(Press-News.org) A new study finds that policies to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from motor vehicles combined with investments in electric vehicles and public transportation would reduce air pollution and bring large benefits to children’s health. They would also save money.
The findings by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health with collaborators at the University of California, Los Angeles, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and the Boston University School of Public Health appear in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
The researchers modeled the benefits of implementing multiple scenarios of the proposed climate policy framework known as the Transportation and Climate Initiative (TCI) in 12 Northeast and Mid-Atlantic states and the District of Columbia. Under the most stringent cap on CO2 emissions and the investment scenario that devoted the most resources to mass transportation, they estimated a total of over 58,000 avoided cases of infant mortality, preterm birth, low birth weight, autism spectrum disorder, new cases of asthma, worsened asthma symptoms, and other respiratory illnesses. The related economic savings were $82 million annually. Assessment of the distribution of avoided cases of worsened asthma symptoms indicated that children in all racial and ethnic groups benefited, with somewhat greater health benefits in non-white populations.
Under TCI, fuel suppliers would be required to purchase carbon emissions allowances, the proceeds of which would go towards clean transportation programs. While this program was not implemented, it serves as a useful model for other climate mitigation policies. Specifically, researchers modeled changes in ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide between 2022 and 2032 associated with on-road transportation sector emissions under nine hypothetical CO2 emissions cap and investment scenarios proposed under TCI. They estimated potential health co-benefits for adverse birth, pediatric respiratory, and neurodevelopmental outcomes using BenMAPR, a health impact assessment platform that builds from the EPA’s Environmental Benefits Mapping and Analysis Program.
“Health benefits assessments often overlook children’s health outcomes. Yet we know that early exposure to air pollutants has multiple detrimental effects on children’s health and well-being; and these are preventable,” says co-author Frederica Perera, PhD, DrPH, professor of environmental health sciences and director of translational research at the Columbia Center for Children’s Environmental Health at Columbia Mailman.
Researchers also note the importance of strategic decarbonization efforts as the climate crisis escalates. “Ambitious carbon caps and policies that focus on vulnerable groups, including children, can both improve health outcomes and help mitigate the impacts of climate change,” says first author Alique G. Berberian, MPH ’19, PhD student and graduate student researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles,
The researchers also note the importance of including health and environmental justice in climate policies. “Climate policies can have major effects not just on climate, but also on health and environmental justice. Our research shows the importance of including these other benefits of policies when evaluating climate policies,” said senior author Jonathan Buonocore, ScD, assistant professor of Environmental Health at Boston University School of Public Health.
Additional study authors include Kaitlyn E. Coomes at Columbia Mailman School of Public Health, Saravanan Arunachalam and Calvin Arter at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; and Jonathan I. Levy, and Laura Buckley at the Boston University School of Public Health.
The study was supported by the John Merck Fund, the John and Wendy Neu Foundation, the New York Community Trust, the Barr Foundation, and the Energy Foundation.
END
Climate polices to reduce motor vehicle emissions can improve children’s health, save money
2024-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research finds a college degree remains a sound investment despite rising tuition
2024-03-12
A new analysis of 5.8 million Americans finds that earning a college degree is still a sound investment, although the rate of economic return varies across college majors and student demographics. The findings come as skepticism continues to grow over the value of a degree in the face of rising college costs, a decline in college enrollment, and a transforming economy.
The study was published today in American Educational Research Journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association. It was conducted by Liang Zhang from New York University, Xiangmin Liu from Rutgers University, and Yitong Hu from New York University.
The study estimated ...
Understanding chronic liver disease through the powerhouse of the cells
2024-03-12
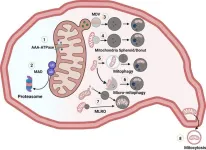
Scientists have identified a new organelle in liver cells called the mitochondria-lysosome-related organelle (MLRO). This discovery could improve our understanding of chronic liver diseases like alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD).
Mitochondria are essential components of cells, often called the "powerhouses" because they generate energy. They also play a crucial role in metabolism, calcium signalling, and cell survival. When mitochondria malfunction, it's linked to various liver diseases.
Cells have intricate mechanisms to maintain healthy mitochondria. One way is to ...
Outstanding achievements of UNIST students at the 30th Samsung Humantech Paper Award ceremony!
2024-03-12
Four exceptional UNIST students were honored for their outstanding academic and research achievements at the prestigious 30th Annual Samsung Humantech Paper Award ceremony.
Among the many eminent individuals, JungSoo Lee (Advisor: Professor Han Gi Chae) from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering notched the highest score and won the Gold Prize within the category of Energy & Environment. His groundbreaking research on enhancing the efficiency of thermoelectric power generation through the development of a new power generation device structure technology earned him this accolade. By focusing on optimizing the structure ...
Increasing disability employment could boost national economy by billions
2024-03-12
-- There is a widening employment gap between people with and without disability --
-- In 2022, only 53.1 per cent of people with work-limiting disability were employed, compared to 81.8 per cent of people without disability --
-- People with disability are 25-30 percentage points less likely to be employed --
-- Over a quarter of people with disability cite transport as a barrier to finding work --
A new report by the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre at Curtin University reveals that there has been no improvement in employment rates for people with disability ...
Novel risk score for cardiovascular complications after bone marrow transplant
2024-03-12
For thousands of Americans each year, a bone marrow transplant has the potential to cure diseases such as leukemias, lymphomas and immune deficiency disorders. While lifesaving, bone marrow transplants are taxing procedures that can affect various organs, including the cardiovascular system.
With advances in medical science and improvement in protocols, more bone marrow transplants, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, are being offered to older patients, a population at greater risk of cardiovascular disease.
Researchers led by ...
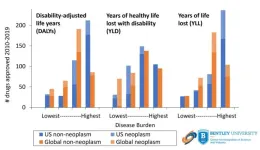
US drug approvals 2010-2019 align with US, but not global, burden of disease; expedited approval programs may make the gap worse
2024-03-12
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
Drug approvals in the United States between 2010-2019 were aligned with the US, but not global, burden of disease and the increasing number of expedited drug approvals could make the gap worse according to a study in the BMJ Open. The study also demonstrates that drugs indicated for conditions with the greatest burden of disease were less likely to be approved through the FDA’s expedited approval programs that reduce the timeline and cost of drug development, thus making it relatively more expensive to develop these products. US markets and FDA approval play an important role in shaping the product portfolios of global pharmaceutical companies; as such, expedited ...
Rising incidence of Legionnaires’ disease due to cleaner air
2024-03-12
A study links a rise in a serious bacterial illness to an unexpected factor: a decline in air pollution. Legionnaires’ disease is a respiratory illness with a fatality rate of 10–25% that is caused by inhaled Legionella bacteria. The bacteria live in water and outbreaks have been linked to water sources such as cooling towers, which cool indoor spaces by dissipating heat into the atmosphere in the form of water droplets and vapor. Other sources include improperly maintained public fountains, hot tubs, ice machines, home humidifiers, and showers. A global rise in Legionnaires’ disease since the year 2000 has puzzled ...
You didn’t see it coming: the spontaneous nature of turbulence
2024-03-12
We experience turbulence every day: a gust of wind, water gushing down a river or mid-flight bumps on an airplane.
Although it may be easy to understand what causes some kinds of turbulence — a felled tree in a river or a bear splashing around for salmon — there is now evidence that a very small disturbance at the start can have dramatic effects later. Instead of a tree, think of a twig — or even the swerving motion of a molecule.
University of California San Diego Chancellor’s Distinguished Professor of Physics Nigel Goldenfeld, along with his former student Dmytro Bandak, and Professors Alexei ...
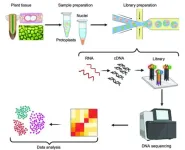
Advancing plant biology with breakthroughs in single-cell RNA sequencing
2024-03-12
Recent breakthroughs in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA), such as the recently developed “RevGel-seq” method, has revolutionized plant cell analysis. This technique, independent of special instruments, streamlines processes and resolves protoplast isolation challenges. Now, a multinational team of researchers review this and other such recent advances in plant scRNA sequencing with the intention of providing guidance for facilitating the appropriate selection of scRNA methods for different plant samples.
In the world of plant biology, understanding ...
Study provides new insights into deadly acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
2024-03-12
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (03/12/2024) - Researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities may have discovered a mechanical explanation for instability observed in the lungs in cases of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), particularly in the aftermath of respiratory illnesses such as COVID-19 or pneumonia.
The research was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), a peer reviewed journal of the National Academy of Sciences.
Currently, there is no known cure for ARDS, a life-threatening ...