-risk population.
"Pregnant people with obesity, especially those with additional risk factors may benefit from timely referral and greater surveillance closer to term, and the presence of additional risk factors may warrant earlier delivery," says Dr. Ramji.
In a related editorialhttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240244, CMAJ editor Dr. Naomi Cahill urges that health care providers take a nuanced approach in prenatal counselling of patients with obesity.
"Focusing on weight during communications of risk may reinforce weight bias, weight stigma, and discrimination for pregnant people," writes Dr. Cahill, a registered dietitian. "Negative weight-related attitudes, beliefs, assumptions, and judgments prevalent in society, and harmful social stereotypes that are held about people living with obesity, are associated with adverse physical and mental health consequences." She ends by saying that pregnant people living with obesity "….should receive respectful prenatal care, free from stigma, that realizes the goals of both health care providers and patients to ensure positive maternal and fetal outcomes."
END
Obesity a risk factor for stillbirth, especially at term
2024-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pioneering research reveals empathetic communication can help overcome vaccine hesitancy
2024-03-04
An international study has shown for the first time how empathetic correction of misinformation among vaccine-hesitant patients can significantly improve attitudes towards vaccination – and potentially boost vaccine uptake.
The research, led by the University of Bristol, also found this new style of communication could help build and maintain a positive relationship with health professionals, increasing trust and public confidence. With the UK currently facing a growing measles outbreak, fuelled by declining rates of the Measles, ...
Rare astrolabe discovery reveals Islamic – Jewish scientific exchange
2024-03-04
The identification of an eleventh century Islamic astrolabe bearing both Arabic and Hebrew inscriptions makes it one of the oldest examples ever discovered and one of only a handful known in the world. The astronomical instrument was adapted, translated and corrected for centuries by Muslim, Jewish and Christian users in Spain, North Africa and Italy.
Dr Federica Gigante, from Cambridge University’s History Faculty, made the discoveries in a museum in Verona, Italy, and published them today in the journal Nuncius.
Dr Gigante first came across a newly-uploaded ...
Sleep apnea symptoms linked to memory and thinking problems
2024-03-03
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 3, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People who experience sleep apnea may be more likely to also have memory or thinking problems, according to a preliminary study released today, March 3, 2024, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 76th Annual Meeting taking place April 13–18, 2024, in person in Denver and online. The study shows a positive association but did not determine whether sleep apnea causes cognitive decline.
Sleep ...
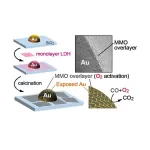
Nanoscale topcoat can turbocharge supported gold nanoparticle catalysts
2024-03-02
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to add single nanosheets of mixed metal oxide to gold nanoparticles supported on silica to enhance their catalytic activity. Converting carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide, they found that the temperature required for the reaction was greatly reduced, with significant improvements over existing methods for coating gold/silica structures. The method paves the way for the development of a wide range of new high-performance catalysts.
Gold nanoparticles, particles less than five nanometers in diameter, are known to be excellent catalysts ...
Beyond the ink: Painting with physics
2024-03-02
Falling from the tip of a brush suspended in mid-air, an ink droplet touches a painted surface and blossoms into a masterpiece of ever-changing beauty. It weaves a tapestry of intricate, evolving patterns. Some of them resemble branching snowflakes, thunderbolts or neurons, whispering the unique expression of the artist's vision.
Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) researchers set out to analyse the physical principles of this fascinating technique, known as dendritic painting. They took inspiration from the artwork ...
Only 9 percent of older Americans were vaccinated against RSV before the disease hit this fall and winter
2024-03-02
A new study from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health found that only 9 percent of older Americans had been vaccinated against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) prior to this fall and winter, despite the threat of increased rates of hospitalization and deaths nationwide from the virus.
“RSV—along with COVID-19 and influenza—form the current ‘tripledemic’ found across the United States this fall and winter,” said Simon Haeder, PhD, the study’s author. “While the elderly, as well as the very young and those with chronic health conditions, typically are affected ...
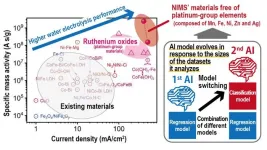
Evolution-capable AI promotes green hydrogen production using more abundant chemical elements
2024-03-02
1. A NIMS research team has developed an AI technique capable of expediting the identification of materials with desirable characteristics. Using this technique, the team was able to discover high-performance water electrolyzer electrode materials free of platinum-group elements—substances previously thought to be indispensable in water electrolysis. These materials may be used to reduce the cost of large-scale production of green hydrogen—a next-generation energy source.
2. Large-scale production of green ...
In wake of powerful cyclone, remarkable recovery of Pacific island’s forests
2024-03-01
After one of the most intense cyclones in world history tore through the Pacific island of Tanna in Vanuatu, new research led by the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa showed the resilience of the island’s forests.
In the Pacific islands, climate change is expected to increase the intensity and frequency of cyclones, causing huge potential risks to forests and the people who depend on them. In March 2015, Cyclone Pam touched down on the island of Tanna as the strongest Pacific island cyclone in history ...
PSU study sheds light on 2020 extreme weather event that brought fires and snow to western US
2024-03-01
The same weather system that led to the spread of the devastating Labor Day wildfires in 2020 brought record-breaking cold and early-season snowfall to parts of the Rocky Mountains. Now, new research from Portland State is shedding light on the meteorology behind what happened and the impacts of such an extreme weather event.
“It’s really interesting to see such an amplified pattern result in opposing extremes in the Pacific Northwest and the Rocky Mountains,” said Emma Russell, a master’s student in geography ...
Rice physicist earns NSF CAREER Award to revolutionize quantum technology
2024-03-01
HOUSTON – (March 1, 2024) – Yonglong Xie, assistant professor of physics at Rice University, has been awarded a Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF). The $888,555 grant over five years will support Xie’s research into harnessing magnons, quantum mechanical wavelike objects in magnetic materials, to create synthetic matter and develop next-generation quantum devices and sensors.
The CAREER program offers NSF’s most prestigious awards in support of early career faculty who have the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education. Xie’s project focuses ...