(Press-News.org) Achille Mbembe is research professor of history and politics at the Wits Institute for Social and Economic Research, at the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. He will receive the award of NOK 6,000,000 (approx. EUR 525,000) during a 6 June ceremony at the University of Bergen, Norway.
Mbembe is one of the most read and cited scholars from the African continent and receives the prize for his pioneering research in African history, postcolonial studies, humanities, and social science over four decades. Both as an academic and as a public intellectual, he is known for his ability to bridge existing thinking on colonialism and decolonisation with pressing questions on topics such as contemporary migration regimes, global citizenship, restitution and reparation, technology, climate change and planetary futures.
As a historian and a political philosopher, Mbembe has been most concerned about the entanglement of Europe and its former colonies. Using Africa as a point of departure for a mode of thinking that is continuous with multiple and interlocking lineages, he has revealed the extent to which the continent is a living laboratory of thought forms and ideas, a vast world of invention, imagination and creativity.
As a critical theorist, his deliberations on the global order have left an enduring mark far beyond debates on postcolonialism. Drawing on African experiences, Mbembe has played a major role in advancing thinking beyond identity and difference, particularly through concepts such as ‘necropolitics’, ‘the universal right to breathe’, or ‘the earthly community’, which speak to the ongoing struggles for recognition and repair as well as care and dignity in a racialized world.
Originally written in French, Mbembe’s books and numerous articles have been translated into seventeen languages. His key books include On the Postcolony (2000/2001), Out of the Dark Night (2010/2021), Necropolitics (2016/2019), Brutalism (2020/2024) and The Earthly Community: Reflections on the Last Utopia (2022), as well as the groundbreaking Critique of Black Reason (2013/2017)—a philosophical study of the meaning of Blackness as it historically emerged. In Necropolitics, Mbembe examines how power structures wield control over life and mortality, shaping the very fabric of existence for oppressed communities.
Describing the key purpose of his work, the Laureate asks: “What are the conditions for rethinking the world in a way that opens up alternative ways of inhabiting it, of being-in-common and of nurturing a planetary consciousness?” “How to think an open future that moves beyond the history of race, colonialism and segregation with which the present is so deeply entangled,” Mbembe continues.“These questions have been at the heart of my research over the span of my career. Behind them lurks an even bigger issue, that of life futures—how can life be repaired, reproduced, sustained and cared for, made durable and universally shared?”
“Mbembe’s oeuvre goes beyond a particularized notion of decolonization to a universalist recentring of the human”, says Holberg Committee Chair Heike Krieger. “For him, this involves a dedication to facing historical truth, while learning and remembering across South-North divides.”
About the Laureate
Achille Mbembe is research professor of history and politics at the Wits Institute for Social and Economic Research (WISER), University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa. He is also the Director of the Innovation Foundation for Democracy. He was educated in Cameroon and in France where he obtained his PhD in History at the Université Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne and a a Diplôme d'études approfondies (DEA) at the Institut d'études politiques de Paris.
Mbembe has taught at various universities in the United States, including Columbia University, the University of Pennsylvania, the University of California at Berkeley and at Irvine, Yale University, Duke University and Harvard University. A winner of the Ernst Bloch Award and the Gerda Henkel Prize, he is a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and a Fellow of the British Academy. Mbembe holds Honorary Doctorates from the Paris 8 University (France), the Catholic University of Louvain (Belgium) and the University of Bergen (Norway). His work has been translated in 17 languages (English, Spanish, Italian, German, Dutch, Portuguese, Arabic, Danish, Swedish, Norwegian, Turkish, Romanian, Polish, Slovenian, Catalan, Finnish, and Mandarin). His latest book is La communaute terrestre (Editions La Découverte, Paris, 2023).
About the Holberg Prize
Established by the Norwegian Parliament in 2003, the Holberg Prize is one of the largest annual international research prizes awarded for outstanding contributions to research in the humanities, social science, law or theology. The Prize is funded by the Norwegian Government through a direct allocation from the Ministry of Education and Research to the University of Bergen. Previous Laureates include Julia Kristeva, Jürgen Habermas, Manuel Castells, Onora O’Neill, Cass Sunstein, Paul Gilroy, and Sheila Jasanoff. To learn more about the Holberg Prize, visit: https://holbergprize.org/en. For press photos, biography, Committee citation, expert contact information, and more, see: http://holbergprize.org/en/press-room.
W: holbergprize.org
X: @HolbergPrize
Facebook: holbergprize
END
Political theorist Achille Mbembe named 2024 Holberg Prize Laureate
2024-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Revolutionary nanoparticle therapy offers new hope for burn victims
2024-03-14
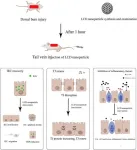
A research has developed a new nanoparticle treatment that significantly improves outcomes for severe burn-induced intestinal barrier disruption. The study introduces Luminol-conjugated cyclodextrin (LCD) nanoparticles, offering a promising therapeutic intervention for one of the most critical complications following severe burn injuries.
Severe burns can cause critical issues, including deep tissue damage and increased risk of fatal conditions like sepsis and organ failure. A major concern is the disruption of the intestinal barrier, leading to inflammation and systemic ...
New study unveiled burn injury disrupts gut microbiome and weakens intestinal mucus barrier
2024-03-14
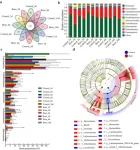
The gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem within the human intestinal tract, is increasingly recognized for its vital role in human health and disease. Notably, its relationship with intestinal damage due to burns has been underexplored. New study has unveiled the pivotal role of gut microbiota in the synthesis and degradation of intestinal mucus following burn injuries in mice. Utilizing advanced 16S rRNA and metagenomic sequencing techniques, researchers have identified significant changes in gut microbiota composition and its impact on the intestinal mucus barrier.
On a study ...
Researchers may have found key to deprogram cells that lead to transplant rejection
2024-03-14
HOUSTON-(Mar. 14, 2024) – Houston Methodist researchers identified a troublesome subset of T-cells in transplant recipients that may be a more effective therapeutic target for preventing transplant rejection in patients.
Each day, 17 people die waiting for organ transplants, but getting a new organ doesn’t guarantee survival. Despite immunosuppressive medications, rejection of transplanted organs happens in up to 50% of patients, depending on the type of organ transplanted and the duration since the transplantation.
Wenhao Chen, Ph.D., associate professor of transplant immunology with the Houston Methodist Research ...
Healing diabetes wounds with a new superhero: stem cell magic
2024-03-14
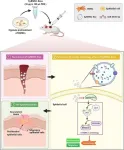
Researchers unveiled a novel therapy for diabetic wound healing. This research highlights the use of exosomal miR-4645-5p from hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) to significantly enhance wound healing by promoting keratinocyte autophagy.
Diabetic wounds, often challenging to treat and prone to complications, can severely impact patients' quality of life. Traditional treatments have struggled with issues like low survival rates of transplanted cells and potential for immune rejection. This research introduces a groundbreaking approach using stem cells' regenerative capabilities.
On ...
New AI model detects ninety percent of lymphatic cancer cases
2024-03-14
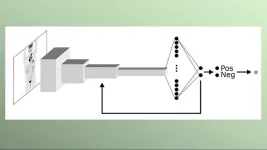
Medical image analysis using AI has developed rapidly in recent years. Now, one of the largest studies to date has been carried out using AI-assisted image analysis of lymphoma, cancer of the lymphatic system. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, have developed a computer model that can successfully find signs of lymph node cancer in 90 percent of cases.
New computer-aided methods for interpreting medical images are being developed for various medical conditions. They can reduce the workload for radiologists, by giving a second opinion or ranking which patients need treatment the fastest.
"An AI-based computer system for interpreting medical images ...
Bariatric surgery linked to heart health improvements in people with severe obesity
2024-03-14
WASHINGTON—Bariatric surgery may result in significant cardiometabolic improvements, particularly among younger, female, or white people and those without comorbidities, according to new research published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
The United States has the highest obesity rates globally. In 2017-2018, about 40% of U.S. adults had obesity and 9% had severe obesity. The prevalence is particularly high among Black adults. Bariatric surgery is one method to help people with severe obesity lose a lot of weight and improve their health.
“Our study highlights how bariatric surgery not only leads to significant weight loss but also substantially improves ...
New report finds public spending on global health innovation delivers blockbuster returns, saving lives while generating billions of dollars in benefits globally and domestically
2024-03-14
WASHINGTON, DC (March 14, 2024)—Over the last 16 years, U.S. government funding for research and development (R&D) targeting global health challenges supported dozens of breakthrough innovations while generating billions of dollars in economic benefits, both global and domestic, and spurring a surge of industry investments, according to a new analysis from the Global Health Technologies Coalition (GHTC) and Policy Cures Research (PCR).
“Public funding for global health R&D is small, relative to the incredible returns it provides for fighting neglected ...
Breast cancer diagnoses plummeted during first year of pandemic
2024-03-14
Key Takeaways
There was a 15-20% decrease in newly diagnosed breast cancer cases reported to American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer sites in 2020 compared to 2019.
These study results have implications for how physicians and policymakers can address issues that may arise due to the diagnostic delays that occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors said.
CHICAGO: Several studies have described the distinct ways the COVID-19 pandemic adversely impacted cancer care, but less is known about the specific ways the pandemic disrupted breast cancer, the ...
Demystifying nano-neuro interactions
2024-03-14
By Shawn Ballard
Nanomaterials already play a vital role in enhancing the performance of everyday products from electronics to cosmetics to food packaging. But, beyond their usefulness in making images sharper and products more stable, researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis have shown nanoparticles may also be an essential tool in advancing our understanding of the brain and opening new avenues for treating neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
Srikanth Singamaneni, the Lilyan & ...
Common viruses trigger most cases of intussusception in children
2024-03-14
Viral infections trigger more cases of intussusception, the common cause of bowel blockages in young children, than previously thought, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, found during the COVID-19 lockdowns hospital admissions for intussusception, a medical emergency involving obstruction of the intestine, among young children significantly decreased.
For the study, 12 years of data was analysed across Victoria, NSW and Queensland. ...