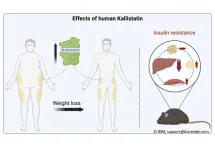
(Press-News.org) After weight loss, people with overweight and obesity express more of the protein Kallistatin* in subcutaneous white adipose tissue. This was demonstrated by researchers from the DZD in a recent study. In addition, Kallistatin improves metabolism and could open up new therapeutic options for people with obesity and type 2 diabetes in future. The results have now been published in Molecular Metabolism.
An increasing number of people are developing type 2 diabetes and obesity. These are highly complex and multifaceted diseases. In order to treat them sustainably, new approaches to therapy are needed. Clinical studies on humans have shown that heavily overweight individuals produce less Kallistatin. Kallistatin is a protein that has various effects in the body. Among other things, it is involved in counteracting inflammation and healing wounds. The role that Kallistatin plays in glucose metabolism and its potential suitability as a therapeutic target are currently being investigated by researchers from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM) of Helmholtz Munich at the Eberhard-Karls-University of Tübingen, and the Department of Diabetology, Endocrinology and Nephrology at the University Hospital Tübingen.
Kallistatin Expression Increases After Weight Loss
To this end, they measured Kallistatin expression in subcutaneous white adipose tissue in 47 individuals with overweight to obesity before and after weight loss. The result: Kallistatin expression increases after weight loss.
Kallistatin Improves Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity
Additionally, the researchers examined the effect of the protein in an animal model. In the process, they observed that human Kallistatin improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice.
“Our results suggest that Kallistatin may be an interesting, yet challenging, therapeutic target for people with obesity and insulin resistance,” says lead author Leontine Sandforth. “Because Kallistatin has insulin-sensitizing effects in the liver, it should be investigated as a potential liver-specific target for emulating the beneficial effects of weight loss and potentially treating type 2 diabetes and obesity,” adds last author Prof. Andreas Birkenfeld.
END
Kallistatin contributes to the beneficial metabolic effects of weight loss
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
WashU engineers manage a first: measuring pH in cell condensates
2024-03-18
Scientists trying to understand the physical and chemical properties that govern biomolecular condensates now have a crucial way to measure pH and other emergent properties of these enigmatic, albeit important cellular compartments.
Condensates are communities of proteins and nucleic acids. They lack a membrane and come together and fall apart as needed. The nucleolus is a prominent condensate in cells. It serves vital roles in cellular physiology and is the site of ribosome production.
Ribosomes are the multi-protein ...
Study with innovative insights into the heterogeneity of type 2 diabetes
2024-03-18
A landmark study by the German Diabetes Center (DDZ), published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, sheds new light on the heterogeneity of type 2 diabetes. The researchers employed an innovative algorithm to stratify people with type 2 diabetes using routine data and thus visualize the metabolic diversity of diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is a disease with highly diverse progression pathways. Using an innovative algorithm, a team led by the German Diabetes Center (DDZ) used routinely measured variables to open up new perspectives on the diversity of type 2 diabetes in terms of insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, ...
Breakthrough in melting point prediction: over 100-year-old physics problem solved by Queen Mary Professor
2024-03-18
A longstanding problem in physics has finally been cracked by Professor Kostya Trachenko of Queen Mary University of London's School of Physical and Chemical Sciences. His research, published in the Physical Review E, unveils a general theory for predicting melting points, a fundamental property whose understanding has baffled scientists for over a century.
For decades, our understanding of the three basic states of matter – solids, liquids, and gases – relied on temperature-pressure phase diagrams. These diagrams depict the conditions under which each state exists, with distinct lines separating them. However, one crucial line, ...
Shining a light on the underpinnings of rare disease impacting children
2024-03-18
A team from the University of Ottawa's Faculty of Medicine has completed an exciting new study that reveals the inner workings of gene mutations that result in an ultra-rare syndrome with fewer than 100 reported cases since its first description in the early 1960s.
The hard-won research discovery may accelerate the development of a treatment for Borjeson-Forssman-Lehmann Syndrome (BFLS), a neurodevelopmental disorder linked to the X chromosome that’s characterized by seizures, intellectual disability, and behavioural ...
Landmark study shows that ‘transcendent’ thinking may grow teens’ brains over time
2024-03-18
Scientists at the USC Rossier School of Education’s Center for Affective Neuroscience, Development, Learning and Education (CANDLE), have shown for the first time that a type of thinking, that has been described for over a century as a developmental milestone of adolescence, may grow teenagers’ brains over time. This kind of thinking, which the study’s authors call “transcendent,” moves beyond reacting to the concrete specifics of social situations to also consider ...
Reimagining the future of solar energy
2024-03-18
Scientists are always on the lookout for ways to make our world a better place, and one area they're focusing on is solar energy. One idea in this area is to make solar cells more efficient by concentrating more solar light onto them. While investigating this recently, a group of scientists at the Cavendish Laboratory and AMOLF (Amsterdam NL) have found that improving solar cells efficiency in this way is harder than we might think but have discovered other avenues by which it might be possible to improve solar energy capture anywhere on the planet.
The researchers ...
Metformin during pregnancy impacts offspring brain development
2024-03-18
With the rise in gestational diabetes and metabolic disorders during pregnancy, metformin is also being prescribed more frequently. Although it is known that the oral antidiabetic agent can cross the placental barrier, the impacts on the brain development of the child are largely unknown. An interdisciplinary research team from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbrücke (DIfE) have now been able to demonstrate in a mouse model that although metformin has positive effects in pregnant animals, it does not in the offspring. The results were published in the specialist ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine-led team develops fluid biomarker for early detection of ALS and FTD
2024-03-18
Two progressively degenerative diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, commonly known as Lou Gehrig’s disease) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD, recently in the news with the diagnoses of actor Bruce Willis and talk show host Wendy Williams), are linked by more than the fact that they both damage nerve cells critical to normal functioning — the former affecting nerves in the brain and spinal cord leading to loss of movement, the latter eroding the brain regions controlling personality, behavior and language.
Research studies have repeatedly shown that in patients with ALS or FTD, the function of TAR DNA-binding protein 43, more commonly called TDP-43, ...
A new antibody capture method reveals G-quadruplex landscape and its regulation
2024-03-18
“[...] we present an improved method for G4 landscape determination and by applying it we show that sequence property-specific constraints of the nuclear environment mitigate G4 formation.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 18, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on March 14, 2024, entitled, “G-quadruplex landscape and its regulation revealed by a new antibody capture method.”
In this new study, researchers Subhamoy Datta, Manthan Patel, Chakkarai Sathyaseelan, Chandrama Ghosh, Akanksha Mudgal, Divyesh Patel, Thenmalarchelvi Rathinavelan, ...
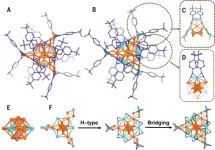
Researchers achieve >99% photoluminescence quantum yield in metal nanoclusters
2024-03-18
Prof. ZHOU Meng’s research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Prof. WANG Quanming’s team from Tsinghua University (THU) achieved near-unity room-temperature photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) (>99%) in the near-infrared (NIR) emission of metal nanoclusters in solution. Their work was published in Science.
Gold nanoclusters (Au NCs) as NIR-emissive materials hold potential in biomedical applications. However, the PLQY of Au NCs in NIR region is typically low, often ...