(Press-News.org) A blood test that can accurately detect when someone has not slept for 24 hours has been developed by experts at Monash University, in Australia, and the University of Birmingham, in the UK.
This level of sleep deprivation increases the risk of serious injury or fatality in safety critical situations.
Published in Science Advances, the biomarker used a combination of markers found in the blood of healthy volunteers. Together, these markers accurately predicted when the study volunteers had been awake for more than 24 hours under controlled laboratory conditions.
The biomarker detected whether individuals had been awake for 24 hours with a 99.2 percent probability of being correct, when compared to their own well-rested sample. When a single sample was considered without the well-rested comparison (similar to a diagnostic blood test), it dropped to 89.1 per cent, which was still very high.
With about 20 per cent of road accidents worldwide caused by sleep deprivation, researchers hope the discovery may inform future tests to quickly and simply identify sleep deprived drivers. The biomarker could also be developed for other situations where sleep deprivation may lead to catastrophic consequences, such as in safety-critical workplaces.
Senior author Professor Clare Anderson led the research while she was with the Monash University School of Psychological Sciences and Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health. She is now Professor of Sleep and Circadian Science at the University of Birmingham in the UK.
“This is a really exciting discovery for sleep scientists, and could be transformative to the future management of health and safety relating to insufficient sleep,” Professor Anderson said. “While more work is required, this is a promising first step.
“There is strong evidence that less than five hours’ sleep is associated with unsafe driving, but driving after 24 hours awake, which is what we detected here, would be at least comparable to more than double the Australian legal limit of alcohol performance wise.”
The test may be also ideal for future forensic use but further validation is required.
First author Dr Katy Jeppe, from the Monash Proteomics and Metabolomics Platform, previously from the School of Psychological Sciences, said it was difficult to say how soon the test could be developed for post-accident use.
“Next steps would be to test it in a less controlled environment and maybe under forensic conditions, particularly if it was to be used as evidence for crashes involving drivers falling asleep,” Dr Jeppe said.
“Given it’s blood, the test is more limited in a roadside context, but future work could examine whether our metabolites, and therefore the biomarker, are evident in saliva or breath.”
This sleep deprivation biomarker is based on 24 hours or more awake, but can detect down to 18 hours awake. A biomarker for limited sleep over the previous night could be developed but more research is required to combine the time since sleep with the amount of sleep in the predictions.
"Much further work would be needed if laws were to change and a sleep deprivation test introduced on the road or in workplaces,” Dr Jeppe said. “This would include further validation of biomarkers, as well as establishing safe levels of sleep to prevent and recover from impairment, not to mention the extensive legal process.”
“A biomarker for limited sleep over the previous night could be developed, and others have made progress in this respect (Depner et al.).”
Sleep deprivation can have fatal consequences for other safety-critical occupations. Major catastrophes including the Chernobyl nuclear reactor meltdown and the Challenger space shuttle Disaster* are thought to be caused, in part, by human error associated with fatigue.
“Objective tests that identify individuals who present as a risk to themselves or others are urgently needed in situations where the cost of a mistake is fatal,” Professor Anderson said.
“Alcohol testing was a game changer for reducing road crashes and associated serious injuries and fatalities, and it is possible that we can achieve the same with fatigue. But much work is still required to meet this goal.”
This research was conducted in association with the Cooperative Research Centre for Alertness, Safety and Productivity.
END
Blood-based marker developed to identify sleep deprivation
2024-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Paclitaxel-coated balloon vs uncoated balloon for coronary in-stent restenosis
2024-03-09
About The Study: Among patients undergoing coronary angioplasty for in-stent restenosis, a paclitaxel-coated balloon was superior to an uncoated balloon with respect to the composite end point of target lesion failure in this multicenter randomized trial that included 600 patients. Paclitaxel-coated balloons are an effective treatment option for patients with coronary in-stent restenosis.
Authors: Robert W. Yeh, M.D., M.Sc., of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, is ...
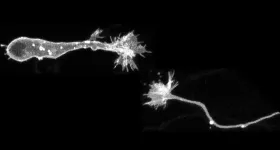
Deciphering the tip of migrating neurons: Discovery of growth cone in migrating neurons involved in promoting neuronal migration and regeneration in the brain after injury
2024-03-09
The structure and functions of the tip of migrating neurons remain elusive. Here, a research group led by Kazunobu Sawamoto, Professor at Nagoya City University and National Institute for Physiological Sciences, and by Chikako Nakajima and Masato Sawada, staff scientists in his laboratory, has found that the PTPσ-expressing growth cone senses the extracellular matrix and drives neuronal migration in the injured brain, leading to functional recovery.
Neural stem cells are present in the postnatal mammalian brain and produce new neurons. New neurons ...
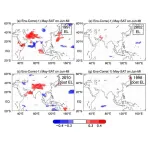
Land or sea? Scientists reveal effect of land conditions on Asian monsoon climate
2024-03-09
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have used numerical simulations to show how conditions on land impact weather during Asian summer monsoons. Focusing on the Tibetan plateau, they studied how varied land conditions combined with fixed maritime conditions illuminate the specific effects of the land on the weather. They found that the significance of land-atmosphere coupling varies greatly from year to year, with unexpectedly low dependence on maritime phenomena like El Niño.
Asian monsoon systems impact some of the most highly populated areas of the world, affecting enormous swathes of Asia and ...
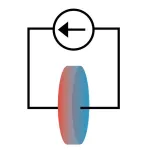
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells
2024-03-08
Batteries are usually studied via electrical properties like voltage and current, but new research suggests that observing how heat flows in conjunction with electricity can give important insights into battery chemistry.
A team of researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has demonstrated how to study chemical properties of lithium-ion battery cells by exploiting the Peltier effect, in which electrical current causes a system to draw heat. Reported in the journal Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, this ...
NRL participates in international campaign investigating polar low phenomena
2024-03-08
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) research meteorologist James Doyle, Ph.D., joins an international team of scientists to investigate meteorological processes associated with Arctic cold air outbreaks.
From late February through early April, the 45-day international field campaign CAESAR, short for Cold-Air outbreak Experiment in the Sub-Arctic Region, is focused on cold-air outbreaks that occur as cold Arctic air flows-out over warmer open waters between northern Norway and ...
Are mountains carbon dioxide sources or sinks? New study finds they can be both
2024-03-08
There’s been a long-running debate in Earth sciences over whether mountains are a source of carbon dioxide or if they remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through mineral weathering. A new study has found that mountains can be sources or sinks and has identified the tipping point at which they switch from one to the other.
The study — by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Colorado State University and the German Research Centre for Geosciences — found that many mountains exist on a spectrum of removing or releasing carbon, and erosion rates determine the impact of mountains ...
Child care costs, availability keeping New York parents at home, poll finds
2024-03-08
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Two out of five New Yorkers with children who participated in a recent poll report that a member of their household opts not to work, mostly because child care is too expensive, while child care workers earn among the lowest wages in the state, according to a report released March 8 by the Cornell School of Industrial and Labor Relations Buffalo Co-Lab.
Continuing a multiyear effort with collaborators to determine the “true” cost of child care, “The Status of Child Care in New York State” finds that recent increases in state subsidies helped stabilize ...
Blood pressure control in veterans declined during the COVID-19 pandemic
2024-03-08
A multi-institution team led by researchers at the White River Junction VA Medical Center in Vermont found that Veterans’ blood pressure control worsened due to disrupted care during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings were published in the journal Medical Care.
The researchers followed a group of nearly 1.65 million Veterans who received their care at VA and who had high blood pressure (hypertension) during two periods—before the pandemic and during the pandemic. In Veterans with controlled blood pressure, researchers found a 7% decline in control during the pandemic compared ...
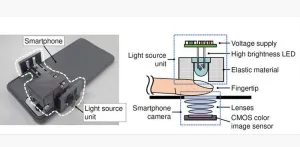
Lighting the way to noninvasive blood glucose monitoring using portable devices
2024-03-08
Diabetes is a very prevalent disease that, unfortunately, still has no treatment. People with diabetes need to monitor their blood glucose levels (BGLs) regularly and administer insulin to keep them in check. In almost all cases, BGL measurements involve drawing blood from a fingertip through a finger prick. Since this procedure is painful, less invasive alternatives that leverage modern electronics are being actively researched worldwide.
Thus far, several methods to measure BGL have been proposed; using infrared light is a prominent example, and mid-infrared light-based devices have shown reasonable performance. However, the required sources, ...
What's behind the surge of fatty liver disease in Latinx kids?
2024-03-08
For Latinx kids, unreliable access to food at age 4 raises the odds of having fatty liver disease later in childhood by nearly four times, a new UC San Francisco-led study found.
About 5% to 10% of children in the United States have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, putting its prevalence on par with asthma. Pediatric cases have spiked in the last decade, with millions now affected by a disease marked by pain, fatigue and jaundice that can lead to cirrhosis, cancer and organ transplantation. Latinx children and adults ...