(Press-News.org) Specialized nursing facility clinicians, or SNFists, may decrease the likelihood of nursing home residents experiencing stressful hospitalizations and improve the quality of life in their last days, according to researchers from Weill Cornell Medicine.
The paper, published in JAMA Network Open on Mar. 15, examined how SNFists uniquely impacted the care of nursing home residents in their last 90 days, compared with those cared for by other clinicians. This large-scale study is the first of its kind.
“The literature has described certain features or outcomes that translate into what we think is poor quality at the end of life,” said Dr. Arnab Ghosh, assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine and a hospitalist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “One example is transferring residents to the hospital and admitting them for conditions like pneumonia or UTIs (urinary tract infections) that may have been managed in the nursing home, or going from nursing home to hospital to another nursing home.”
The physical act of transferring the residents to new environments increases their risk of delirium and discomfort, the researchers said. Transfers also interrupt communication and continuity of care, burdening patients and making them more uncomfortable.
The study defined SNFists as healthcare professionals (physicians, nurse practitioners and physician assistants) who provided at least 80 percent of their patient visits in the nursing home setting. They noted this specialization gives SNFists deeper insight into the clinical conditions facing nursing home residents, which allows for better communication between the residents, their families and other staff members.
The study of 2,091,954 nursing home residents aged 65 and older, during a period from January 2012 to December 2019, found that SNFists managed about 46 percent of this group. The researchers determined that care from an SNFist decreased risk up to 6 percent for hospitalizations due to any reason including pneumonia, urinary tract infection, dehydration or sepsis.
The need for SNFists will only grow as the U.S. population ages and more people develop dementia—two-thirds of all deaths related to Alzheimer’s disease occur in nursing homes. Other professions may also need to step up. “We need more research comparing the quality of care from different nursing home clinicians including medical doctors, nurse practitioners and physician assistants, but we clearly see fewer MDs working in nursing homes while NPs and PAs are increasing,” said Dr. Hye-Young Jung, associate professor of Population Health Sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The researchers suggest that medical schools and residency programs may need to offer more nursing home care experiences to increase the number of physicians in this field. They also emphasize the need for designating an official specialization, as with other areas of medicine like hospitalists, which would provide certification of the unique knowledge and skills needed in the nursing home setting.
END
Specialized nursing facility clinicians improve end-of-life care
2024-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fatty food before surgery may impair memory in old, young adults
2024-03-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Eating fatty food in the days leading up to surgery may prompt a heightened inflammatory response in the brain that interferes for weeks with memory-related cognitive function in older adults – and, new research in animals suggests, even in young adults.
The study, building upon previous research from the same lab at The Ohio State University, also showed that taking a DHA omega-3 fatty acid supplement for a month before the unhealthy eating and surgical procedure prevented the effects on memory linked to both the high-fat diet and the surgery in aged ...
Newly discovered receptor influences gut development in fruit flies
2024-03-15
Adhesion GPCRs belong to the large family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). There are about 700 variants in humans, which are responsible for sensory impressions, hormonal cycles, controlling the cardiovascular system and more. GPCRs translate stimuli that hit a cell from outside into an intracellular biochemical signal.
The use of the fruit fly as a model animal allows researchers in this field to gain a deep understanding of human diseases, because the animals are genetically very similar to humans. Scientists estimate that around 75 per cent of the genes involved in human diseases ...
New research suggests that our universe has no dark matter
2024-03-15
The current theoretical model for the composition of the universe is that it’s made of ‘normal matter,’ ‘dark energy’ and ‘dark matter.’ A new uOttawa study challenges this.
A University of Ottawa study published today challenges the current model of the universe by showing that, in fact, it has no room for dark matter.
In cosmology, the term “dark matter” describes all that appears not to interact with light or the electromagnetic field, or that can only be explained through gravitational force. We can’t see it, nor do we know what ...
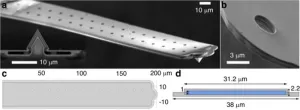
A breakthrough in tiny tool tuning: making microscopic measurements more accurate
2024-03-15
A study introduces a novel method for calibrating the spring constant of FluidFM micropipette cantilevers, crucial for the accurate measurement of forces in microfluidic environments. This method addresses the limitations of current calibration techniques, offering a significant advancement in the field of force microscopy.
Fluidic force microscopy (FluidFM) combines the sensitivity of atomic force microscopy with microfluidics' capabilities, necessitating precise calibration of its cantilevers for reliable data. Traditional methods, however, struggle with the unique internal structure of FluidFM cantilevers, leading to ...
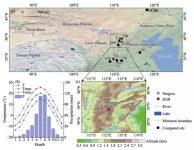
Unlocking the climate secrets of North China with ancient tree rings
2024-03-15
A recent study published in the Journal of Geographical Sciences in December 2023 reveals a novel method for reconstructing historical warm season temperatures in North China. Utilizing the blue intensity (BI) of tree rings of Picea meyeri, researchers have developed a 281-year chronology, offering unprecedented insights into the region’s climatic past.
The escalating public concern over climate warming, due to its significant impacts on society, ecosystems, and the environment, underscores the importance of understanding long-term climatic conditions across different regions. As the limited observational records constrain our comprehensive grasp of climate change, tree-ring data prove ...
Aston University wins funding to improve sustainability in the Philippines
2024-03-15
Funding will prepare three scientists to improve sustainable development in their country
The University has won British Council International Science Partnerships funding of £180,000
The University already has close ties with the sustainability sector in the Philippines.
Aston University is to help tackle sustainability problems in the Philippines by offering training to three of the country’s early career researchers.
The University has won British Council International Science Partnerships funding of £180,000 to host three scientists ...
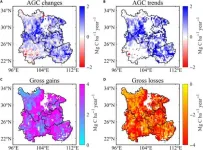
Revealing nature's secrets from space: satellite data unlocks drought's impact on Southwest China's carbon cycle
2024-03-15
A new study reveals a significant increase in aboveground carbon (AGC) in Southwest China from 2013 to 2021, defying the adverse effects of extreme droughts. This achievement underscores the region's pivotal role as a carbon sink, attributed to extensive ecological projects and innovative remote sensing techniques.
Over the past four decades, Southwest China has been a major carbon sink, significantly mitigating anthropogenic CO2 emissions. However, recent severe droughts, especially from 2009-2013 and in 2022, have drastically reduced its carbon ...
Health and economic value of eliminating socioeconomic disparities in U.S. youth physical activity
2024-03-15
About The Study: This study quantified the potential savings from eliminating or reducing physical activity disparities, which can help policymakers, health care systems, schools, funders, sports organizations, and other businesses better prioritize investments toward addressing these disparities.
Authors: Bruce Y. Lee, M.D., M.B.A., of Public Health Informatics, Computational, and Operations Research (PHICOR), CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy in New York, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Pain exposure and brain connectivity in preterm infants
2024-03-15
About The Study: Greater exposure to early-life pain was associated with altered maturation of neonatal structural connectivity, particularly in female infants in this study of 150 very preterm infants. Alterations in structural connectivity were associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes, with potential regional specificities.
Authors: Steven P. Miller, M.D.C.M., M.A.S., of the BC Children’s Hospital Research Institute and University of British Columbia in Vancouver, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Eliminating socioeconomic disparities in youth physical activity can save over $15 billion
2024-03-15
What would happen if the existing disparities in physical activity levels between youth of lower and higher socioeconomic statuses were eliminated? Previous studies have shown that those between 6-17 years of age in lower socioeconomic groups get on average 10-15% less physical activity than those of higher socioeconomic groups. A new study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum on Mar. 15 shows that eliminating such disparities could end up saving society over $15 billion in direct medical costs and productivity losses. This in turn could end up benefiting all taxpayers, anyone who pays insurance ...