(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (03/15/2024) — For the first time, researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities showed that non-invasive brain stimulation can change a specific brain mechanism that is directly related to human behavior. This is a major step forward for discovering new therapies to treat brain disorders such as schizophrenia, depression, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease.
The study was recently published in Nature Communications, a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal.
Researchers used what is called “transcranial alternating current stimulation” to modulate brain activity. This technique is also known as neuromodulation. By applying a small electrical current to the brain, the timing of when brain cells are active is shifted. This modulation of neural timing is related to neuroplasticity, which is a change in the connections between brain cells that is needed for human behavior, learning, and cognition.
“Previous research showed that brain activity was time-locked to stimulation. What we found in this new study is that this relationship slowly changed and the brain adapted over time as we added in external stimulation,” said Alexander Opitz, University of Minnesota biomedical engineering associate professor. “This showed brain activity shifting in a way we didn’t expect.”
This result is called “neural phase precession.” This is when the brain activity gradually changes over time in relation to a repeating pattern, like an external event or in this case non-invasive stimulation. In this research, all three investigated methods (computational models, humans, and animals) showed that the external stimulation could shift brain activity over time.
“The timing of this repeating pattern has a direct impact on brain processes, for example, how we navigate space, learn, and remember,” Opitz said.
The discovery of this new technique shows how the brain adapts to external stimulation. This technique can increase or decrease brain activity, but is most powerful when it targets specific brain functions that affect behaviors. This way, long-term memory as well as learning can be improved. The long-term goal is to use this technique in the treatment of psychiatric and neurological disorders.
Opitz hopes that this discovery will help bring improved knowledge and technology to clinical applications, which could lead to more personalized therapies for schizophrenia, depression, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease.
In addition to Opitz, the research team included co-first authors Miles Wischnewski and Harry Tran. Other team members from the University of Minnesota Biomedical Engineering Department include Zhihe Zhao, Zachary Haigh, Nipun Perera, Ivan Alekseichuk, Sina Shirinpour and Jonna Rotteveel. This study was in collaboration with Dr. Jan Zimmermann, associate professor in the University of Minnesota Medical School.
This work was supported primarily by the National Institute of Health (NIH) along with the Behavior and Brain Research Foundation and the University of Minnesota’s Minnesota’s Discovery, Research, and InnoVation Economy (MnDRIVE) Initiative. Computational resources were provided by the Minnesota Supercomputing Institute (MSI).
To read the entire research paper titled, “Induced neural phase precession through exogenous electric fields”, visit the Nature Communications website.
END
New study reveals breakthrough in understanding brain stimulation therapies
For the first time, researchers show how the brain can precisely adapt to external stimulation
2024-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Abnormal brain structure identified in children with developmental language problems
2024-03-15
WASHINGTON – A rigorous analysis of numerous studies concludes that a part of the brain traditionally associated with movement is abnormal in children with developmental language impairments, according to Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists. The discovery has the potential to improve both the diagnosis and treatment of the language difficulties.
The researchers investigated brain abnormalities in developmental language disorder. This condition, which impacts the development of various aspects of language, is about as common as attention-deficit/hyperactivity ...
DNA origami-based vaccines toward safe and highly-effective precision cancer immunotherapy
2024-03-15
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Therapeutic cancer vaccines are a form of immunotherapy in the making that could not only destroy cancer cells in patients, but keep a cancer from coming back and spreading. Multiple therapeutic cancer vaccines are being studied in clinical trials, but despite their promise, they are not routinely used yet by clinical oncologists to treat their patients.
The central ingredient of therapeutic cancer vaccines is antigens, which are preferentially produced or newly produced (neoantigens) by tumor cells and enable a patient’s immune system to search and destroy the cancerous ...
Printed polymer allows researchers to explore chirality and spin interactions at room temperature
2024-03-15
A printable organic polymer that assembles into chiral structures when printed has enabled researchers to reliably measure the amount of charge produced in spin-to-charge conversion within a spintronic material at room temperature. The polymer’s tunable qualities and versatility make it desirable not only for less expensive, environmentally friendly, printable electronic applications, but also for use in understanding chirality and spin interactions more generally.
Spintronic devices are electronic devices that harness the spin of an electron, ...
Special section of The Permanente Journal focuses on how early-life trauma correlates to poor health outcomes
2024-03-15
For Immediate Release
OAKLAND, Calif., March 15, 2024 — Innovation in trauma-informed health care is the core focus of a special section in today’s issue of The Permanente Journal. The special section features 13 articles that touch on this increasingly prominent approach and reaches into several diverse subdomains such as mental health, physical health, body size diversity and systems-level implementation. Workplace wellness, clinician training and medical school curricula related to trauma are also covered in the issue.
Trauma-informed health care has grown ...
New insights could improve treatment of liver fibrosis
2024-03-15
The liver is not only the largest internal organ but also vital for human life as a metabolic center. It also possesses remarkable self-healing powers: even when large portions are removed, such as during surgery, they quickly regenerate in healthy individuals. However, in cases of repeated or chronic injury to the liver tissue, as caused by excessive alcohol consumption or viral hepatitis, this regenerative capacity fails. Scarring occurs, known as fibrosis, where liver cells are replaced by fibrous tissue. The liver hardens and becomes increasingly unable to perform its functions - in the worst case, this leads to liver failure.
To ...
Women involved in car crashes may be more likely to go into shock than men
2024-03-15
It is well known that car safety equipment was originally designed with male-representative bodies in mind. This means women sitting in the front row are more likely to suffer severe or fatal injuries in the case of a crash. They are also more likely to be trapped in crashed cars.
Interested in the inequalities of car design and the resulting injuries, a team of researchers in the US has used trauma injury data from car crash victims to evaluate differences in injury patterns typical for males and females.
“We found that vehicle crash injury patterns and injury severity differ between men and women. We also show that women are arriving ...
Researchers attempt to clarify correlation between strain and catalytic activities for 2D catalysts
2024-03-15
Researchers led by Prof. WANG Bin at National Center for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently reported that strain generated at bubbles of 2D materials can benefit the catalytic activity of the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The study was published in Chem Catalysis.
Green hydrogen produced by electrochemical water splitting offers the potential to achieve carbon-neutral production processes. Catalysts play a crucial role in facilitating HER at the anode, making it a key component in the transition to a sustainable energy future. Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), particularly MoS2, have drawn attention ...
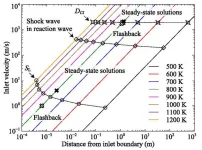
A theory linking ignition with flame provides roadmap to better combustion engines
2024-03-15
In a study published on January 18, 2024 in the journal Physics of Fluids, researchers from Tohoku University theoretically linked ignition and deflagration in a combustion system, unlocking new configurations for stable, efficient combustion engines due to the possible existence of any number of steady-state solutions.
"This research directly tackles the challenge of reducing carbon dioxide emissions by enhancing the efficiency of combustion engines, a significant source of these emissions," said Youhi Morii from the ...
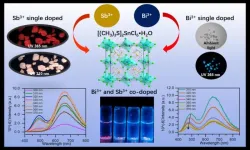
Doping engineering in halide perovskite, an efficient synthesis method of white LEDs
2024-03-15
In 1879, Edison invented the incandescent lamp, which brought light to the night. In 1969, the first red light emitting diodes (LEDs) lamp came out. However, as the key to making white light bulbs, high-energy blue light has not been successfully commercialized. Until 1998, the Japan’s Nakamura Shoji made white LEDs, which marked the official entry of LEDs into the lighting era. LEDs have the advantages of high efficiency, environmental protection and energy saving. Metal halide perovskites (MHPs) have become a powerful candidate for new LEDs ...
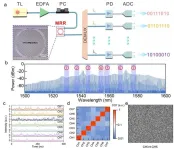
Parallel physical random bit generation towards rates of order 100 Tb/s
2024-03-15
In our digital networked society, random bit generators (RBGs) are vital for services and state-of-the-art technologies such as cryptographically secured communication, blockchain technologies, and quantum key distribution. An ever-increasing demand to improve the security of digital information has shifted the generation of random bits from sole reliance on pseudorandom algorithms to the use of physical entropy sources. Shannon’s theorem establishes that it is required for the ultimate security to achieve bit rate matching that of the true RBGs with that of the communication systems. For this purpose, optical chaos has been widely studied in the past decades as a means for the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
[Press-News.org] New study reveals breakthrough in understanding brain stimulation therapiesFor the first time, researchers show how the brain can precisely adapt to external stimulation