(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC – The Editorial Board of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) has selected six papers published by PNAS in 2023 to receive the Cozzarelli Prize, an award that recognizes outstanding contributions to the scientific disciplines represented by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Papers were chosen from more than 3,000 research articles that appeared in the journal last year and represent the six broadly defined classes under which the NAS is organized. Additionally, the Editorial Board has recognized six papers—one in each class—as finalists for the 2023 Cozzarelli Prize.
The annual Cozzarelli Prize acknowledges papers that reflect scientific excellence and originality. The award was established in 2005 as the Paper of the Year Prize and was renamed in 2007 to honor late PNAS Editor-in-Chief Nicholas R. Cozzarelli. The 2023 awardees will be recognized at an awards ceremony during the NAS Annual Meeting in April 2024.
2023 Cozzarelli Prize Recipients
Class I: Physical and Mathematical Sciences
Winner:
Supermassive Dark Star candidates seen by JWST
Cosmin Ilie, Jillian Paulin, and Katherine Freese
“Dark stars” have been proposed as stars in the early universe that are powered by the annihilation of dark matter within a hydrogen cloud. Such dark stars could grow to become objects a million times the size of the Sun and a billion times as bright as the Sun. The authors of this study report three objects imaged by the James Webb Space Telescope that are candidate dark stars. The telescope’s resolution is insufficient to discern whether the objects are point sources of light, such as puffy dark stars or an entire galaxy. The authors suggest that future observations of gravitationally magnified objects may enable measurements that could confirm the existence of dark stars.
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2305762120
Finalist:
Coupled atmospheric chemistry, radiation, and dynamics of an exoplanet generate self-sustained photochemistry
Yangcheng Luo, Yongyun Hu, Jun Yang, Michael Zhang, and Yuk L. Yung
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2309312120
Class II: Biological Sciences
Winner:
Reversal of an existing hearing loss by gene activation in Spns2 mutant mice
Elisa Martelletti, Neil J. Ingham, and Karen P. Steel
Mechanical aids can mitigate the symptoms of hearing loss, but the underlying causes are generally considered irreversible. One common form of hearing loss in mice results in the loss of electrical potential in the endolymph, which is the fluid in contact with hair cells in the cochlea. The authors of this study used a genetic mechanism in mice that lack the Spns2 gene and develop hearing loss as a result. When it was delivered early, the mechanism, which was triggered by a drug and re-instated Spns2 gene transcription, restored hearing in deaf mice. Delays in treatment resulted in diminished restoration, suggesting a critical period of reversibility. The authors suggest that the method may be used to explore the reversibility of other genetic disorders.
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2307355120
Finalist:
Horizontal gene transfer underlies the painful stings of asp caterpillars (Lepidoptera: Megalopygidae)
Andrew A. Walker, Samuel D. Robinson, David J. Merritt, Fernanda C. Cardoso, Mohaddeseh Hedayati Goudarzi, Raine S. Mercedes, David A. Eagles, Paul Cooper, Christina N. Zdenek, Bryan G. Fry, Donald W. Hall, Irina Vetter, and Glenn F. King
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2305871120
Class III: Engineering and Applied Sciences
Winner:
A minimal physics-based model for musical perception
Kosar Mozaffari, Fatemeh Ahmadpoor, Qian Deng, and Pradeep Sharma
Musical perception is a complex phenomenon. Variation in the physical properties of the auditory system, such as the hair cells of the internal ear, may partially account for differences in people’s ability to perceive musical tones. The authors of this study developed a model of the mechanics of the hair cells of the inner ear. The physics-based model explains how the geometry and electromechanical properties of hair cells may influence musical perception. The model also explores the impact of factors external to the auditory system, including medications such as ibuprofen.
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2216146120
Finalist:
Carbon–cement supercapacitors as a scalable bulk energy storage solution
Nicolas Chanut, Damian Stefaniuk, James C. Weaver, Yunguang Zhu, Yang Shao-Horn, Admir Masic, and Franz-Josef Ulm
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2304318120
Class IV: Biomedical Sciences
Winner:
Steroid receptor coactivator 3 is a key modulator of regulatory T cell–mediated tumor evasion
Sang Jun Han, Prashi Jain, Yosef Gilad, Yan Xia, Nuri Sung, Mi Jin Park, Adam M. Dean, Rainer B. Lanz, Jianming Xu, Clifford C. Dacso, David M. Lonard, and Bert W. O'Malley
Steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC-3) is highly expressed in regulatory T cells (Tregs), which play a key role in restraining the immune system and preventing autoimmune diseases. SRC-3 and Tregs have both been associated with tumor progression. The authors of this study eliminated SRC-3 expression in the Tregs of genetically engineered mice, resulting in long-lasting eradication of aggressive breast and prostate cancers, without apparent autoimmune side effects. Transfer of SRC-3-deleted Tregs from the genetically engineered mice into wild-type mice with preexisting tumors similarly resulted in tumor elimination without recurrence. The results suggest that SRC-3-deleted Tregs may hold promise for improved cancer treatments.
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2221707120
Finalist:
Losartan controls immune checkpoint blocker-induced edema and improves survival in glioblastoma mouse models
Meenal Datta, Sampurna Chatterjee, Elizabeth M. Perez, Simon Gritsch, Sylvie Roberge, Mark Duquette, Ivy X. Chen, Kamila Naxerova, Ashwin S. Kumar, Mitrajit Ghosh, Kyrre E. Emblem, Mei R. Ng, William W. Ho, Pragya Kumar, Shanmugarajan Krishnan, Xinyue Dong, Maria C. Speranza, Martha R. Neagu, J. Bryan Iorgulescu, Raymond Y. Huang, Gilbert Youssef, David A. Reardon, Arlene H. Sharpe, Gordon J. Freeman, Mario L. Suvà, Lei Xu, and Rakesh K. Jain
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2219199120
Class V: Behavioral and Social Sciences
Winner:
Vaccination, immunity, and the changing impact of COVID-19 on infant health
Florencia Torche and Jenna Nobles
Maternal COVID-19 infection has been associated with increased risk of preterm birth, which can have lifelong health and socioeconomic consequences. The authors of this study analyzed population-level data on live births and maternal COVID-19 infection status in California between 2014 and 2023. Comparing siblings born before and during the pandemic allowed the authors to identify the impact of maternal COVID-19 infection and the protective role of vaccination. Prenatal COVID-19 exposure increased preterm birth risk early in the pandemic, but this effect fully disappeared by 2022. The negative impact ended almost 1 year earlier in ZIP codes with high COVID-19 vaccination rates. The results suggest that the deployment of COVID-19 vaccines may have prevented thousands of preterm births.
https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2311573120
Finalist:
Agricultural intensification and childhood cancer in Brazil
Marin Elisabeth Skidmore, Kaitlyn M. Sims, and Holly K. Gibbs
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2306003120
Class VI: Applied Biological, Agricultural, and Environmental Sciences
Winner:
Forgotten food crops in sub-Saharan Africa for healthy diets in a changing climate
Maarten van Zonneveld, Roeland Kindt, Stepha McMullin, Enoch G. Achigan-Dako, Sognigbé N'Danikou, Wei-hsun Hsieh, Yann-rong Lin, and Ian K. Dawson
As the climate changes, major staple crop production in sub-Saharan Africa becomes increasingly vulnerable. Underutilized traditional food plants offer opportunities for diversifying cropping systems. In this study, the authors used climate niche modeling to assess the potential of 138 traditional food plants to diversify or replace staple crop production in sub-Saharan Africa by 2070. The authors report that staple crops may no longer be able to grow at approximately 10% of locations by 2070. Further, the authors identified 58 traditional crops that provide complementary micronutrient contents suitable for integration into staple cropping systems under current and projected climatic conditions. The results suggest that diversifying sub-Saharan African food production with underutilized crops could improve climate resilience and dietary health.
https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2205794120
Finalist:
Climate presses and pulses mediate the decline of a migratory predator
T. J. Clark-Wolf, P. Dee Boersma, Ginger A. Rebstock, and Briana Abrahms
https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2209821120
About PNAS
PNAS is one of the world's most-cited multidisciplinary scientific journals. It covers the biological, physical, and social sciences and mathematics and publishes cutting-edge Research Reports, Commentaries, Perspectives, Colloquium Papers, and actions of the Academy. PNAS publishes daily online and in weekly issues.
For more information about PNAS or the NAS, visit www.pnas.org or www.nasonline.org.
END
PNAS announces six 2023 Cozzarelli prize recipients
2024-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Association for Psychological Science announces new convention plan to foster global psychological research
2024-03-12
Washington, D.C. (March 12, 2024) — The Association for Psychological Science, the leading global organization dedicated to advancing scientific psychology for the benefit of science and society, is revamping its roster of regularly scheduled events to better foster global scientific collaboration and environmental sustainability.
Starting in 2025, APS will merge its Annual Convention and the biennial International Convention of Psychological Science (ICPS). The new APS Annual Convention will rotate outside of North America ...
Mount Sinai establishes Department of Public Health
2024-03-12
Watch the video announcement here.
New York, NY (March 12, 2024) – The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, fulfilling its commitment to connecting medical care with public health, today established a new Department of Public Health under the visionary leadership of Rosalind J. Wright, MD, MPH, the Horace W. Goldsmith Professor in Children’s Health Research at Icahn Mount Sinai.
The Department of Public Health will bridge the school’s existing excellence in environmental medicine, population health, global health, infectious disease, climate science, digital health, data science and artificial intelligence, community engagement, ...
Who benefits from direct-to-consumer pharmaceutical advertising?
2024-03-12
A new study co-authored by a University of Massachusetts Amherst economist reveals the value of government vaccine recommendations to drugmakers, as well as potential benefits of advertising pharmaceuticals directly to consumers — a practice that is banned in every country apart from the United States and New Zealand. The research is the most comprehensive investigation to date of manufacturer marketing and consumer response to adult vaccine recommendations.
After the U.S. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended in 2014 that people aged 65 and over receive the pneumococcal vaccine Prevnar 13, Medicare and private ...
Discovery of a natural protective response in the brain could lead to treatments for concussions
2024-03-12
A team of Medical University of South Carolina researchers, led by Onder Albayram, Ph.D., reports in PNAS Nexus that they have discovered a novel protective response by which the brain naturally repairs itself after traumatic brain injury. Findings could lead to drug treatments that improve the brain’s ability to recover after concussions and prevent long-term brain disease.
“Brain recovery mechanisms are very, very powerful,” said Albayram. “We don’t always have to develop new treatment approaches. We can also just give the brain a chance to heal itself properly.”
Repetitive mild ...
Climate polices to reduce motor vehicle emissions can improve children’s health, save money
2024-03-12
A new study finds that policies to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from motor vehicles combined with investments in electric vehicles and public transportation would reduce air pollution and bring large benefits to children’s health. They would also save money.
The findings by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health with collaborators at the University of California, Los Angeles, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and the Boston University School of Public Health appear in the journal Environmental Research ...
Research finds a college degree remains a sound investment despite rising tuition
2024-03-12
A new analysis of 5.8 million Americans finds that earning a college degree is still a sound investment, although the rate of economic return varies across college majors and student demographics. The findings come as skepticism continues to grow over the value of a degree in the face of rising college costs, a decline in college enrollment, and a transforming economy.
The study was published today in American Educational Research Journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association. It was conducted by Liang Zhang from New York University, Xiangmin Liu from Rutgers University, and Yitong Hu from New York University.
The study estimated ...
Understanding chronic liver disease through the powerhouse of the cells
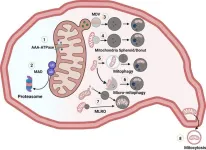
2024-03-12
Scientists have identified a new organelle in liver cells called the mitochondria-lysosome-related organelle (MLRO). This discovery could improve our understanding of chronic liver diseases like alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD).
Mitochondria are essential components of cells, often called the "powerhouses" because they generate energy. They also play a crucial role in metabolism, calcium signalling, and cell survival. When mitochondria malfunction, it's linked to various liver diseases.
Cells have intricate mechanisms to maintain healthy mitochondria. One way is to ...
Outstanding achievements of UNIST students at the 30th Samsung Humantech Paper Award ceremony!
2024-03-12
Four exceptional UNIST students were honored for their outstanding academic and research achievements at the prestigious 30th Annual Samsung Humantech Paper Award ceremony.
Among the many eminent individuals, JungSoo Lee (Advisor: Professor Han Gi Chae) from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering notched the highest score and won the Gold Prize within the category of Energy & Environment. His groundbreaking research on enhancing the efficiency of thermoelectric power generation through the development of a new power generation device structure technology earned him this accolade. By focusing on optimizing the structure ...
Increasing disability employment could boost national economy by billions
2024-03-12
-- There is a widening employment gap between people with and without disability --
-- In 2022, only 53.1 per cent of people with work-limiting disability were employed, compared to 81.8 per cent of people without disability --
-- People with disability are 25-30 percentage points less likely to be employed --
-- Over a quarter of people with disability cite transport as a barrier to finding work --
A new report by the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre at Curtin University reveals that there has been no improvement in employment rates for people with disability ...
Novel risk score for cardiovascular complications after bone marrow transplant
2024-03-12
For thousands of Americans each year, a bone marrow transplant has the potential to cure diseases such as leukemias, lymphomas and immune deficiency disorders. While lifesaving, bone marrow transplants are taxing procedures that can affect various organs, including the cardiovascular system.
With advances in medical science and improvement in protocols, more bone marrow transplants, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, are being offered to older patients, a population at greater risk of cardiovascular disease.
Researchers led by ...