(Press-News.org) A multi-institution team led by researchers at the White River Junction VA Medical Center in Vermont found that Veterans’ blood pressure control worsened due to disrupted care during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings were published in the journal Medical Care.
The researchers followed a group of nearly 1.65 million Veterans who received their care at VA and who had high blood pressure (hypertension) during two periods—before the pandemic and during the pandemic. In Veterans with controlled blood pressure, researchers found a 7% decline in control during the pandemic compared to before the pandemic. Longer follow-up intervals were associated with a decreased likelihood of maintaining blood pressure control in both periods.
Most of the difference in control was explained by delays in follow-up care, according to the research team, led by Dr. Caroline Korves. But the pandemic itself was responsible for a small (2%) effect on blood pressure control.
Researchers also discovered that Veterans who had not yet achieved blood pressure control and who experienced longer intervals between follow-up care were modestly more likely to gain control during the pandemic, but not before the pandemic. The finding suggests that providers focused slightly more on people with uncontrolled blood pressure, an appropriate clinical response, according to the team.
“Opportunities for further research into the cause of the pandemic effect—whether lower maintenance of control stemmed from missed opportunity for treatment modifications, changes in patient behavior, or other factors―and investigating whether a modestly higher likelihood of gaining control was due to focusing on patients with more extreme conditions, would offer valuable insights in how to prevent disruptions in care during similar crises,” wrote the researchers.
High blood pressure remains one of the top public health challenges in the country and contributes to serious health problems, like heart disease and kidney failure. It is a modifiable risk factor for heart disease―meaning it can respond to treatment―and is an important marker to track for disruptions in care, according to the research team.
The research was part of the VA Health Services Research and Development Disrupted Care National Project (DCNP), that aims to better understand disruptions in care during the COVID-19 pandemic. The DCNP is led by Dr. Louise Davies, Dr. Amy Justice, and Dr. Anita Vashi, and is based at the White River Junction VA Medical Center, Vermont, with additional sites at West Haven, Connecticut, and Palo Alto, California.
END
Blood pressure control in veterans declined during the COVID-19 pandemic
Researchers identified a 7% decline in blood pressure control during the pandemic
2024-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lighting the way to noninvasive blood glucose monitoring using portable devices
2024-03-08
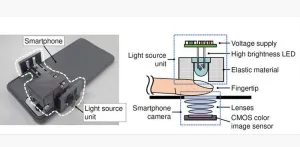
Diabetes is a very prevalent disease that, unfortunately, still has no treatment. People with diabetes need to monitor their blood glucose levels (BGLs) regularly and administer insulin to keep them in check. In almost all cases, BGL measurements involve drawing blood from a fingertip through a finger prick. Since this procedure is painful, less invasive alternatives that leverage modern electronics are being actively researched worldwide.
Thus far, several methods to measure BGL have been proposed; using infrared light is a prominent example, and mid-infrared light-based devices have shown reasonable performance. However, the required sources, ...
What's behind the surge of fatty liver disease in Latinx kids?
2024-03-08
For Latinx kids, unreliable access to food at age 4 raises the odds of having fatty liver disease later in childhood by nearly four times, a new UC San Francisco-led study found.
About 5% to 10% of children in the United States have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, putting its prevalence on par with asthma. Pediatric cases have spiked in the last decade, with millions now affected by a disease marked by pain, fatigue and jaundice that can lead to cirrhosis, cancer and organ transplantation. Latinx children and adults ...
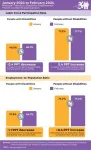
nTIDE February 2024 Jobs Report: Overall employment trend still positive despite recent declines for people with disabilities
2024-03-08
East Hanover, NJ – March 8, 2024 – Despite recent declines in the labor force participation rate and employment-to-population ratio, the overall employment trend remains positive for people with disabilities, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing January 2024 to February 2024)
Based on data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics ...
Locating single neurons that monitor and regulate the heart and lungs
2024-03-08
The body self-regulates in a process known as homeostasis, and the brain is responsible for this
as it is constantly monitoring all of the body’s vital signals. If you need more oxygen, for
example, then a message is sent to the brain that then tells the body to adjust your breathing
and your heart rate. But the neurons involved in regulating breathing and cardiac rhythm had
never been directly observed, until now, thanks to brain recording technology during brain
surgery.
EPFL neuroscientists, in a collaboration with surgeons and neuroscientists at West Virginia
University Rockefeller Neuroscience ...
Primary care scarcity linked to more surgical emergencies & problems
2024-03-08
America’s shortage of primary care doctors and nurse practitioners has a downstream effect in the nation’s operating rooms, a new study finds.
And patients suffer as a result.
In all, people living in areas with the most severe shortages of primary care providers have a much higher risk of having emergency surgery, rather than a scheduled operation,
compared with people with the same condition who live in areas with less-dire primary care shortages.Those living in the areas with the lowest availability of primary care providers ...
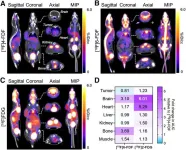
Novel PET tracer maps fructose metabolism to identify cardiac and neural disorders
2024-03-08
Reston, VA—A new PET radiotracer can differentiate diseased tissues from healthy tissues based on fructose metabolism, according to new research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Fructose metabolism—or fructolysis—is indicative of a variety of diseases, and by noninvasively mapping fructolysis physicians can more accurately detect diseases and treat them earlier.
Glucose is used as the primary biochemical fuel throughout the body, powering key processes like tissue function, growth, and repair. Glucose is also consumed extensively during inflammation and cancer growth and can be visualized with PET scans. Evidence continues to mount that ...
Pushing the boundary on ultralow frequency gravitational waves
2024-03-08
A team of physicists has developed a method to detect gravity waves with such low frequencies that they could unlock the secrets behind the early phases of mergers between supermassive black holes, the heaviest objects in the universe.
The method can detect gravitational waves that oscillate just once every thousand years, 100 times slower than any previously measured gravitational waves.
“These are waves reaching us from the farthest corners of the universe, capable of affecting how light travels,” said Jeff Dror, Ph.D., an assistant ...
New study reveals molecular fingerprint of biological aging
2024-03-08
University of Pittsburgh researchers have uncovered blood-based markers linked with healthy and rapid aging, allowing them to predict a person’s biological age — how fast a person’s cells and organs age regardless of their birthdate.
The new research, published in Aging Cell, points to pathways and compounds that may underlie biological age, shedding light on why people age differently and suggesting novel targets for interventions that could slow aging and promote healthspan, the length of time a person is healthy.
“Age is more than just a number,” said senior author Aditi Gurkar, Ph.D., assistant professor of geriatric medicine at ...
Glowing flowers illuminate homes and gardens with organic light
2024-03-08
Sun Valley, ID - March 8, 2024 – Recent discoveries published in Science Advances have unveiled a native plant gene that enables researchers to more effortlessly harness the captivating glow of bioluminescent plants. This gene, which varies across different plant species, allows for the redirection of living energy into organic light. The advancement reveals the intricate inner rhythms and dynamics of plants through continuously evolving luminosity, offering a natural source of illumination for homes, gardens, and beyond.
The study received support from Light Bio, a pioneer in the development of bioluminescent plants. Light Bio is dedicated to fostering ...
Research sheds light on new strategy to treat infertility
2024-03-08
New research from Oregon Health & Science University describes the science behind a promising technique to treat infertility by turning a skin cell into an egg that is capable of producing viable embryos.
Researchers at OHSU documented in vitro gametogenesis, or IVG, in a mouse model through the preliminary steps of a technique that relies upon transferring the nucleus of a skin cell into a donated egg whose nucleus has been removed. Experimenting in mice, researchers coaxed the skin cell’s nucleus into reducing its chromosomes by half, so that it could then be fertilized ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
Flagging claims about cancer treatment on social media as potentially false might help reduce spreading of misinformation, per online experiment with 1,051 US adults
Yawns in healthy fetuses might indicate mild distress
Conservation agriculture, including no-dig, crop-rotation and mulching methods, reduces water runoff and soil loss and boosts crop yield by as much as 122%, in Ethiopian trial
Tropical flowers are blooming weeks later than they used to through climate change
Risk of whale entanglement in fishing gear tied to size of cool-water habitat
Climate change could fragment habitat for monarch butterflies, disrupting mass migration
Neurosurgeons are really good at removing brain tumors, and they’re about to get even better
[Press-News.org] Blood pressure control in veterans declined during the COVID-19 pandemicResearchers identified a 7% decline in blood pressure control during the pandemic