(Press-News.org) Inspired by amphibians such as the wood frog, investigators designed and synthesized a new type of camouflage skin involving one-dimensional photonic crystal structures assembled in three-dimensional flexible gels.
As described in Advanced Optical Materials, the camouflage skin can quickly recognize and match the background by modulating the optical signals of external stimuli. It demonstrated excellent mechanical performance, self-adaptive camouflage capabilities in response to complex surroundings, and long-term stability in real-world living environments. Bright structural color and mechanical flexibility were maintained even at temperatures as low as -80℃.
The advance could have a range of applications in areas such as artificial intelligence, self-adaptive camouflage, soft robotics, and flexible wearable electronics.
“There is a strong driving force toward artificial camouflage skin innovation in terms of flexibility, integration, and miniaturization,” said co–corresponding author Wen-Yong Lai, PhD, of Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, in China. “We expect active cooperation with professionals of diverse backgrounds to enable further progress in high-performance amphibian-inspired artificial camouflage research.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adom.202302234
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Advanced Optical Materials is an international, interdisciplinary forum for peer-reviewed papers on materials science which focuses on all aspects of light-matter interactions. The scope of Advanced Optical Materials is dedicated to breakthrough discoveries and fundamental research in photonics, plasmonics, metamaterials, and more.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Researchers develop amphibian-inspired camouflage skin
2024-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Network of quantum sensors boosts precision
2024-03-04
The quantum systems employed in quantum technologies, for example single atoms, are also very sensitive: any interaction with the environment can induce changes in the quantum system, leading to errors. However, this remarkable sensitivity of quantum systems to environmental factors actually represents a unique advantage. This sensitivity enables quantum sensors to surpass conventional sensors in precision, for example when measuring magnetic or gravitational fields.
Noise cancellation using correlation spectroscopy
The delicate quantum properties needed for sensing can be covered up ...
Robotic hip exoskeleton shows promise for helping stroke patients regain their stride
2024-03-04
Robotic Hip Exoskeleton Shows Promise for Helping Stroke Patients Regain Their Stride
A portable robotic device created by UMass Amherst researchers provides new avenue for making state-of-the-art gait rehabilitation methods more effective and accessible
AMHERST, Mass. – More than 80% of stroke survivors experience walking difficulty, significantly impacting their daily lives, independence, and overall quality of life. Now, new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst pushes forward the bounds of stroke recovery ...
Conservation value of field research stations grossly misunderstood and underfunded according to 173 conservation scientists in new study
2024-03-04
SAN DIEGO – Funding of field conservation research stations worldwide has been drastically reduced since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, raising the alarm of more than 170 conservation researchers representing 157 field stations in 56 countries in a new paper published in Conservation Letters. The authors contend that field research stations have a high return on investment and are essential and highly effective tools for biodiversity conservation.
Trillions of U.S. dollars were mobilized in economic recovery following the pandemic, yet the authors raise concerns ...
Study underscores social factors of low breast cancer screening in the US
2024-03-04
There is a pressing need to explore and understand which social determinants of health (SDOH) and health inequities act as significant influential factors that contribute to low breast cancer screening behaviors in the United States.
Health disparities have been consistently associated with delayed screening, which then contributes to higher mortality rates among both Hispanic and Black populations. Moreover, poverty, lack of education, neighborhood disadvantage, residential segregation, racial discrimination, lack of social support and social isolation ...
Nanomedicine research aims to transform treatment of aortic aneurysms
2024-03-04
Aortic aneurysms are bulges in the aorta, the largest blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, or injury can all increase the risk of aneurysms, which tend to occur more often in Caucasian male smokers over the age of 65.
“The soft tissues that make up blood vessels act essentially like rubber bands, and it’s the elastic fibers within these tissues that allow them to stretch and snap back,” says Professor Anand Ramamurthi, chair of the Department of Bioengineering in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering ...
HIV medication can be used safely with gender-affirming hormone therapy
2024-03-04
New research definitively shows that HIV antiretrovirals can be taken together with gender-affirming hormone therapy without changing how well either drug works. The study findings can help healthcare providers address potential patient concerns that one drug will counteract the other.
“This study is the first head-to-head pharmacokinetic analysis of two common HIV medications and long-term feminizing hormone therapy use,” says Walter Kraft, MD, director of the Division of Clinical ...
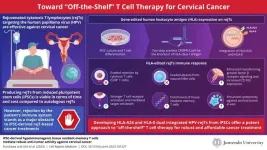
Gene-edited lymphocytes and the path toward ‘off-the-shelf’ therapy against cervical cancer
2024-03-04
Cervical cancer is among the most common malignancies affecting women worldwide. In 2020 alone, approximately 600,000 women were diagnosed with this disease, and over 314,000 died from it. In 99% of the cases, cervical cancer cells harbor human papilloma virus (HPV), and thus, HPV vaccines are an effective way to mitigate the risk of developing this disease. Unfortunately, such preventive measures are useless against established cancers, which are generally incurable once they become metastatic or relapsing.
Fortunately, scientists have made substantial progress in developing a promising ...
Humans have driven the Earth’s freshwater cycle out of its stable state
2024-03-04
A new analysis of freshwater resources across the globe shows that human activity has pushed variation in the planet’s freshwater cycle well outside of its pre-industrial range. The study shows that the updated planetary boundary for freshwater change was surpassed by the mid-twentieth century. In other words, for the past century, humans have been pushing the Earth’s freshwater system far beyond the stable conditions that prevailed before industrialization.
This is the first time that global water cycle change has been assessed over such a long timescale with an appropriate reference baseline. The findings, published in Nature Water, show that human ...
Exposure to different kinds of music influences how the brain interprets rhythm
2024-03-04
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When listening to music, the human brain appears to be biased toward hearing and producing rhythms composed of simple integer ratios — for example, a series of four beats separated by equal time intervals (forming a 1:1:1 ratio).
However, the favored ratios can vary greatly between different societies, according to a large-scale study led by researchers at MIT and the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics and carried out in 15 countries. The study included 39 groups of participants, many of whom came from societies ...
Study shows differences in how patients with impulse control disorder process consequences
2024-03-04
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – March 4, 2024 – Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that affects movement and muscle control. One characteristic of the disease is the deficiency of dopamine, a neurotransmitter or brain chemical that plays a role in movement and can impact how people think and feel.
Dopaminergic medicines can help alleviate the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. However, in some patients, the medications can cause impulse control disorder (ICD), characterized by risky behavior such as excessive gambling, shopping, ...