(Press-News.org) A team of scientists from the University of Exeter, Met Office and Imperial College have found a new way to calculate the total carbon emissions consistent with the Paris climate targets of 1.5oC and 2oC of global warming.
Although the exceptionally warm climate in 2023 was close to exceeding the 1.5oC level, the Paris targets relate to the average warming over ten or more years.
The new study answers the question: how much carbon have we got left before we pass the Paris limits?
About 15 years ago, climate scientists discovered a remarkably useful fact about climate change.
Despite the vast complexity of the climate system, global warming depends overwhelmingly on the total carbon dioxide emissions since pre-industrial times.
This discovery opened up the possibility of defining total carbon budgets consistent with the Paris targets, and led to the definition of Net Zero as the point at which global warming essentially stops.
The problem is, the Earth System Models used to make climate projections disagree hugely about how much global warming we will get for a billion tonnes of carbon emissions.
The new study solves this problem by showing that observed global warming and estimated carbon emissions up to the current day are a really good indicator of how much carbon emissions are left before we pass the Paris climate targets.
The authors do this by what they call an “Emergent Constraint”, which is a fancy name for something quite simple.
Basically, they look at results from all of the available Earth System Models, which form a lovely straight line linking emissions per oC of global warming up to now, with emissions for a given level of future global warming.
This means that best estimates of global warming and emissions up to the current day can be converted simply into estimates of the total carbon budget for the Paris climate targets.
The good news is that the new study estimates emissions budgets that are at least 10% larger than the average value for the models.
The bad news is that if humankind continues to emit carbon at the currently rate, we have a little more than a decade before we exceed the Paris 1.5oC target, even for decade-mean warming.
Co-author Chris Jones, from the Met Office, said: “This emergent constraint is elegant and powerful. It both uses observations to narrow the possible range of future emissions, but also lets us consider other greenhouse gases than just CO2. In this way the remaining carbon budget is made much more policy relevant.”
Lead author Peter Cox, Director of the Global Systems Institute at the University of Exeter, said: “Our study clarifies the climate problem that needs to be solved, and we hope that it will stimulate greater efforts to reduce our emissions to Net Zero.”
Peter Cox, Mark Williamson, Pierre Friedlingstein, Chris Jones, Nina Raoult, Joeri Rogelj, Rebecca Varney, 2024. Emergent constraints on carbon budgets as a function of global warming. Nat Comm. 15, 1885. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46137-7
END
A better handle on the emissions budget for the Paris climate targets
2024-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High cholesterol was twice as prevalent among American Indian teens and young adults
2024-03-08
Research Highlights:
A study of more than 1,400 people in U.S. tribal communities found that high cholesterol was twice as prevalent among American Indian adolescents and young adults compared to the overall U.S. population.
The study also noted that few study participants with high cholesterol sought or received treatment during the study period.
DALLAS, March 8, 2024 — Young American Indians, ages 15-39, had cholesterol levels more than two times higher than the general U.S. population, according to new research published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access, peer-reviewed journal of the American ...
Good news for coral reef restoration efforts: Study finds “full recovery” of reef growth within four years
2024-03-08
While the majority of the world’s reefs are now under threat or even damaged potentially beyond repair, a new study reported in the journal Current Biology on March 8 offers some encouraging news: efforts to restore coral reefs not only increase coral cover, but they can also bring back important ecosystem functions, and surprisingly fast.
“We found that restored coral reefs can grow at the same speed as healthy coral reefs just four years after coral transplantation,” says Ines Lange (@InesLange9) of University of Exeter, UK. “This means that they provide lots of habitat for ...
Balancing training data and human knowledge makes AI act more like a scientist
2024-03-08
When you teach a child how to solve puzzles, you can either let them figure it out through trial and error, or you can guide them with some basic rules and tips. Similarly, incorporating rules and tips into AI training—such as the laws of physics—could make them more efficient and more reflective of the real world. However, helping the AI assess the value of different rules can be a tricky task.
Researchers report March 8 in the journal Nexus that they have developed a framework for assessing the ...
Restored coral reefs can grow as fast as healthy reefs
2024-03-08
Planting new coral in degraded reefs can lead to rapid recovery – with restored reefs growing as fast as healthy reefs after just four years, new research shows.
Reefs worldwide are severely threatened by local and global pressures. In Indonesia, where the study was carried out, destructive blast fishing destroyed large reef areas 30-40 years ago – with no signs of recovery until now.
The Mars Coral Reef Restoration Programme attempts to restore degraded reefs by transplanting coral fragments onto a network of interconnected ...
Continuous Medicaid eligibility during the pandemic and postpartum coverage, health care, and outcomes
2024-03-08
About The Study: In this study including 47,000 participants, continuous Medicaid eligibility during the COVID-19 pandemic significantly reduced loss of Medicaid after birth, suggesting similar uninsurance reductions may be expected from post-pandemic postpartum Medicaid extensions, which most states plan to implement.
Authors: Jamie R. Daw, Ph.D., of the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.0004)
Editor’s ...
Perspectives of Black patients on racism within emergency care
2024-03-08
About The Study: This qualitative study including 25 interviews with Black patients discharged from the emergency department described these patients’ perspectives about racism in health care, recent clinical experiences, and thoughts on system improvements. Black patients described a notable amount of medical mistrust, anticipation of racism in emergency care, and personal experiences with clinical instances of racism in emergency treatment.
Authors: Anish K. Agarwal, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding ...
Impact of onset time, number, type, and sequence of extrahepatic organ failure on prognosis of acute-on-chronic liver failure
2024-03-08
Background and Aims
The impact of the characteristics of extrahepatic organ failure (EHOF) including the onset time, number, type, and sequence on the prognosis of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) patients remains unknown. This study aimed to identify the association between the characteristics of EHOF and the prognosis of ACLF patients.
Methods
ACLF subjects enrolled at six hospitals in China were included in the analysis. The risk of mortality based on the characteristics of EHOF was evaluated. Survival of study groups was ...
High-tech 'paint' could spare patients repeated surgeries
2024-03-08
UVA Health researchers have received $2.8 million to advance their development of a high-tech way to save heart and dialysis patients from the need for multiple surgeries.
Researchers Lian-Wang Guo, PhD, and K. Craig Kent, MD, are pioneering a quick and gentle technique to “paint” tiny nanoparticles on transplanted veins to prevent the veins from becoming clogged in the future. This type of blockage often causes cardiovascular and dialysis patients to require repeated surgeries; approximately half of all heart ...
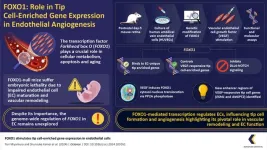
Unveiling the role of FOXO1 in vascular development and transcriptional dynamics in endothelial cells
2024-03-08
The human vascular system, a complex network of blood vessels, plays an essential role in maintaining health. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying vascular development is important for tackling age-related disorders. The Forkhead box O (FOXO1) transcription factor is crucial in processes related to aging, cellular metabolism, and apoptosis. Despite its significance, the comprehensive regulation of FOXO1 across the genome in endothelial cells (EC) has not been investigated.
In a new paper published in iScience in February 2024, a research team from Kumamoto University ...
Call for papers| Special Issue on advanced robotics and tissue engineering
2024-03-08
Scope
For decades, robotic systems have played a pivotal role in nurturing the growth of tissue-engineered constructs in controlled environments through the provision of mechanical stimulation. The importance of physical stresses in tissue maturation is not only intuitive from our own bodily experiences but is also supported by a growing body of mechanotransduction research. However, experimental studies have predominantly remained confined to basic in vitro setups, hampering our ability to produce functional grafts that can translate into clinical practice. Emerging evidence suggests that replicating physiological stresses more faithfully could further enhance the functionality of tissue ...