(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 6, 2024—Black male elementary school students matched to Black teachers are less likely to be identified for special education services, according to new research published today. The relationship is strongest for economically disadvantaged students. The study, by Cassandra Hart at the University of California, Davis, and Constance Lindsay at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill appeared in the American Educational Research Journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
The researchers also found that the connection is especially strong in special education categories that are more open to teacher discretion, such as learning disabilities. For their study, Hart and Lindsay drew on rich statewide administrative data from North Carolina that included more than 540,000 observations of Black children in grades 1 to 4 and their assigned teachers from 2008–08 through 2012–13.
“Our findings add to the growing body of evidence that having access to Black teachers matters to Black children’s educational journeys,” said Hart, a professor of education at the University of California, Davis. “We show that access to Black teachers most strongly affects precisely the types of special disability placements that are more subject to teacher discretion, and therefore where the need for services is more questionable.”
“It may be that Black teachers interpret certain behaviors as simple inattentiveness rather than a disability, or that Black students respond to Black teachers with more engagement,” said Lindsay, an assistant professor of educational leadership at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Hart and Lindsay noted that special education placement, when appropriate, can be beneficial for children. However, concerns arise when children are exposed to the potential stigma of special education in cases where the benefits may be less pronounced and the need for services may be more discretionary. Prior research has also suggested that Black teachers hold higher expectations for Black students.
Approximately 7 percent of teachers nationwide are Black, compared to 15 percent of students, according to the U.S. Department of Education.
“Our results add to the growing evidence for why diversifying the teacher workforce is important for improving student outcomes from all backgrounds,” said Hart. “Beyond that, school districts may want to consider providing clear guidance to teachers around when they should urge screening for disabilities, to minimize the role of teacher discretion in the identification process.”
Hart and Lindsay also found that Black teachers were less likely to identify White children for disability services than non-Black teachers, although the relationship was not as strong as it was with Black boys.
“Black teachers may be simply less likely across the board to suggest screening for disabilities,” Lindsay said. “Regardless of the reason, this finding is consistent with prior research showing that diversifying teachers does not harm, and often benefits, non-Black students as well.”
Study citation: Hart, C. & Lindsay, C. (2024). Teacher-student race match and identification for discretionary educational services. American Educational Research Journal. Prepublished March 6, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312241229413
###
About AERA
The American Educational Research Association (AERA) is the largest national interdisciplinary research association devoted to the scientific study of education and learning. Founded in 1916, AERA advances knowledge about education, encourages scholarly inquiry related to education, and promotes the use of research to improve education and serve the public good. Find AERA on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, Threads, and Bluesky.
END
Study: Black boys are less likely to be identified for special education when matched with Black teachers
Relationship is strongest for students from economically disadvantaged backgrounds
2024-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new genus of fungi on grasses
2024-03-06
While ecologically important, small mushrooms on monocots (grasses and sedges) are rarely studied and a lack of information about their habitat and DNA sequences creates difficulties in determining their presence or absence in ecological studies and their genetic relationships to other mushroom taxa.
This study led by Drs. Karen W. Hughes and Ronald H. Petersen (University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA) examined a mushroom species, Campanella subdendrophora, (also known as Tetrapyrgos subdendrophora), which fruits on grasses in the US Pacific Northwest.
The researchers evaluated its phylogenetic position concerning both Campanella and Tetrapyrgos ...
Allen Institute joins the Weill Neurohub
2024-03-06
SEATTLE, WASH.—March 6, 2024—The Allen Institute has officially become the newest member of the Weill Neurohub, a collaborative research network advancing treatments for neurological diseases.
Founded in 2003 by philanthropist Paul G. Allen, the Allen Institute focuses on big questions in biology through a team-based, open science approach, and currently has moonshot projects in neuroscience, cell biology, and immunology institutes.
The new partnership will integrate the Allen Institute’s expertise ...
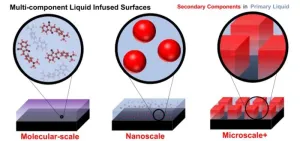
Revolutionizing surface technology: Introducing multi-component liquid-infused surfaces for adaptive and functional coatings
2024-03-06
Surface coatings have long been essential in various industries, offering protection and functionality. In recent years, liquid-infused surfaces (LIS) have emerged as a groundbreaking technology, revolutionizing how we approach surface coatings. In a review article recently published in Industrial Chemistry & Materials on Feb. 23, 2024, authors Zachary Applebee and Dr. Caitlin Howell explore a novel approach in surface technology that could significantly impact various industries, including healthcare and environmental conservation. A new frontier is emerging: multi-component ...
Nanodevices can produce energy from evaporating tap or seawater
2024-03-06
Evaporation is a natural process so ubiquitous that most of us take it for granted. In fact, roughly half of the solar energy that reaches the earth drives evaporative processes. Since 2017, researchers have been working to harness the energy potential of evaporation via the hydrovoltaic (HV) effect, which allows electricity to be harvested when fluid is passed over the charged surface of a nanoscale device. Evaporation establishes a continuous flow within nanochannels inside these devices, which act as passive pumping mechanisms. This effect is also seen in the microcapillaries of plants, where ...
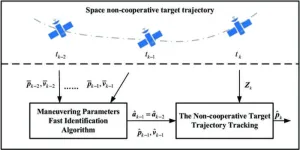
Scientist proposed a research on space noncooperative target trajectory tracking based on maneuvering parameter estimation
2024-03-06
Firstly, the authors briefly describe two models for tracking the maneuvering trajectories of non-cooperative space targets: the relative dynamics model and the indirect measurement model. In the relative dynamics model, tracking the maneuvering trajectory of the target is modeled as a problem of tracking the target's position over short discrete time intervals. On the other hand, the indirect measurement model transforms radar-derived values directly into measurements in the Local Vertical Local Horizontal (LVLH) coordinate system.
Next, the authors address the tracking problem of targets ...
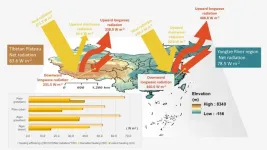
Scientists uncover comparable net radiation between the high-elevation Tibetan Plateau and the low-elevation Yangtze River region
2024-03-06
Land–atmosphere interactions play a crucial role in shaping Earth’s climate system, profoundly influencing weather patterns, climate variables, and ecological processes. Despite being located at similar latitude, the Tibetan Plateau (TP) and Yangtze River region (YRR) represent two distinct climate zones, garnering significant attention in this field. The former, situated in western China at an altitude exceeding 4000 m, is characterized by an arid climate, whereas the latter, located in the eastern Chinese plain, experiences a humid climate. Although both the TP and YRR have ...
Why some RNA drugs work better than others
2024-03-06
Spinal muscular atrophy, or SMA, is the leading genetic cause of infant death. Less than a decade ago, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Adrian Krainer showed this brutal disease can be treated by tweaking a process called RNA splicing. This breakthrough resulted in Spinraza, the first effective treatment for SMA. It also opened a new frontier in drug development. Now, CSHL research could push RNA-splicing drugs even further. CSHL Associate Professor Justin Kinney, Krainer, and postdoc Yuma Ishigami have ...
Scientists-CT scanned thousands of natural history specimens, which you can access for free
2024-03-06
Read the online version (Available 8:00 a.m. ET, March 6, 2024)
Watch the video (Embargoed. Do not distribute before 8:00 a.m. ET, March 6, 2024)
Natural history museums have entered a new stage of scientific discovery and accessibility with the completion of openVertebrate (oVert), a five-year collaborative project among 18 institutions to create 3D reconstructions of vertebrate specimens and make them freely available online.
Researchers published a summary of the project in the journal BioScience in which they review the specimens that have been scanned to date and offer a glimpse of how the data might be used to ask new questions ...
INFUSE workshop gives private and public fusion partners a chance to network and share experiences
2024-03-06
More than 120 people gathered for the 2024 Innovation Network for Fusion Energy (INFUSE) Workshop at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) from Feb. 27-28.
The event, which was sponsored by the DOE’s Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES), is a part of the INFUSE awards program that funds laboratories or universities so they can partner with private sector companies working on the science and technology ...
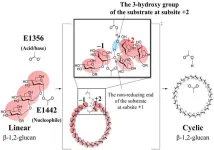
Uncovering the cyclization mechanism of cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase
2024-03-06
The polysaccharide β-1,2-glucan consists of repeating units of glucose linked together by β-1,2-glycosidic bonds. Cyclic β-1,2-glucans (CβGs) occur in different bacterial species and have a role in bacterial infections and symbiotic relationships. CβG biosynthesis is catalyzed by cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase (CGS), an enzyme that catalyzes the cyclization (closed ring formation) of linear β-1,2-glucan (LβG).
Since the method for large-scale enzymatic synthesis of linear β-1,2-glucan has already been established, combining it with this enzyme is technically feasible for efficient ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Study: Black boys are less likely to be identified for special education when matched with Black teachersRelationship is strongest for students from economically disadvantaged backgrounds