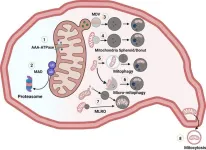
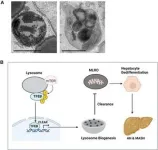
(Press-News.org) Scientists have identified a new organelle in liver cells called the mitochondria-lysosome-related organelle (MLRO). This discovery could improve our understanding of chronic liver diseases like alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD).
Mitochondria are essential components of cells, often called the "powerhouses" because they generate energy. They also play a crucial role in metabolism, calcium signalling, and cell survival. When mitochondria malfunction, it's linked to various liver diseases.
Cells have intricate mechanisms to maintain healthy mitochondria. One way is to get rid of damaged parts through a process called mitophagy. However, researchers have now found a new pathway involving MLRO.
MLRO is a unique organelle formed by the fusion of a mitochondrion and a lysosome, a cellular "garbage disposal" unit. This hybrid organelle appears to be an alternative way to break down damaged parts of mitochondria, potentially offering a more efficient process than traditional mitophagy.
The study suggests that MLRO formation might be linked to a process called dedifferentiation, where liver cells lose their specialized functions. This dedifferentiation is a hallmark of late-stage chronic liver diseases.
Understanding how MLRO functions could lead to new therapeutic strategies for chronic liver diseases. By regulating MLRO formation, scientists might be able to promote healthy liver cell function and potentially slow disease progression.
While this discovery is exciting, many questions remain unanswered. Researchers are still investigating the exact mechanisms of MLRO formation and its role in liver health and disease.
See the article:
Ma X, Ni H-M, Ding W-X. Perspectives of mitochondria-lysosome-related organelle in hepatocyte dedifferentiation and implications in chronic liver disease. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100046. doi:10.1136/egastro-2023-100046
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
Four exceptional UNIST students were honored for their outstanding academic and research achievements at the prestigious 30th Annual Samsung Humantech Paper Award ceremony.
Among the many eminent individuals, JungSoo Lee (Advisor: Professor Han Gi Chae) from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering notched the highest score and won the Gold Prize within the category of Energy & Environment. His groundbreaking research on enhancing the efficiency of thermoelectric power generation through the development of a new power generation device structure technology earned him this accolade. By focusing on optimizing the structure ...
-- There is a widening employment gap between people with and without disability --
-- In 2022, only 53.1 per cent of people with work-limiting disability were employed, compared to 81.8 per cent of people without disability --
-- People with disability are 25-30 percentage points less likely to be employed --
-- Over a quarter of people with disability cite transport as a barrier to finding work --
A new report by the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre at Curtin University reveals that there has been no improvement in employment rates for people with disability ...
For thousands of Americans each year, a bone marrow transplant has the potential to cure diseases such as leukemias, lymphomas and immune deficiency disorders. While lifesaving, bone marrow transplants are taxing procedures that can affect various organs, including the cardiovascular system.
With advances in medical science and improvement in protocols, more bone marrow transplants, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, are being offered to older patients, a population at greater risk of cardiovascular disease.
Researchers led by ...
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
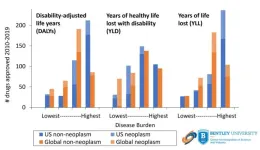
Drug approvals in the United States between 2010-2019 were aligned with the US, but not global, burden of disease and the increasing number of expedited drug approvals could make the gap worse according to a study in the BMJ Open. The study also demonstrates that drugs indicated for conditions with the greatest burden of disease were less likely to be approved through the FDA’s expedited approval programs that reduce the timeline and cost of drug development, thus making it relatively more expensive to develop these products. US markets and FDA approval play an important role in shaping the product portfolios of global pharmaceutical companies; as such, expedited ...
A study links a rise in a serious bacterial illness to an unexpected factor: a decline in air pollution. Legionnaires’ disease is a respiratory illness with a fatality rate of 10–25% that is caused by inhaled Legionella bacteria. The bacteria live in water and outbreaks have been linked to water sources such as cooling towers, which cool indoor spaces by dissipating heat into the atmosphere in the form of water droplets and vapor. Other sources include improperly maintained public fountains, hot tubs, ice machines, home humidifiers, and showers. A global rise in Legionnaires’ disease since the year 2000 has puzzled ...
We experience turbulence every day: a gust of wind, water gushing down a river or mid-flight bumps on an airplane.
Although it may be easy to understand what causes some kinds of turbulence — a felled tree in a river or a bear splashing around for salmon — there is now evidence that a very small disturbance at the start can have dramatic effects later. Instead of a tree, think of a twig — or even the swerving motion of a molecule.
University of California San Diego Chancellor’s Distinguished Professor of Physics Nigel Goldenfeld, along with his former student Dmytro Bandak, and Professors Alexei ...
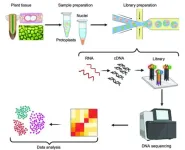
Recent breakthroughs in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA), such as the recently developed “RevGel-seq” method, has revolutionized plant cell analysis. This technique, independent of special instruments, streamlines processes and resolves protoplast isolation challenges. Now, a multinational team of researchers review this and other such recent advances in plant scRNA sequencing with the intention of providing guidance for facilitating the appropriate selection of scRNA methods for different plant samples.
In the world of plant biology, understanding ...
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (03/12/2024) - Researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities may have discovered a mechanical explanation for instability observed in the lungs in cases of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), particularly in the aftermath of respiratory illnesses such as COVID-19 or pneumonia.
The research was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), a peer reviewed journal of the National Academy of Sciences.
Currently, there is no known cure for ARDS, a life-threatening ...
Lignin is an abundant natural polymer which is eliminated as a byproduct in the pulp and paper industry. A recent review article explored different microbial processes available for sustainable lignin valorization, yielding not only environmental, but also economic benefits. Researchers highlighted the current advancements as well as challenges faced while using naturally occurring and engineered microbes to transform depolymerized lignin into valuable high-value products.
The increasing focus on transitioning to a low-carbon ...
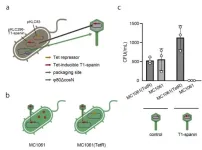
Given the worldwide prevalence of drug-resistance bacteria, the research fraternity is on the lookout for alternative bactericidal treatment approaches. In a recent study, Japanese researchers have now compared bacteriophage-derived enzymes for combating drug-resistant bacteria. Examination of T1-spanin revealed that it shows superior bactericidal activity against various strains, including E.coli. Furthermore, a novel phage-based technology effectively delivers T1-spanin genes into target bacteria. This breakthrough holds promise for the development of ...