(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that pediatric atopic dermatitis (AD) was generally associated with greater odds of reported difficulties in learning and memory. However, this association was primarily limited to children with neurodevelopmental comorbidities, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder or learning disabilities. These results may improve the risk stratification of children with AD for cognitive impairments and suggest that evaluation for cognitive difficulties should be prioritized among children with AD and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Authors: Joy Wan, M.D., M.S.C.E., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.0015)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.0015?guestAccessKey=acf90071-b414-45e8-9728-508a12b66c60&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=030624
END
Symptoms of cognitive impairment among children with atopic dermatitis
JAMA Dermatology
2024-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Charge fractionalisation observed spectroscopically
2024-03-06
A research team led by the Paul Scherrer Institute has spectroscopically observed fractionalisation of electronic charge in an iron-based metallic ferromagnet. Experimental observation of the phenomenon is not only of fundamental importance. Since it appears in an alloy of common metals at accessible temperatures, it holds potential for future exploitation in electronic devices. The discovery is published in the journal Nature.
Basic quantum mechanics tells us that the fundamental unit of charge is unbreakable: the electron charge is quantised. Yet, we have come to understand that exceptions exist. In some situations, ...
Bee-2-Bee influencing: Bees master complex tasks through social interaction
2024-03-06
In a groundbreaking discovery, bumblebees have been shown to possess a previously unseen level of cognitive sophistication. A new study, published in Nature, reveals that these fuzzy pollinators can learn complex, multi-step tasks through social interaction, even if they cannot figure them out on their own. This challenges the long-held belief that such advanced social learning is unique to humans, and even hints at the presence of key elements of cumulative culture in these insects.
Led by Dr Alice Bridges and Professor Lars Chittka , the research team designed a two-step puzzle box requiring ...
New study may broaden the picture of the consequences of childhood adversity
2024-03-06
A research team has examined the link between adverse childhood experiences and the risk of mental health problems later in life, according to a study in JAMA Psychiatry. The researchers from Karolinska Institutet and University of Iceland have found that the risk of suffering from mental illness later in life among those experiencing significant adversity in childhood can be partly explained by factors shared by family members, such as genetics and environment.
Several previous studies have shown that people who have experienced ...
Revealing the evolutionary origin of genomic imprinting
2024-03-06
Some of our genes can be expressed or silenced depending on whether we inherited them from our mother or our father. The mechanism behind this phenomenon, known as genomic imprinting, is determined by DNA modifications during egg and sperm production. The Burga Lab at the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences uncovered a novel gene regulation process, associated with the silencing of selfish genes, that could represent the first step in the evolution of imprinting. Their discovery, reported in Nature, ...
Universal tool for tracking cell-to-cell interactions
2024-03-06
One of the fundamental goals of basic biology is understanding how diverse cell types work in concert to form tissues, organs, and organ systems. Recent efforts to catalog the different cell types in every tissue in our bodies are a step in the right direction, but only one piece of the puzzle. The great mystery of how those cells communicate with one another remains unsolved.
Now, a new paper in Nature describes uLIPSTIC, a tool capable of laying the groundwork for a dynamic map tracking the physical interactions between different cells—the elusive cellular interactome. The authors have been perfecting the technology since 2018 and the latest iteration ...
Synthetic DNA sheds light on mysterious difference between living cells at different points in evolution
2024-03-06
“Random DNA” is naturally active in the one-celled fungi yeast, while such DNA is turned off as its natural state in mammalian cells, despite their having a common ancestor a billion years ago and the same basic molecular machinery, a new study finds.
The new finding revolves around the process by which DNA genetic instructions are converted first into a related material called RNA and then into proteins that make up the body’s structures and signals. In yeast, mice, and humans, the first step in a gene’s expression, transcription, proceeds as DNA molecular “letters” (nucleobases) are read in one direction. While 80% of the human genome ...
AI can speed design of health software
2024-03-06
Artificial intelligence helped clinicians to accelerate the design of diabetes prevention software, a new study finds.
Publishing online March 6 in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, the study examined the capabilities of a form of artificial intelligence (AI) called generative AI or GenAI, which predicts likely options for the next word in any sentence based on how billions of people used words in context on the internet. A side effect of this next-word prediction is that the generative AI “chatbots” like chatGPT can generate replies to questions in realistic language, and produce clear summaries of complex texts.
Led ...
Shrinking technology, expanding horizons
2024-03-06
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and its collaborators have delivered a small but mighty advancement in timing technology: compact chips that seamlessly convert light into microwaves. This chip could improve GPS, the quality of phone and internet connections, the accuracy of radar and sensing systems, and other technologies that rely on high-precision timing and communication.
This technology reduces something known as timing jitter, which is small, random changes in the timing of microwave signals. Similar to when a musician is trying to keep a steady beat in music, the timing of these signals can sometimes waver a bit. The researchers ...
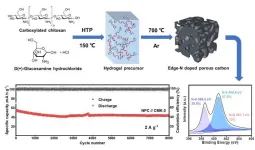
Edge-nitrogen doped porous carbon for energy-storage potassium-ion hybrid capacitors
2024-03-06
They published their work on March. 4th in Energy Material Advances, a Science Partner Journal (https://spj.science.org/journal/energymatadv).
"The development of cost-effective and high-performance electrochemical energy storage devices is imperative," said paper's corresponding author Wei Chen, a professor in the School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC). "Currently, lithium-ion batteries still dominate the market, but they are limited in both lithium as a resource and in their power densities."
Chen ...
Revolutionary elephant iPSC milestone reached in Colossal’s Woolly Mammoth Project
2024-03-06
Dallas, TX – March 06, 2024 - Colossal Biosciences (“Colossal”), the world’s first de-extinction company, announces today that their Woolly Mammoth team has achieved a global-first iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cells) breakthrough. This milestone advancement was one of the primary early goals of the mammoth project, and supports the feasibility of future multiplex ex utero mammoth gestation.
iPSC cells represent a single cell source that can propagate indefinitely and give rise to every other type of cell in a body. As such, the progress with elephant iPSCs extends far beyond ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Symptoms of cognitive impairment among children with atopic dermatitisJAMA Dermatology