(Press-News.org) After the egg has been fertilized by a sperm, the surrounding egg coat tightens, mechanically preventing the entry of additional sperm and the ensuing death of the embryo. This is according to a new study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet and published in the journal Cell. The work also explains how mutations in egg coat proteins can cause female infertility and may eventually lead to new contraceptive methods.
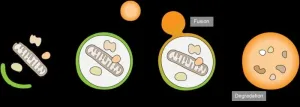
Fertilization in mammals begins when a sperm attaches to the egg coat, a filamentous extracellular envelope that sperm must penetrate in order to fuse with the egg. Now an international team of researchers has mapped in detail the structure and function of the protein ZP2, an egg coat filament component that plays a key role in regulating how egg and sperm interact with each other at fertilization.
“It was known that ZP2 is cleaved after the first sperm has entered the egg, and we explain how this event makes the egg coat harder and impermeable to other sperm,” says Luca Jovine, Professor at the Department of Biosciences and Nutrition, Karolinska Institutet, who led the study. “This prevents polyspermy – the fusion of multiple sperm with a single egg – which is a fatal condition for the embryo.”
The changes in the egg coat after fertilization are also crucial to female fertility by ensuring the protection of the developing embryo until this implants in the uterus. The new knowledge may therefore have implications for the development of non-hormonal contraceptives that interfere with the formation of the egg coat. Moreover, the study explains egg coat-associated forms of female infertility.
“Mutations in the genes encoding egg coat proteins can cause female infertility, and more and more such mutations are being discovered,” explains Luca Jovine. “We hope that our study will contribute to the diagnosis of female infertility and, possibly, the prevention of unwanted pregnancies.”
Importantly, the study also shows that a part of ZP2 that was previously thought to act as a receptor for sperm is not necessary for sperm to attach to the egg. This raises the question of what is the true sperm receptor on the egg coat, which the researchers plan to investigate further.
The researchers combined X-ray crystallography and cryo-EM to study the 3D structure of egg coat proteins. The interaction between sperm and eggs carrying mutations in the ZP2 protein was functionally studied in mice, while the AI program AlphaFold was used to predict the structure of the egg coat in humans.
The study was carried out in collaboration with Osaka and Sophia universities in Japan and the University of Pittsburgh, USA, using data collected at SciLifeLab and the ESRF, DLS and BESSY II synchrotrons.
The research was mainly funded by the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and the Centre for Innovative Medicine (CIMED). There are no reported conflicts of interest.
Publication: “ZP2 cleavage blocks polyspermy by modulating the architecture of the egg coat", Shunsuke Nishio, Chihiro Emori, Benjamin Wiseman, Dirk Fahrenkamp, Elisa Dioguardi, Sara Zamora-Caballero, Marcel Bokhove, Ling Han, Alena Stsiapanava, Blanca Algarra, Yonggang Lu, Mayo Kodani, Rachel E. Bainbridge, Kayla M. Komondor, Anne E. Carlson, Michael Landreh, Daniele de Sanctis, Shigeki Yasumasu, Masahito Ikawa, Luca Jovine, Cell, online 14 March 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.02.013.
END
New discovery reveals how the egg controls sperm entry
2024-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Teen pregnancy and risk of premature mortality
2024-03-14
About The Study: Teen pregnancy was associated with future premature mortality in this study of 2.2 million female teenagers. It should be assessed whether supports for female teenagers who experience a pregnancy can enhance the prevention of subsequent premature mortality in young and middle adulthood.
Authors: Joel G. Ray, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.1833)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Mental health conditions in partners and adult children of stroke survivors
2024-03-14
About The Study: In this study of partners and adult children of stroke survivors, risks of several mental health conditions and self-harm or suicide were moderately higher compared with the general population and, to a lesser extent, partners and adult children of heart attack survivors. These findings highlight the potential consequences of stroke among family members, particularly partners, and its findings may possibly serve as a quantitative foundation for the development of future stroke rehabilitation services.
Authors: Nils Skajaa, Ph.D., of Aarhus University Hospital in Aarhus, Denmark, is the corresponding author.
To ...
New study - chimp moms play with their offspring through good times and bad
2024-03-14
When it comes to nurturing their young, mother chimpanzees go the extra mile, according to a new study. Using 10 years of observational data on wild chimpanzees, researchers found that while adults often play, and young chimps play a lot, when food gets scarce, the adults put mutual play aside and focus on survival.
But in the meantime, mother chimps continue to be their offspring’s primary playmate, tickling, chasing, playing ‘airplane’. That suggests the mother chimps take on an indispensable role ...
Tissue samples show the deep genetic and cellular impacts of smoking
2024-03-14
It’s no secret that smoking is extremely detrimental to health. Tobacco smoke contains thousands of chemicals, including carcinogens, increasing the risk of cancer, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
A new study from the University of Chicago analyzed data from more than 900 samples of nine different human tissue types to understand just how deep the cellular and genetic damage from smoking goes. The research team generated epigenetic data to assess the effects of smoking on DNA methylation, or genetic locations where a handful ...
SickKids program provides integrated, trauma-informed care for pregnant and parenting adolescents
2024-03-14
The pregnancy and post-partum experience is stressful, but for pregnant adolescents the barriers to accessing supportive care can have fatal consequences.
A recent study from The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) identified that compared with those who had no teen pregnancy, teenagers in Ontario who experienced a pregnancy were at a 50 per cent higher risk of premature death before the age of 31. This risk was even higher for people who had two or more teen pregnancies and amongst those who were pregnant before 16 years of age.
Published in JAMA Network Open, the study also found that ...
Even cells know the importance of recycling
2024-03-14
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) uncover the specific protein interactions needed for cells to break down and remove damaged mitochondria
Tokyo, Japan – Autophagy is a process used by cells as a recycling system to transport and break down organelles and other cytosolic components, which become enveloped in a membrane called the autophagosome (Fig 1). When this involves the removal of damaged mitochondria, commonly called the “powerhouse” of the cell, it is known as mitophagy. In a recent article ...
Political theorist Achille Mbembe named 2024 Holberg Prize Laureate
2024-03-14
Achille Mbembe is research professor of history and politics at the Wits Institute for Social and Economic Research, at the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. He will receive the award of NOK 6,000,000 (approx. EUR 525,000) during a 6 June ceremony at the University of Bergen, Norway.
Mbembe is one of the most read and cited scholars from the African continent and receives the prize for his pioneering research in African history, postcolonial studies, humanities, and social science over four decades. ...
Revolutionary nanoparticle therapy offers new hope for burn victims
2024-03-14
A research has developed a new nanoparticle treatment that significantly improves outcomes for severe burn-induced intestinal barrier disruption. The study introduces Luminol-conjugated cyclodextrin (LCD) nanoparticles, offering a promising therapeutic intervention for one of the most critical complications following severe burn injuries.
Severe burns can cause critical issues, including deep tissue damage and increased risk of fatal conditions like sepsis and organ failure. A major concern is the disruption of the intestinal barrier, leading to inflammation and systemic ...
New study unveiled burn injury disrupts gut microbiome and weakens intestinal mucus barrier
2024-03-14
The gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem within the human intestinal tract, is increasingly recognized for its vital role in human health and disease. Notably, its relationship with intestinal damage due to burns has been underexplored. New study has unveiled the pivotal role of gut microbiota in the synthesis and degradation of intestinal mucus following burn injuries in mice. Utilizing advanced 16S rRNA and metagenomic sequencing techniques, researchers have identified significant changes in gut microbiota composition and its impact on the intestinal mucus barrier.
On a study ...
Researchers may have found key to deprogram cells that lead to transplant rejection
2024-03-14
HOUSTON-(Mar. 14, 2024) – Houston Methodist researchers identified a troublesome subset of T-cells in transplant recipients that may be a more effective therapeutic target for preventing transplant rejection in patients.
Each day, 17 people die waiting for organ transplants, but getting a new organ doesn’t guarantee survival. Despite immunosuppressive medications, rejection of transplanted organs happens in up to 50% of patients, depending on the type of organ transplanted and the duration since the transplantation.
Wenhao Chen, Ph.D., associate professor of transplant immunology with the Houston Methodist Research ...