(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new catheter-based device that combines two powerful optical techniques to image the dangerous plaques that can build up inside the arteries that supply blood to the heart. By providing new details about plaque, the device could help clinicians and researchers improve treatments for preventing heart attacks and strokes.
Atherosclerosis occurs when fats, cholesterol and other substances accumulate on the artery walls, which can cause these vessels to become thick and stiff. A heart attack or stroke may occur if an atherosclerotic plaque inside the blood vessels ruptures or parts of it break off.
“Atherosclerosis, leading to heart attacks and strokes, is the number one cause of death in Western societies — exceeding all combined cancer types — and, therefore, a major public health issue,” said research team member leader Laura Marcu from University of California, Davis. “Better clinical management made possible by advanced intravascular imaging tools will benefit patients by providing more accurate information to help cardiologists tailor treatment or by supporting the development of new therapies.”
In the Optica Publishing Group journal Biomedical Optics Express, researchers describe their new flexible device, which combines fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM) and polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography (PSOCT) to capture rich information about the composition, morphology and microstructure of atherosclerotic plaques. The work was a collaborative project with Brett Bouma and Martin Villiger, experts in OCT from the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital.
“With further testing and development, our device could be used for longitudinal studies where intravascular imaging is obtained from the same patients at different timepoints, providing a picture of plaque evolution or response to therapeutic interventions,” said Julien Bec, first author of the paper. “This will be very valuable to better understand disease evolution, evaluate the efficacy of new drugs and treatments and guide stenting procedures used to restore normal blood flow.”
Gaining an unprecedented view
Most of what scientists know about how atherosclerosis forms and develops over time comes from histopathology studies of postmortem coronary specimens. Although the development of imaging systems such as intravascular ultrasound and intravascular OCT has made it possible to study plaques in living patients, there is still a need for improved methods and tools to investigate and characterize atherosclerosis.
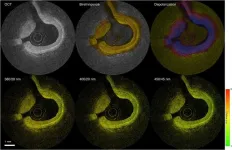
To address this need, the researchers embarked on a multi-year research project to develop and validate multispectral FLIM as an intravascular imaging modality. FLIM can provide insights into features such as the composition of the extracellular matrix (the protein scaffolding between cells), the presence of inflammation and the degree of calcification inside an artery. In earlier work, they combined FLIM with intravascular ultrasound, and in this new work they combined it with PSOCT. PSOCT provides high-resolution morphological information along with birefringence and depolarization measurements. When used together, FLIM and PSOCT provide an unprecedented amount of information on plaque morphology, microstructure and biochemical composition.
“Birefringence provides information about the plaque collagen, a key structural protein that helps with lesion stabilization, and depolarization is related to lipid content that contributes to plaque destabilization,” said Bec. “Holistically, this hybrid approach can provide the most detailed picture of plaque characteristics of all intravascular imaging modalities reported to date.”
Getting two imaging modalities into one device
The development of multimodal intravascular imaging systems compatible with coronary catheterization is technologically challenging. It requires very thin — less than 1 mm — flexible catheters that can operate in vessels with sharp twists and turns. A high imaging speed of around 100 frames/second is also necessary to limit cardiac motion artifacts and ensure proper imaging inside an artery.
To integrate FLIM and PSOCT into a single device without compromising the performance of either imaging modality, the researchers used optical components previously developed by Marcu’s lab and other research groups. Key to achieving high PSOCT performance was a newly designed rotary collimator with high light throughput and a high return loss — the ratio of power reflected back toward the light source compared to the power incident on the device. The catheter system they developed has similar dimensions and flexibility as the intravascular imaging devices that are currently in clinical use.
After testing the new system with artificial tissue to demonstrate basic functionality on well characterized samples, the researchers also showed that it could be used to measure properties of a healthy coronary artery removed from a pig. Finally, in vivo testing in swine hearts demonstrated that the hybrid catheter system’s performance was sufficient to support work toward clinical validation. These tests all showed that the FLIM-PSOCT catheter system could simultaneously acquire co-registered FLIM data over four distinct spectral bands and PSOCT backscattered intensity, birefringence and depolarization information.
Next, the researchers plan to use the intravascular imaging system to image plaques in ex vivo human coronary arteries. By comparing the optical signals acquired using the system with plaque characteristics identified by expert pathologists, they can better understand which features can be identified by FLIM-PSOCT and use this to develop prediction models. They also plan to move forward with testing in support of clinical validation of the system in patients.
Paper: J. Bec, X. Zhou, M. Villiger, J. A. Southard, B. Bouma, L. Marcu, “Dual modality intravascular catheter system combining pulse-sampling fluorescence lifetime imaging and polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography,” Biomed. Opt. Express, Vol. 15, Issue 4, pp. 2114-2132 (2024).
DOI: doi.org/10.1364/OE.516515
About Biomedical Optics Express
Biomedical Optics Express serves the biomedical optics community with rapid, open-access, peer-reviewed papers related to optics, photonics and imaging in biomedicine. The journal scope encompasses fundamental research, technology development, biomedical studies and clinical applications. It is published monthly by Optica Publishing Group and edited by Ruikang (Ricky) Wang, University of Washington, USA. For more information, visit Biomedical Optics Express.
About Optica Publishing Group
Optica Publishing Group is a division of Optica, the society progressing light science and technology. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers from more than 835 conferences, including 6,500+ associated videos. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, Optica Publishing Group represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
END
New cardiovascular imaging approach provides a better view of dangerous plaques
Combining FLIM with polarization sensitive OCT could lead to new ways to prevent heart attacks and strokes
2024-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
BU study finds robotic-assisted surgery for gallbladder cancer as effective as traditional surgery
2024-03-05
(Boston)—Each year, approximately 2,000 people die annually of gallbladder cancer (GBC) in the U.S., with only one in five cases diagnosed at an early stage. With GBC rated as the first biliary tract cancer and the 17th most deadly cancer worldwide, pressing attention for proper management of disease must be addressed. For patients diagnosed, surgery is the most promising curative treatment. While there has been increasing adoption of minimally invasive surgical techniques in gastrointestinal malignancies, including utilization of laparoscopic ...
We know the Arctic is warming -- What will changing river flows do to its environment?
2024-03-05
AMHERT, Mass.– Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently combined satellite data, field observations and sophisticated numerical modeling to paint a picture of how 22.45 million square kilometers of the Arctic will change over the next 80 years. As expected, the overall region will be warmer and wetter, but the details—up to 25% more runoff, 30% more subsurface runoff and a progressively drier southern Arctic, provides one of the clearest views yet of how the landscape will respond to climate change. The results were published in the journal The Cryosphere.
The Arctic is defined ...
BU researcher examines clinicians’ attitudes towards major changes from the 2020 ACS Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines
2024-03-05
(Boston)—Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). New evidence has led to dramatic changes in cervical cancer screening recommendations over the past 20 years. In 2020, the American Cancer Society (ACS) released updated guidelines for cervical cancer screening. The main changes to current practices were to initiate screening at age 25 instead of age 21 and to screen using primary HPV testing rather than cytology (PAP test) alone or in combination with HPV testing. Since adoption of guidelines often occurs slowly, understanding clinician attitudes is important ...
The Arctic could become ‘ice-free’ within a decade
2024-03-05
The Arctic could see summer days with practically no sea ice as early as the next couple of years, according to a new study out of the University of Colorado Boulder.
The findings, published March 5 in the journal Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, suggest that the first ice-free day in the Arctic could occur over 10 years earlier than previous projections, which focused on when the region would be ice-free for a month or more. The trend remains consistent under all future emission scenarios.
By ...
Habitual short sleep duration, diet, and development of type 2 diabetes in adults
2024-03-05
About The Study: In this study involving 247,000 UK residents, habitual short sleep duration was associated with increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This association persisted even among participants who maintained a healthy diet. To validate these findings, further longitudinal studies are needed, incorporating repeated measures of sleep (including objective assessments) and dietary habits.
Authors: Christian Benedict, Ph.D., of Uppsala University in Uppsala, Sweden, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Screen time, sociodemographic factors, and psychological well-being among young children
2024-03-05
About The Study: In this multiyear cross-sectional study of a representative sample of young children in the U.S., the increased prevalence of high screen time in 2020 returned to pre-pandemic levels in 2021; however, it remained elevated in children living in poverty. Two hours or more of daily screen time was associated with lower psychological well-being among preschool-aged children.
Authors: Soyang Kwon, Ph.D., of Northwestern University in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Too little sleep raises risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-03-05
Adults who sleep only three to five hours a day are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is demonstrated in a new study from Uppsala University, published in JAMA Network Open. It also shows that chronic sleep deprivation cannot be compensated by healthy eating alone.
“I generally recommend prioritising sleep, although I understand it’s not always possible, especially as a parent of four teenagers,” says Christian Benedict, Associate Professor and sleep researcher at the Department of Pharmaceutical Biosciences at Uppsala University and leading researcher behind the study.
He and a team of researchers have examined the link between type 2 ...
Toward understanding sperm quality
2024-03-05
A novel screening system developed at Kyoto University enables researchers to investigate sperm cell development and health at the molecular level. The new approach, published in Cell Genomics, promises breakthroughs in male contraception and infertility treatments.
The study, led by Professor Jun Suzuki of the Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS), addresses a critical gap by directly targeting genes within testicular cells inside living organisms. Utilizing a genetic tool called CRISPR, which can ...
Game-changing sensor unveiled for spotting chemical threats
2024-03-05
Scientists have unveiled a groundbreaking sensor that can wirelessly detect chemical warfare agents, marking a significant leap in public safety technology. This innovative device, capable of identifying substances like dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP), offers a new level of efficiency and reliability in monitoring and responding to chemical threats, without the need for direct power sources or physical connections.
The urgent need for advanced detection of chemical warfare agents (CWAs) to ensure global security has led to the development of a novel gas sensor. This sensor is distinguished ...
The many faces of a zinc anode: Configurations can make a difference in performance
2024-03-05
Sometimes the solution to a problem can be as simple as changing the way the components are structured
Researchers have proposed a reconfiguration of zinc anodes, a component of renewable energy sources, to help improve the battery and reduce the reliance society has on fossil fuels. The potential that different configurations of a zinc anode can have could reduce costs and side reactions while increasing the safety of the rechargeable zinc metal battery (RZMB) and, of course, improve its “green” rating.
The results were published in Energy Materials and Devices ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
[Press-News.org] New cardiovascular imaging approach provides a better view of dangerous plaquesCombining FLIM with polarization sensitive OCT could lead to new ways to prevent heart attacks and strokes