(Press-News.org) Climate change has significantly increased crop water demand in the San Joaquin Valley, and the shift since 2011 is a volume of water the size of a major reservoir.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000184
Article Title: An invisible water surcharge: Climate warming increases crop water demand in the San Joaquin Valley’s groundwater-dependent irrigated agriculture
Author Countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) Agriculture and Food Research Initiative (Award No. 2021-69012-35916 to KM, JTA, AEB, JMA, and JHV) and by NSF and USDA-NIFA under the AI Research Institutes program for the AgAID Institute (Agricultural AI for Transforming Workforce and Decision Support) (Award No. 2021-67021-3534 to JTA, JMA, and JHV). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
END
Climate change has significantly increased crop water demand in the San Joaquin Valley, and the shift since 2011 is a volume of water the size of a major reservoir
2024-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Being in therapy prior to COVID-19 pandemic prevented anxiety uptick during its peak
2024-03-13
Researchers compared levels of anxiety among psychotherapy outpatients based on whether they initiated therapy before, during or after the onset of COVID-19 pandemic
Authors say findings suggest that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) can provide tools to help individuals manage anxiety in the face of major world events and upheaval
Belmont, Mass. – (March 13, 2024) The start of the COVID-19 pandemic led to unprecedented exposure to stressors driven by fears of a novel and deadly disease, intense uncertainty, and resulting ...
Crucial insights into animal defense mechanisms and tradeoffs revealed
2024-03-13
New study reveals insights into predator-prey dynamics in the animal kingdom, focusing on sea anemones. The surprising discovery of a native anemone population lacking the Nv1 neurotoxin led to an investigation into its impact on defending against grass shrimp, a native predator. Anemones without Nv1 showed weakened defensive abilities, while the neurotoxin, when present, attracted mummichog fish, natural predators of grass shrimp. This research enhances our understanding of marine ecosystems and the intricate balance of predator-prey interactions and tradeoffs.
A new ...
Drug design at the atomic level to thwart COVID-19
2024-03-13
Although COVID-19 has faded from the headlines, SARS-CoV-2 – the coronavirus behind the pandemic – is still rampantly infecting people around the world. Public health officials fear as the virus continues to evolve, it will eventually hit upon a diabolical mutation that renders current treatments ineffective, triggering a new wave of severe infection and social disruption.
In pursuit of new therapies to avoid this dark fate, researchers at Stanford have now unveiled a compound that measures up as a potentially powerful anti-coronavirus drug, detailed in a paper published March 13 in Science Translational Medicine. ...
SwRI receives $2 million NASA grant to develop lunar-regolith-measuring instrument
2024-03-13
SAN ANTONIO — March 13, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has been awarded a three-year, $2,041,000 grant from NASA’s Development and Advancement of Lunar Instrumentation (DALI) program to further develop a novel ground-penetrating radar instrument. The Synthetic Pulse Artemis Radar for Crustal Imaging (SPARCI, pronounced “sparky”) instrument is designed to characterize the depth of the regolith and upper megaregolith, the upper broken-up layers of lunar crust associated with ...
ANYmal can do parkour and walk across rubble
2024-03-13
ANYmal has for some time had no problem coping with the stony terrain of Swiss hiking trails. Now researchers at ETH Zurich have taught this quadrupedal robot some new skills: it is proving rather adept at parkour, a sport based on using athletic manoeuvres to smoothly negotiate obstacles in an urban environment, which has become very popular. ANYmal is also proficient at dealing with the tricky terrain commonly found on building sites or in disaster areas.
To teach ANYmal these new skills, two teams, both from the group led by ETH Professor Marco Hutter of the Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, followed different approaches.
Exhausting the mechanical options
Working ...
Scientists unravel mystery of drug response in small cell lung cancer
2024-03-13
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive tumour of the lung that occurs especially in heavy smokers. Due to the rapid spread of this tumour type, most patients can only be treated with chemotherapy with remarkable initial anti-tumour efficacy. However, relapse often occurs over the course of time. A research team at the University of Cologne led by Professor Dr Roman Thomas, director of the Department of Translational Genomics and speaker of the Collaborative Research Center 1399 (CRC 1399, ...
Peter Flemings wins Robert R. Berg Outstanding Research Award
2024-03-13
Jackson School of Geosciences Professor Peter Flemings is the recipient of the 2024 Robert R. Berg Outstanding Research Award, a top honor bestowed by the American Association of Petroleum Geologists, a worldwide professional association.
Over the course of his career, Flemings has worked to apply his academic research to effect real-world breakthroughs. His work analyzing how pressure within Earth’s crust is controlled by geology and fluid flow, for example, shaped how oil companies now safely search for hydrocarbons.
Flemings and his students explored how the evolution of rock layers controls the flow of fluids within them and the distribution ...
Study shows important role gut microbes play in airway health in persons with cystic fibrosis
2024-03-13
Findings from a new study conducted by a team of researchers at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine and published in the journal mBio, reflect the important role that the gut microbiome (communities of bacteria) plays in the airway health of persons with cystic fibrosis.
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease that causes sticky, thick mucus to build up in the lungs and other organs, causing persistent infections that can be deadly. Until relatively recently, CF microbiology research has largely ...
With discovery of roundworms, Great Salt Lake’s imperiled ecosystem gets more interesting
2024-03-13
Scientists have long suspected nematodes, commonly known as roundworms, inhabit Utah’s Great Salt Lake sediments, but until recently, no one had actually recovered any there.
It took a University of Utah postdoc with a hammer and loads of field experience to solve the puzzle. Along with biology professor Michael Werner, postdoctoral researcher Julie Jung announced in a study published March 13 that they discovered thousands of tiny worms in the lake’s microbialites, those reef-like structures that cover about a fifth of the lakebed.
Their initial attempts failed to find nematodes in lakebed sediments, prompting Jung to take a hammer to samples ...
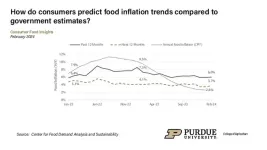
Most consumers continue to expect rising food prices
2024-03-13
Most U.S. consumers surveyed in February 2024 predicted that they would see an increase in food prices over the next 12 months. Sixty-four percent of respondents predict food prices to rise in the next year, and the average predicted increase is 3.7%, according to the February Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conducted and evaluated the survey, which ...