(Press-News.org) Farmers rely on pesticides to control agricultural pests. But insects often develop resistance to the toxins in pesticides. University of Maryland researchers have developed and successfully tested a strategy for using genomics to monitor for and identify emerging resistance to specific toxins early, well before it becomes a widespread problem. The work will enable farmers to mitigate resistance and prolong the effectiveness of pest management tools.
The research was published on March 18, 2024, in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Science.
“Global food security and protection of public health rely on the availability of effective strategies to manage pests, but as it currently stands, the evolution of resistance across many pests of agricultural and public health importance is outpacing the rate at which we can discover new technologies to manage them,” said Megan Fritz, an associate professor of entomology at UMD and senior author of the study. “I'm really excited about this study, because we're developing the framework for use of genomic approaches to monitor and manage resistance in any system.”
For many years, farmers have been planting corn that has been bred to contain natural chemicals that are harmless to humans but toxic to many pests, including the voracious, crop-damaging caterpillar known as corn earworm. But corn earworm has developed widespread resistance to some of these toxins, and it is unclear how farmers can prolong effectiveness of the remaining toxins, largely because it is difficult to monitor and identify emerging resistance before it’s too late.
In a previous paper in 2021, Fritz and her team showed that genomic tools could be used to detect signs that resistance was evolving in corn earworms four years prior to the insect being able to cause widespread failure in managed crops. But the approaches the team used were more suited for research than widespread use in agriculture, because they required two separate experiments to distinguish the genomic changes linked to toxin resistance from those associated with other factors such as environmental changes.
For this study, the researchers modified their strategy and identified the specific genomic changes responsible for resistance to multiple types of toxins called Bt toxins. Corn earworm have largely developed resistance to two of the three Bt toxins, Cry1Ab and Cry1F. The third toxin, known as Vip3A, is the only Bt toxin that remains effective against corn earworm.
To test their new strategy, the researchers first sequenced the genomes of corn earworm collected from corn that expressed only individual Cry toxins and compared it to those collected from non-toxin-expressing corn.
They found that genomic signatures of resistance to toxins could be detected after only a single generation of exposure.The team also identified specific genes with mutations that could explain toxin resistance. These genes encode digestive enzymes that chop Cry toxins into smaller pieces, perhaps preventing them from killing the caterpillars.
Fritz and her team then used the same genome sequencing approach to identify changes in corn earworm collected from corn expressing the Vip3A toxin. Not only did they identify early warning signs of emerging resistance to Vip3A, but they also described how common strategies for preventing resistance could actually be facilitating Vip3A resistance.
Non-Bt expressing corn is often planted near Bt corn, so that corn earworm have a refuge from Bt toxins. It was believed that corn earworm feeding on non-Bt corn would not be exposed to Vip3A and thus maintain their susceptibility to it. That would allow susceptible corn earworm to persist and multiply in greater abundance than resistant corn earworm. The thinking is that this strategy prevents or slows the buildup of resistance in a corn earworm population.
However, Fritz’s team found that non-Bt corn planted within four rows of Bt corn expresses some level of Bt toxins, including Vip3A. This is likely due to wind pollination that causes Bt pollen to land on non-Bt corn. As they grow, some non-Bt kernels are “contaminated” and express Vip3A toxin. The team’s results suggest that inter-planting non-Bt corn with Bt corn to prevent resistance, sometimes called “seed-blended refuge” may in fact expose caterpillars to low levels of Vip3A and hasten the emergence of Vip3A resistance.
Fritz’s work indicates that true resistance prevention might require changing strategies, both for how Bt corn is planted, as well as how resistance is monitored. This study offers a genomic testing framework for monitoring the success of resistance prevention in the future.
This work was funded by USDA NIFA 542 Biotechnology Risk Assessment Grants 2018-33522-28741 and 2019-33522-29992.
This study was conducted with colleagues from University of North Carolina. Post Doctoral Associate Katherine Taylor, from UMD Department of Entomology is a co-author on this study.
END
UMD researchers develop genomic method of monitoring for pesticide resistance
Study identifies genomic changes responsible for Bt resistance in corn earworm, and finds VIP3 contamination in non-Bt corn could trigger resistance
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Backyard insect inspires invisibility devices, next gen tech
2024-03-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Leafhoppers, a common backyard insect, secrete and coat themselves in tiny mysterious particles that could provide both the inspiration and the instructions for next-generation technology, according to a new study led by Penn State researchers. In a first, the team precisely replicated the complex geometry of these particles, called brochosomes, and elucidated a better understanding of how they absorb both visible and ultraviolet light.
This could allow the development of bioinspired optical materials with possible applications ranging from invisible cloaking devices to coatings to more efficiently harvest ...
Americans support democratic norms, elected officials don't
2024-03-18
Following the attack on the U.S. Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021, and efforts to overturn the results of the 2020 presidential election, many Americans have raised concerns about the future of democracy in the United States.
Yet the American public, including Democrats and Republicans alike, strongly oppose anti-democratic actions and partisan violence, according to a new study by the Polarization Research Lab.
"Democracy is under threat in America, but these data show we are not on the brink of a citizen-supported push toward authoritarianism," says the lab's ...
Harnessing hydrogen at life’s origin
2024-03-18
A new report uncovers how hydrogen gas, the energy of the future, provided energy in the past, at the origin of life 4 billion years ago. Hydrogen gas is clean fuel. It burns with oxygen in the air to provide energy with no CO2. Hydrogen is a key to sustainable energy for the future. Though humans are just now coming to realize the benefits of hydrogen gas (H2 in chemical shorthand), microbes have known that H2 is good fuel for as long as there has been life on Earth. Hydrogen is ancient energy. The very first cells on Earth lived from H2 produced in hydrothermal vents, using the reaction of H2 with CO2 to make the molecules of ...
Sustainable biomass production capacity could triple US bioeconomy, report finds
2024-03-18
The United States could triple its current bioeconomy by producing more than 1 billion tons per year of plant-based biomass for renewable fuels, while meeting projected demands for food, feed, fiber, conventional forest products and exports, according to the Department of Energy’s latest Billion-Ton Report led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
The 2023 Billion-Ton Report, or BT23, announced by DOE, is the fourth in a series of national biomass resource assessments spanning two decades. The report identifies feedstocks that could be ...
Cure Mito Foundation and Hope for PDCD Foundation announce a patient registry collaboration
2024-03-18
March 18, 2024 – Cure Mito Foundation and Hope for PDCD foundation, both patient-led foundations focused on advancing research and supporting families affected by Leigh syndrome and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Deficiency (PDCD), respectively, are excited to announce a launch of a PDCD patient registry. This innovative registry will be led by the Hope for PDCD foundation and hosted on the same registry platform as the well-established Leigh Syndrome patient registry, developed by the Cure Mito Foundation. This strategic move is aimed at enhancing patient convenience and improving data alignment and research ...
Newborn piglets serve as a model for studying influenza
2024-03-18
Although prevention and treatment strategies are available for influenza, they are not sufficient for vulnerable populations such as young children and newborns. In a new study, published in Virology, a multidisciplinary team of researchers have studied newborn piglets to better understand the progression of influenza infections.
The influenza A virus can infect a variety of birds and mammals, including humans and pigs, due to which it is a threat to public health and food security. While it causes mild ...
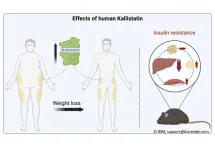
Kallistatin contributes to the beneficial metabolic effects of weight loss
2024-03-18
After weight loss, people with overweight and obesity express more of the protein Kallistatin* in subcutaneous white adipose tissue. This was demonstrated by researchers from the DZD in a recent study. In addition, Kallistatin improves metabolism and could open up new therapeutic options for people with obesity and type 2 diabetes in future. The results have now been published in Molecular Metabolism.
An increasing number of people are developing type 2 diabetes and obesity. These are highly complex and multifaceted diseases. In order to treat them sustainably, new approaches to therapy are needed. Clinical studies on humans have ...
WashU engineers manage a first: measuring pH in cell condensates
2024-03-18
Scientists trying to understand the physical and chemical properties that govern biomolecular condensates now have a crucial way to measure pH and other emergent properties of these enigmatic, albeit important cellular compartments.
Condensates are communities of proteins and nucleic acids. They lack a membrane and come together and fall apart as needed. The nucleolus is a prominent condensate in cells. It serves vital roles in cellular physiology and is the site of ribosome production.
Ribosomes are the multi-protein ...
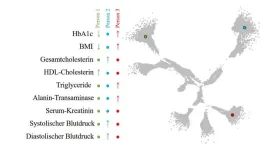
Study with innovative insights into the heterogeneity of type 2 diabetes
2024-03-18
A landmark study by the German Diabetes Center (DDZ), published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, sheds new light on the heterogeneity of type 2 diabetes. The researchers employed an innovative algorithm to stratify people with type 2 diabetes using routine data and thus visualize the metabolic diversity of diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is a disease with highly diverse progression pathways. Using an innovative algorithm, a team led by the German Diabetes Center (DDZ) used routinely measured variables to open up new perspectives on the diversity of type 2 diabetes in terms of insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, ...
Breakthrough in melting point prediction: over 100-year-old physics problem solved by Queen Mary Professor
2024-03-18
A longstanding problem in physics has finally been cracked by Professor Kostya Trachenko of Queen Mary University of London's School of Physical and Chemical Sciences. His research, published in the Physical Review E, unveils a general theory for predicting melting points, a fundamental property whose understanding has baffled scientists for over a century.
For decades, our understanding of the three basic states of matter – solids, liquids, and gases – relied on temperature-pressure phase diagrams. These diagrams depict the conditions under which each state exists, with distinct lines separating them. However, one crucial line, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
[Press-News.org] UMD researchers develop genomic method of monitoring for pesticide resistanceStudy identifies genomic changes responsible for Bt resistance in corn earworm, and finds VIP3 contamination in non-Bt corn could trigger resistance