(Press-News.org) A research team, affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a cutting-edge catalyst with exceptional oxidizing power, capable of extracting electrons from compounds. Anticipated to revolutionize various fields, including the development of metal catalysts and synthetic chemistry, this catalyst marks a significant breakthrough in catalytic research.
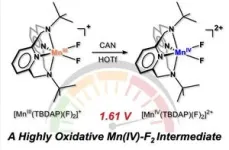
Led by Professor Jaeheung Cho in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, the research team successfully synthesized the pioneering manganese-fluorine catalyst, utilizing the Macrocyclic Pyridinophane System. This catalyst demonstrates the ability to induce oxidation reactions, facilitating efficient electron loss from toxic toluene derivatives.
Through meticulous analysis, the research team has uncovered the underlying mechanisms responsible for the catalyst’s exceptional performance in oxidation reactions. By modulating the electronic environment of various compounds, the team verified the catalyst’s capability to catalyze the oxidation of toluene derivatives with unparalleled efficiency. This groundbreaking research represents the first exploration of the physicochemical properties of transition metal-fluorine species, introducing a new paradigm for carbon-hydrogen bond decomposition based on electron transfer reactions.
Professor Cho emphasized the significance of activating organic matter with robust carbon-hydrogen bonds, emphasizing their propensity to accept electrons and undergo reduction through high-reduction potential chemical reactions. The unique characteristics of manganese-fluorine species enable catalytic transformations in this context.
The advancement of organic catalysts through carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond activation is a crucial research area with extensive applications in pharmaceuticals and industrial processes. Efforts are underway to develop cost-effective metal catalysts by emulating the activities of diverse metal enzymes through bio-simulation research.
Recent focus has been directed towards metal-halide materials that combine transition metals like iron and manganese with halogen atoms, particularly fluorine, acting as intermediates for oxidizing diverse organic substances. The newly synthesized manganese-fluorine catalyst emerges as the most reactive metal-halide species disclosed to date, offering promising applications in industrial processes.
The research team meticulously analyzed the oxidation mechanism facilitated by the catalyst, showcasing enhanced reaction rates by manipulating the electronic environment of various compounds. Noteworthy is the catalyst’s remarkable efficiency in oxidizing toluene derivatives, a feat previously unseen with existing metal-halide species.
The groundbreaking study, co-authored by researchers Donghyun Jeong and Yujeong Lee under the guidance of Professor Cho, has been published in the online version of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on February 4, underscoring its significance in the realm of chemistry. Supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), this research propels carbon-neutral technologies forward and contributes to the advancement of next-generation academics and pivotal progress in the environmental and industrial sectors.
Journal Reference
Donghyun Jeong, Yujeong Lee, Yuri Lee, et al., “Synthesis, Characterization, and Reactivity of a Highly Oxidative Mononuclear Manganese(IV)–Bis(Fluoro) Complex,” JACS (2024).
END
A new manganese-fluorine catalyst with exceptional oxidizing power
2024-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An aspirin a day? Poll of older adults suggests some who take it may be following outdated advice
2024-03-07
One in four older adults take aspirin at least three times a week, mostly in hopes of preventing heart attacks and strokes, a new poll shows.
But many people aged 50 to 80 who said they take aspirin may not need to, the findings from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging suggest.
In all, 57% of people aged 50 to 80 who say they take aspirin regularly also said they don’t have a history of cardiovascular disease. Such people should have a conversation with their health care provider about what’s best for them before stopping or starting aspirin use.
National guidelines have changed in recent years for using aspirin for prevention, ...
What makes a pathogen antibiotic-resistant?
2024-03-07
Antimicrobial resistance is a story of constantly moving parts and players. With every new or tweaked antibiotic or antimicrobial drug, the targeted pathogens begin the evolutionary dance of acquiring resistance, prompting researchers to constantly develop workarounds or entirely new classes of medicine.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of acquired antimicrobial resistance is critical to the fight, a case of knowing one’s enemy. In a new paper published March 2, 2024 in npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, part of the Nature Portfolio, researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys, working with Roche Pharma Research and Early Development, ...
Method rapidly verifies that a robot will avoid collisions
2024-03-07
Before a robot can grab dishes off a shelf to set the table, it must ensure its gripper and arm won’t crash into anything and potentially shatter the fine china. As part of its motion planning process, a robot typically runs “safety check” algorithms that verify its trajectory is collision-free.
However, sometimes these algorithms generate false positives, claiming a trajectory is safe when the robot would actually collide with something. Other methods that can avoid false positives are typically too slow for robots in the real world.
Now, MIT researchers have developed a safety check technique which can prove with 100 percent accuracy ...
Eating habits, physical activity practice and clinical prognosis of colorectal cancer patients with overweight/obesity
2024-03-07
Background and objectives
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease associated with the development of several other diseases, including cancer. The present study aims to evaluate the eating habits, physical activity, and clinical profiles of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with overweight/obesity.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with data collected from the medical records of patients diagnosed with CRC (n = 41) from June 2019 to June 2022. Additionally, a questionnaire (n = 35) was applied to gather information on eating habits and physical activity. The data were ...
Exploring the effectiveness of a novel pain management device for endometriosis pain
2024-03-07
Endometriosis is a chronic condition affecting women, often resulting in painful symptoms such as menstrual cramps and pelvic pain. Pain caused by endometriosis significantly lowers the quality of life and reproductive health of affected women, with around one-third of women still experiencing pain and discomfort despite treatment. While hormonal therapies and surgeries are common treatments, they often do not result in complete alleviation of symptoms. Effectively managing pain is, therefore, crucial for managing ...
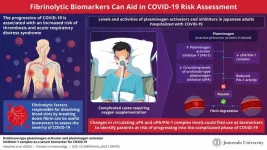
Fibrinolytic biomarkers for identifying patients at risk of severe COVID-19
2024-03-07
The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare systems has been significant. The sudden surge in infected cases overwhelmed hospitals and disrupted routine healthcare services, thus further worsening public health. Managing patients, too, has been challenging due to the variation of COVID-19 symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, that require medical intervention.
To help hospitals prioritize patients in need of care, researchers have been looking into various biological markers that can determine the risk of the disease becoming more severe. Among these, proteins in the blood related to blood clot formation, increased inflammation, and ...
Exploring the surface properties of NiO with low-energy electron diffraction
2024-03-07
Spintronics is a field that deals with electronics that exploit the intrinsic spin of electrons and their associated magnetic moment for applications such as quantum computing and memory storage devices. Owing to its spin and magnetism exhibited in its insulator-metal phase transition, the strongly correlated electron systems of nickel oxide (NiO) have been thoroughly explored for over eight decades. Interest in its unique antiferromagnetic (AF) and spin properties has seen a revival lately, since NiO is a potential material for ultrafast spintronics devices.
Despite this rise in popularity, exploration of its surface magnetic properties using ...
What drives students to take up teaching? New study explores aspirations and challenges faced by prospective teachers in Japan
2024-03-07
As role models and mentors for the youth, teachers play an important role in guiding children into well-rounded adults. However, excessive workloads and high skill expectations have allegedly led to teacher shortages in Japan. In 2022, the Ministry of Education Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) reported a record low in applicants for primary school teaching positions, and a survey from the same year revealed that 65.8% of 924 full-time educators expressed a desire to quit due to overwhelming demands.
To address the teacher shortage, Associate Professor Akihiro Saito from ...
Baby quasars: Growing supermassive black holes
2024-03-07
The James Webb Space Telescope makes one of the most unexpected findings within its first year of service: A high number of faint little red dots in the distant Universe could change the way we understand the genesis of supermassive black holes. The research, led by Jorryt Matthee, Assistant Professor in astrophysics at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), is now published in The Astrophysical Journal.
A bunch of little red dots found in a tiny region of our night sky might be an unexpected breakthrough for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) within its first year of service. These objects were indistinguishable from normal galaxies through the ...
Carnegie Mellon researchers develop new machine learning method for modeling of chemical reactions
2024-03-07
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Los Alamos National Laboratory have used machine learning to create a model that can simulate reactive processes in a diverse set of organic materials and conditions.
"It's a tool that can be used to investigate more reactions in this field," said Shuhao Zhang, a graduate student in Carnegie Mellon University's Department of Chemistry. "We can offer a full simulation of the reaction mechanisms."
Zhang is the first author on the paper that explains the creation and results of this new machine learning model, ...