(Press-News.org) Winter storms that provide crucial snow and rainfall to northern India are arriving significantly later in the year compared to 70 years ago, a new study has found, exacerbating the risk of catastrophic flooding while also reducing vital water supplies for millions of Indians.
The cyclonic storms, known as western disturbances, typically bring heavy snow to the Himalayas from December to March. This snowpack slowly melts in spring, providing a steady supply of irrigation water for wheat and other crops downstream.
The study, published today (Tuesday, 12 March 2024), in the journal Weather and Climate Dynamics, reveals western disturbances are occurring more often during India’s summer. Over the past 70 years, the storms have increased in frequency by 60% from April to July, reducing snowfall and increasing the risk of heavy flooding.
Author Dr Kieran Hunt, of the University of Reading, said: "Strong storms are now twice as likely to occur in the north of India in June compared to 70 years ago. With warmer and moister air at this time of year, these late storms are dumping heavy rainfall instead of snow. This raises the risk of deadly flooding like we saw in Uttarakhand in 2013 and around Delhi in 2023.
"Some areas of Kashmir saw no snow at all in December or January. This is a serious concern for the 750 million people in the Indus and upper Ganges basins who rely on these winter snows for water supplies.
"The loss of winter snow and the increasing late-season storms that heighten flood risks is a one-two suckerpunch that underscores the urgent need to respond to the far-reaching impacts of climate change in this sensitive region."
Warming the Tibetan Plateau
The research team attributes this seasonal shift to changes in the subtropical jet stream, a high-altitude air current that steers western disturbances. The rapid warming of the Tibetan Plateau - which is a long stretch of level high ground at the intersection of Central, South, and East Asia - is creating a larger temperature contrast with surrounding areas, fueling a stronger jet stream that powers more frequent and intense storms.
At the same time, global warming is weakening the temperature difference between the equator and poles that normally draws the jet stream northward in summer. As a result, the jet stream is increasingly lingering at southerly latitudes later into spring and summer, allowing more storms to strike North India after the winter snow season.
Arriving in the pre-monsoon heat, these increasingly frequent late-season storms unleash heavy rainfall instead of snow, raising risks of devastating flooding. Meanwhile, winter snowfall is declining as the region warms, threatening spring water supplies.
END
India's water problems set to get worse as the world warms
2024-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GPS nanoparticle platform precisely delivers therapeutic payload to cancer cells
2024-03-11
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A newly developed “GPS nanoparticle” injected intravenously can home in on cancer cells to deliver a genetic punch to the protein implicated in tumor growth and spread, according to researchers from Penn State. They tested their approach in human cell lines and in mice to effectively knock down a cancer-causing gene, reporting that the technique may potentially offer a more precise and effective treatment for notoriously hard-to-treat basal-like breast cancers.
They published their work today (March 11) in ACS Nano. They also filed a provisional application to patent the technology ...
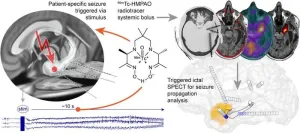
New method for triggering and imaging seizures can help guide epilepsy surgery
2024-03-11
Researchers have developed a new method for triggering and imaging seizures in epilepsy patients, offering physicians the ability to collect real-time data to tailor epilepsy surgery. In contrast to previous practice, where physicians from neurology and nuclear medicine had to wait for hours to days in hopes of capturing the onset of a seizure, the new method is convenient, spares resources, and is clinically feasible. This research was published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
People with epilepsy and seizures who do not respond to medication are often helped by brain surgery. The goal ...
Giving particle detectors a boost
2024-03-11
Device could help facilitate the operation of new particle colliders, such as the Electron-Ion Collider.
In particle colliders that reveal the hidden secrets of the tiniest constituents of our universe, minute particles leave behind extremely faint electrical traces when they are generated in enormous collisions. Some detectors in these facilities use superconductivity — a phenomenon in which electricity is carried with zero resistance at low temperatures — to function.
For scientists to more accurately observe the behavior of these particles, these weak electrical signals, or currents, need ...
Aging at AACR Annual Meeting 2024
2024-03-11
BUFFALO, NY- March 11, 2024 – Impact Journals publishes scholarly journals in the biomedical sciences with a focus on all areas of cancer and aging research. Aging is one of the most prominent journals published by Impact Journals.
Impact Journals will be participating as an exhibitor at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2024 from April 5-10 at the San Diego Convention Center in San Diego, California. This year, the AACR meeting theme is “Inspiring Science • Fueling ...
Oncotarget at AACR Annual Meeting 2024
2024-03-11
BUFFALO, NY- March 11, 2024 – Impact Journals publishes scholarly journals in the biomedical sciences with a focus on all areas of cancer and aging research. Oncotarget is one of the most prominent journals published by Impact Journals.
Impact Journals will be participating as an exhibitor at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2024 from April 5-10 at the San Diego Convention Center in San Diego, California. This year, the AACR meeting theme is “Inspiring Science • Fueling Progress • Revolutionizing Care.”
Visit booth #4159 at the AACR Annual Meeting 2024 to connect with members of ...
Analysis reveals long-term impact of calcium and vitamin D supplements on health in postmenopausal women
2024-03-11
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 11 March 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also ...
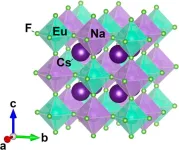
Design rules and synthesis of quantum memory candidates
2024-03-11
In the quest to develop quantum computers and networks, there are many components that are fundamentally different than those used today. Like a modern computer, each of these components has different constraints. However, it is currently unclear what materials can be used to construct those components for the transmission and storage of quantum information.
In new research published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, University of Illinois Urbana Champaign materials science & engineering professor Daniel Shoemaker and graduate student Zachary Riedel ...
BIDMC-led trial leads to FDA approval of coronary drug-coated balloons
2024-03-11
BOSTON – In the largest randomized clinical trial and first of its kind to date in the United States, a team led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) assessed the efficacy and safety of using a drug-coated balloon in patients undergoing coronary angioplasty. In an original investigation presented at the Cardiology Research Technology conference in Washington, D.C. and published simultaneously in JAMA, the team reports that patients treated with a balloon coated with paclitaxel, a drug to prevent restenosis, experienced lower rates of failure compared with patients treated with an uncoated balloon.
The findings of the trial—which ...
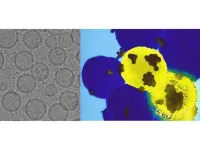
This protein pic could help develop new cancer treatments
2024-03-11
Some cancerous tumors hijack proteins that act as “brakes” on our immune system and use them to form a sort of shield against immune recognition. Immunotherapy treatments have been created that turn off these “brakes” and allow our body to attack foreign-looking cancer cells. To further advance such treatments, researchers at Stanford University and New York University have published a new structure of one of these brake proteins, LAG-3. Their work contains key details of the molecule’s structure, as well as information about how the LAG-3 protein functions.
Although over a dozen immunotherapies targeting LAG-3 are in development, and one is already FDA approved, ...
Mathematicians use AI to identify emerging COVID-19 variants
2024-03-11
Scientists at The Universities of Manchester and Oxford have developed an AI framework that can identify and track new and concerning COVID-19 variants and could help with other infections in the future.
The framework combines dimension reduction techniques and a new explainable clustering algorithm called CLASSIX, developed by mathematicians at The University of Manchester. This enables the quick identification of groups of viral genomes that might present a risk in the future from huge volumes of data.
The study, presented this week ...