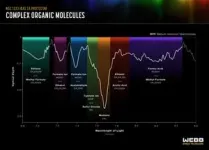
(Press-News.org) What do margaritas, vinegar, and ant stings have in common? They contain chemical ingredients that NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has identified surrounding two young protostars known as IRAS 2A and IRAS 23385. Although planets are not yet forming around those stars, these and other molecules detected there by Webb represent key ingredients for making potentially habitable worlds.
An international team of astronomers used Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) to identify a variety of icy compounds made up of complex organic molecules like ethanol (alcohol) and likely acetic acid (an ingredient in vinegar). This work builds on previous Webb detections of diverse ices in a cold, dark molecular cloud.
What is the origin of complex organic molecules (COMs) ?
“This finding contributes to one of the long-standing questions in astrochemistry,” said team leader Will Rocha of Leiden University in the Netherlands. “What is the origin of complex organic molecules, or COMs, in space? Are they made in the gas phase or in ices? The detection of COMs in ices suggests that solid-phase chemical reactions on the surfaces of cold dust grains can build complex kinds of molecules.”
As several COMs, including those detected in the solid phase in this research, were previously detected in the warm gas phase, it is now believed that they originate from the sublimation of ices. Sublimation is to change directly from a solid to a gas without becoming a liquid. Therefore, detecting COMs in ices makes astronomers hopeful about improved understanding of the origins of other, even larger molecules in space.
Scientists are also keen to explore to what extent these COMs are transported to planets at much later stages of protostellar evolution. COMs in cold ices are thought to be easier to transport from molecular clouds to planet-forming disks than warm, gaseous molecules. These icy COMs can therefore be incorporated into comets and asteroids, which in turn may collide with forming planets, delivering the ingredients for life to possibly flourish.
The science team also detected simpler molecules, including formic acid (which causes the burning sensation of an ant sting), methane, formaldehyde, and sulfur dioxide. Research suggests that sulfur-containing compounds like sulfur dioxide played an important role in driving metabolic reactions on the primitive Earth.
Similar to the early stages of our own solar system?
Of particular interest is that one of the sources investigated, IRAS 2A, is characterized as a low-mass protostar. IRAS 2A may therefore be similar to the early stages of our own solar system. As such, the chemicals identified around this protostar were likely present in the first stages of development of our solar system and later delivered to the primitive Earth.
“All of these molecules can become part of comets and asteroids and eventually new planetary systems when the icy material is transported inward to the planet-forming disk as the protostellar system evolves,” said Ewine van Dishoeck of Leiden University, one of the coordinators of the science program. “We look forward to following this astrochemical trail step-by-step with more Webb data in the coming years.”
These observations were made for the JOYS+ (James Webb Observations of Young ProtoStars) program. The team dedicated these results to team member Harold Linnartz, who unexpectedly passed away in December 2023, shortly after the acceptance of this paper.
This research has been accepted for publication in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world's premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
END
Cheers! NASA’s Webb finds ethanol, other icy ingredients for worlds
2024-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Intervention with surgeons improves the accuracy of predicted operating room time
2024-03-13
Waltham — March 13, 2024 — Reducing the manipulation of operating room (OR) scheduling can improve scheduling accuracy and potentially maximize OR usage, avoid delays, and enhance patient satisfaction, according to a study published in the March/April issue of the Journal of Healthcare Management (JHM). An official journal of the American College of Healthcare Executives, JHM is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Accurate prediction of OR time is critical for maximizing OR use
"Traditional OR scheduling, based on the surgeon's self-estimation ...
The future is likely less skiable, thanks to climate change
2024-03-13
Annual snow cover days in all major skiing regions are projected to decrease dramatically as a result of climate change, with 1 in 8 ski areas losing all natural snow cover this century under high emission scenarios. These results are published in a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Veronika Mitterwallner from the University of Bayreuth, Germany and colleagues.
Popular skiing destinations experience the impacts of climate change, which include reduced snowfall in regions around the world. Despite the social, economic, and ecological significance of the skiing industry, little research exists on how ski area distributions are affected by climate change ...
Photo project reveals life with a pet while experiencing homelessness
2024-03-13
In a new study, people experiencing homelessness with a pet documented their lives in photos and participated in interviews, revealing their experiences and potentially informing support initiatives. Gemina Garland-Lewis of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues present this project in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 13, 2024.
Having a pet while experiencing homelessness can boost physical and mental health and provide social benefits. However, it can pose unique challenges, such as making it difficult to access medical care, shelters, and other services at facilities ...
The Wim Hof method may reduce inflammation, per systematic review
2024-03-13
The Wim Hof method may produce a beneficial anti-inflammatory response characterized by increased epinephrine levels and a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines, according to a systematic review published March 13, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Omar Almahayni and Lucy Hammond from the University of Warwick, UK.
The Wim Hof method is touted by founder and extreme athlete Wim Hof as a practical way to improve physical and mental health. It consists of three pillars—the Wim Hof breathing method, cold therapy, and commitment.
Several studies have assessed the impact of the Wim Hof method on ...
Just one mindfulness and compassion session was associated with reduced symptoms of anxiety, depression and stress a week later, in clinical trial with 91 participants
2024-03-13
Just one mindfulness and compassion session was associated with reduced symptoms of anxiety, depression and stress a week later, in clinical trial with 91 participants
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299300
Article Title: Efficacy of a single session mindfulness based intervention: A randomized clinical trial
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Interactions with dogs can increase brainwaves associated with stress relief and heightened concentration
2024-03-13
Spending quality time with dogs reduces stress and increases the power of brain waves associated with relaxation and concentration, according to a study published on March 13, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Onyoo Yoo from Konkuk University, South Korea, and colleagues.
Animal-assisted interventions, like canine therapy, are widely used in hospitals, schools, and beyond to help reduce anxiety, relieve stress, and foster feelings of trust. Studies of the potential benefits of animal interactions often take a holistic approach, comparing people’s mood or hormone levels before and after spending time with a service animal. But this approach doesn’t ...
Climate change has significantly increased crop water demand in the San Joaquin Valley, and the shift since 2011 is a volume of water the size of a major reservoir
2024-03-13
Climate change has significantly increased crop water demand in the San Joaquin Valley, and the shift since 2011 is a volume of water the size of a major reservoir.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000184
Article Title: An invisible water surcharge: Climate warming increases crop water demand in the San Joaquin Valley’s groundwater-dependent irrigated agriculture
Author Countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) ...
Being in therapy prior to COVID-19 pandemic prevented anxiety uptick during its peak
2024-03-13
Researchers compared levels of anxiety among psychotherapy outpatients based on whether they initiated therapy before, during or after the onset of COVID-19 pandemic
Authors say findings suggest that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) can provide tools to help individuals manage anxiety in the face of major world events and upheaval
Belmont, Mass. – (March 13, 2024) The start of the COVID-19 pandemic led to unprecedented exposure to stressors driven by fears of a novel and deadly disease, intense uncertainty, and resulting ...
Crucial insights into animal defense mechanisms and tradeoffs revealed
2024-03-13
New study reveals insights into predator-prey dynamics in the animal kingdom, focusing on sea anemones. The surprising discovery of a native anemone population lacking the Nv1 neurotoxin led to an investigation into its impact on defending against grass shrimp, a native predator. Anemones without Nv1 showed weakened defensive abilities, while the neurotoxin, when present, attracted mummichog fish, natural predators of grass shrimp. This research enhances our understanding of marine ecosystems and the intricate balance of predator-prey interactions and tradeoffs.
A new ...
Drug design at the atomic level to thwart COVID-19
2024-03-13
Although COVID-19 has faded from the headlines, SARS-CoV-2 – the coronavirus behind the pandemic – is still rampantly infecting people around the world. Public health officials fear as the virus continues to evolve, it will eventually hit upon a diabolical mutation that renders current treatments ineffective, triggering a new wave of severe infection and social disruption.
In pursuit of new therapies to avoid this dark fate, researchers at Stanford have now unveiled a compound that measures up as a potentially powerful anti-coronavirus drug, detailed in a paper published March 13 in Science Translational Medicine. ...