(Press-News.org) Problems with iron levels in the blood and the body’s ability to regulate this important nutrient as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection could be a key trigger for long COVID, new research has discovered.
The discovery not only points to possible ways to prevent or treat the condition, but could help explain why symptoms similar to those of long COVID are also commonly seen in a number of post-viral conditions and chronic inflammation.
Although estimates are highly variable, as many as three in 10 people infected with SARS-CoV-2 could go on to develop long COVID, with symptoms including fatigue, shortness of breath, muscle aches and problems with memory and concentration (‘brain fog’). An estimated 1.9 million people in the UK alone were experiencing self-reported long COVID as of March 2023, according to the Office of National Statistics.
Shortly after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at the University of Cambridge began recruiting people who had tested positive for the virus to the COVID-19 cohort of the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) BioResource. These included asymptomatic healthcare staff identified via routine screening through to patients admitted to Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, some to its intensive care unit.
Over the course of a year, participants provided blood samples, allowing researchers to monitor changes in the blood post-infection. As it became clear that a significant number of patients would go on to have symptoms that persisted – long COVID – researchers were able to track back through these samples to see whether any changes in the blood correlated with their later condition.
In findings published in Nature Immunology, researchers at the Cambridge Institute of Therapeutic Immunology and Infectious Disease (CITIID), University of Cambridge, together with colleagues at Oxford, analysed blood samples from 214 individuals. Approximately 45% of those questioned about their recovery reported symptoms of long COVID between three and ten months later.
Professor Ken Smith, who was Director of CITIID at the time of the study and is now based at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research (WEHI) in Melbourne, Australia, said: “Having recruited a group of people with SARS-CoV-2 early in the pandemic, analysis of several blood samples and clinical information collected over a 12 month period after infection has proved invaluable in giving us important and unexpected insights into why, for some unlucky individuals, initial SARS-CoV-2 infection is followed by months of persistent symptoms.”
The team discovered that ongoing inflammation – a natural part of the immune response to infection – and low iron levels in blood, contributing to anaemia and disrupting healthy red blood cell production, could be seen as early as two weeks post COVID-19 in those individuals reporting long COVID many months later.
Early iron dysregulation was detectable in the long COVID group independent of age, sex, or initial COVID-19 severity, suggesting a possible impact on recovery even in those who were at low risk for severe COVID-19, or who did not require hospitalisation or oxygen therapy when sick.
Dr Aimee Hanson, who worked on the study while at the University of Cambridge, and is now at the University of Bristol, said: “Iron levels, and the way the body regulates iron, were disrupted early on during SARS-CoV-2 infection, and took a very long time to recover, particularly in those people who went on to report long COVID months later.
“Although we saw evidence that the body was trying to rectify low iron availability and the resulting anaemia by producing more red blood cells, it was not doing a particularly good job of it in the face of ongoing inflammation.”
Interestingly, although iron dysregulation was more profound during and following severe COVID-19, those who went on to develop long COVID after a milder course of acute COVID-19 showed similar patterns in the blood. The most pronounced association with long COVID was how quickly inflammation, iron levels and regulation returned to normal following SARS-CoV-2 infection – though symptoms tended to continue long after iron levels had recovered.
Co-author Professor Hal Drakesmith, from the MRC Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine at the University of Oxford, said iron dysregulation is a common consequence of inflammation and is a natural response to infection.
“When the body has an infection, it responds by removing iron from the bloodstream. This protects us from potentially lethal bacteria that capture the iron in the bloodstream and grow rapidly. It’s an evolutionary response that redistributes iron in the body, and the blood plasma becomes an iron desert.
“However, if this goes on for a long time, there is less iron for red blood cells, so oxygen is transported less efficiently affecting metabolism and energy production, and for white blood cells, which need iron to work properly. The protective mechanism ends up becoming a problem.”
The findings may help explain why symptoms such as fatigue and exercise intolerance are common in long COVID, as well as in several other post-viral syndromes with lasting symptoms.
The researchers say the study points to potential ways of preventing or reducing the impact of long COVID by rectifying iron dysregulation in early COVID-19 to prevent adverse long-term health outcomes.
One approach might be controlling the extreme inflammation as early as possible, before it impacts on iron regulation. Another approach might involve iron supplementation; however as Dr Hanson pointed out, this may not be straightforward.
“It isn't necessarily the case that individuals don't have enough iron in their body, it's just that it’s trapped in the wrong place,” she said. “What we need is a way to remobilise the iron and pull it back into the bloodstream, where it becomes more useful to the red blood cells.”
The research also supports ‘accidental’ findings from other studies, including the IRONMAN study, which was looking at whether iron supplements benefited patients with heart failure – the study was disrupted due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but preliminary findings suggest that trial participants were less likely to develop severe adverse effects from COVID-19. Similar effects have been observed among people living with the blood disorder beta-thalassemia, which can cause individuals to produce too much iron in their blood.
The research was funded by Wellcome, the Medical Research Council, NIHR and European Union Horizon 2020 Programme.
Reference
Hanson, AL et al. Iron dysregulation and inflammatory stress erythropoiesis associates with long-term outcome of COVID-19. Nat Imm; 1 March 2024; DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-01754-8
END
Low iron levels resulting from infection could be key trigger of long COVID
2024-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Swapping meat for Quorn lowers bad cholesterol by 10-percent
2024-03-04
Regularly substituting meat for mycoprotein such as Quorn could help to lower bad cholesterol by 10-percent, which is comparable to switching to a Mediterranean or vegan diet.
New research by the University of Exeter, published in Clinical Nutrition, also found substituting meat for Quorn reduces blood glucose and c-peptide concentrations associated with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality.
With one in six UK adults suffering from raised cholesterol, the findings indicate that mycoprotein - the high protein, high-fibre food source that’s the main ingredient in Quorn - could play a key role in ...
We must stop technology-driven AI and focus on human impact first, global experts warn
2024-03-04
We need to stop designing new AI technology just because we can, causing people to adapt practices, habits and laws to fit the new technology; instead we need to design AI that fits exactly with what we need, according to human-centred AI advocates.
Fifty experts from around the world have contributed research papers to a new book on how to make AI more ‘human-centred,’ exploring the risks — and missed opportunities — of not using this approach and practical ways to implement it.
The experts come from over 12 countries, including Canada, France, Italy, Japan, New Zealand and the UK, and more ...
NCI-MATCH cancer trial discovers a potentially broader role for an established dual HER2-blocking treatment
2024-03-04
An important discovery from the NCI-MATCH precision medicine initiative is being published today in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. Trastuzumab-pertuzumab, a drug combination approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer, shrunk tumors in patients with several other types of cancer with high levels of the HER2 gene. NCI-MATCH (Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice) is one of the first ...
Obesity a risk factor for stillbirth, especially at term
2024-03-04
Obesity is a risk factor for stillbirth, and the risk increases as pregnancy advances to term, according to a large study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221450.
The overall risk of stillbirth in pregnancy is approximately 0.4% in Canada. "Our findings suggest that an earlier delivery date may help reduce the risk of stillbirth for pregnant people with obesity," says lead author Dr. Naila Ramji, a high-risk pregnancy specialist in Fredericton, New Brunswick, and ...
Pioneering research reveals empathetic communication can help overcome vaccine hesitancy
2024-03-04
An international study has shown for the first time how empathetic correction of misinformation among vaccine-hesitant patients can significantly improve attitudes towards vaccination – and potentially boost vaccine uptake.
The research, led by the University of Bristol, also found this new style of communication could help build and maintain a positive relationship with health professionals, increasing trust and public confidence. With the UK currently facing a growing measles outbreak, fuelled by declining rates of the Measles, ...
Rare astrolabe discovery reveals Islamic – Jewish scientific exchange
2024-03-04
The identification of an eleventh century Islamic astrolabe bearing both Arabic and Hebrew inscriptions makes it one of the oldest examples ever discovered and one of only a handful known in the world. The astronomical instrument was adapted, translated and corrected for centuries by Muslim, Jewish and Christian users in Spain, North Africa and Italy.
Dr Federica Gigante, from Cambridge University’s History Faculty, made the discoveries in a museum in Verona, Italy, and published them today in the journal Nuncius.
Dr Gigante first came across a newly-uploaded ...
Sleep apnea symptoms linked to memory and thinking problems
2024-03-03
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 3, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People who experience sleep apnea may be more likely to also have memory or thinking problems, according to a preliminary study released today, March 3, 2024, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 76th Annual Meeting taking place April 13–18, 2024, in person in Denver and online. The study shows a positive association but did not determine whether sleep apnea causes cognitive decline.
Sleep ...
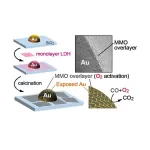
Nanoscale topcoat can turbocharge supported gold nanoparticle catalysts
2024-03-02
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to add single nanosheets of mixed metal oxide to gold nanoparticles supported on silica to enhance their catalytic activity. Converting carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide, they found that the temperature required for the reaction was greatly reduced, with significant improvements over existing methods for coating gold/silica structures. The method paves the way for the development of a wide range of new high-performance catalysts.
Gold nanoparticles, particles less than five nanometers in diameter, are known to be excellent catalysts ...
Beyond the ink: Painting with physics
2024-03-02
Falling from the tip of a brush suspended in mid-air, an ink droplet touches a painted surface and blossoms into a masterpiece of ever-changing beauty. It weaves a tapestry of intricate, evolving patterns. Some of them resemble branching snowflakes, thunderbolts or neurons, whispering the unique expression of the artist's vision.
Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) researchers set out to analyse the physical principles of this fascinating technique, known as dendritic painting. They took inspiration from the artwork ...
Only 9 percent of older Americans were vaccinated against RSV before the disease hit this fall and winter
2024-03-02
A new study from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health found that only 9 percent of older Americans had been vaccinated against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) prior to this fall and winter, despite the threat of increased rates of hospitalization and deaths nationwide from the virus.
“RSV—along with COVID-19 and influenza—form the current ‘tripledemic’ found across the United States this fall and winter,” said Simon Haeder, PhD, the study’s author. “While the elderly, as well as the very young and those with chronic health conditions, typically are affected ...