(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine published a new study in the Journal of Infectious Diseases investigating the antibody response following SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Long-lived plasma cells are responsible for durable antibody responses that persist for decades after immunization or infection. For example, infection with measles, mumps, rubella, or immunization with vaccines against tetanus or diphtheria elicit antibody responses that can last for many decades. By contrast, other infections and vaccines elicit short-lived antibody responses that last only a few years at most. For example, vaccines against HIV elicit antibody responses that persist for less than a year. Although the COVID-19 epidemic is less than five years old, it is known that infection or vaccination with SARS-CoV-2 elicits short-lived protective antibody responses, but the mechanism underlying this problem is unknown.
“We know long-lived plasma cells can produce antibodies against specific pathogens for decades, so we wanted to investigate their role in COVID-19 infection,” said study co-author Mohammad Sajadi, MD, associate professor of Medicine, Division of Clinical Care and Research, Institute of Human Virology.
The study by the Sajadi and Lewis teams examined the contribution of long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow to anti-spike antibodies after COVID-19 infection. The study studied 20 individuals with a history of COVID-19 infection but no vaccination. Bone marrow aspirates and plasma samples were analyzed to characterize antibody responses. The research found deficient generation of spike-specific long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow, offering insight into the short duration of antibody responses observed in recovering COVID-19 patients.
“The rapid waning of spike-specific antibodies we observed indicates a lack of durable antibody production after natural infection,” said study co-author George Lewis, PhD, director of the Division of Vaccine Research, Institute of Human Virology. “This appears to be due to insufficient generation of long-lived plasma cells that would sustain antibody levels, a phenomenon we’ve noted before with certain viruses.”
Ten years ago, the researchers discussed the possible mechanisms for this problem with HIV in a peer-reviewed publication and have been working on it since. Their work on the poor persistence of antibody responses to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein shows that the antibody persistence problem extends to Covid-19 as well and that it is likely due to lack of long-lived antibody-secreting cells in the bone marrow.
Shyam Kottilil, PhD, Interim IHV Director, added, “Sustained antibody responses to viral infections are critical for vaccine development and long-term immunity. The presence of long-lived plasma cells in bone marrow is a crucial component for the generation of prolonged effective antiviral immunity. This study by Drs. Sajadi and Lewis and colleagues provide vital information about protracted immunity to COVID-19, which is a breakthrough in our understanding of antiviral immunity due to COVID-19 and other viruses.”
The researchers say the findings will help inform the development of vaccines and therapeutics that can induce robust long-term antibody production against SARS-CoV-2 and HIV. New studies have been designed in people to work out the cellular and molecular basis of this problem.
“This intriguing new study provides a possible explanation for why antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 decay quickly,” said Mark T. Gladwin, MD, who is the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean of UMSOM, and Vice President for Medical Affairs at University of Maryland, Baltimore. “Future studies will be key to further investigate the cellular and molecular basis of why SARS-CoV-2 does not elicit long lived antibody secreting cells specific for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with the ultimate goal of correcting this deficit in future vaccine designs.”
The team aims to secure further funding to continue pursuing this critical area of vaccine research.
“We were fortunate to be able to study this problem in context of first exposure to a new human pathogen and disease,” said Dr. Sajadi. “We are grateful to our volunteer participants and colleagues, especially co-first authors Drs. Zahra Rikhtegaran Tehrani and Parham Habibzadeh, as well as Robin Flinko, whose efforts made this impactful study possible.”
About the Institute of Human Virology
Formed in 1996 as a partnership between the State of Maryland, the City of Baltimore, the University System of Maryland, and the University of Maryland Medical System, the IHV is an institute of the University of Maryland School of Medicine and is home to some of the most globally-recognized and world-renowned experts in all of virology. The IHV combines the disciplines of basic research, epidemiology, and clinical research in a concerted effort to speed the discovery of diagnostics and therapeutics for a wide variety of chronic and deadly viral and immune disorders, most notably HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. For more information, visit ihv.org and follow us on Twitter @IHVmaryland.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has nearly $600 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The combined School of Medicine and Medical System ("University of Maryland Medicine") has an annual budget of over $6 billion and an economic impact of nearly $20 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2021, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #9 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 15 percent (#27) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu.
END
New study reveals insights into COVID-19 antibody response durability
Researchers at the Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine published a new study in the Journal of Infectious Diseases investigating the antibody response following SARS-CoV-2 infection
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate change alters the hidden microbial food web in peatlands
2024-03-18
DURHAM, N.C. -- The humble peat bog conjures images of a brown, soggy expanse. But it turns out to have a superpower in the fight against climate change.
For thousands of years, the world’s peatlands have absorbed and stored vast amounts of carbon dioxide, keeping this greenhouse gas in the ground and not in the air. Although peatlands occupy just 3% of the land on the planet, they play an outsized role in carbon storage -- holding twice as much as all the world’s forests do.
The fate of all that carbon is uncertain in the face of climate change. And ...
Text nudges can increase uptake of COVID-19 boosters– if they play up a sense of ownership of the vaccine
2024-03-18
New research published in Nature Human Behavior suggests that text nudges encouraging people to get the COVID-19 vaccine, which had proven effective in prior real-world field tests, are also effective at prompting people to get a booster.
The key in both cases is to include in the text a sense of ownership in the dose awaiting them.
The paper, led by Hengchen Dai, an associate professor of management and organizations and behavioral decision making at the UCLA Anderson School of Management, and Silvia Saccardo, an associate professor of social and decision sciences at Carnegie Mellon University, draws on previous research published in Nature that examined the effectiveness ...
A new study shows how neurochemicals affect fMRI readings
2024-03-18
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The brain is an incredibly complex and active organ that uses electricity and chemicals to transmit and receive signals between its sub-regions.
Researchers have explored various technologies to directly or indirectly measure these signals to learn more about the brain. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), for example, allows them to detect brain activity via changes related to blood flow.
Yen-Yu Ian Shih, PhD, professor of neurology and associate director of UNC’s Biomedical Research Imaging Center, and his fellow lab members have long been curious about how neurochemicals in the brain regulate and influence neural activity, ...
Digital reminders for flu vaccination improves turnout, but not clinical outcomes in older adults
2024-03-18
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 18 March 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Digital reminders for flu vaccination improves ...
Avatar will not lie... or will it? Scientists investigate how often we change our minds in virtual environments
2024-03-18
How confident are you in your judgments and how well can you defend your opinions? Chances are that they will change under the influence of a group of avatars in a virtual environment. Scientists from SWPS University investigated the human tendency to be influenced by the opinions of others, including virtual characters.
We usually conform to the views of others for two reasons. First, we succumb to group pressure and want to gain social acceptance. Second, we lack sufficient knowledge and perceive the group as a source of a better interpretation of the current situation, describes Dr. Konrad Bocian from the Institute of Psychology at SWPS University.
So far, only a few studies ...
8-hour time-restricted eating linked to a 91% higher risk of cardiovascular death
2024-03-18
Research Highlights:
A study of over 20,000 adults found that those who followed an 8-hour time-restricted eating schedule, a type of intermittent fasting, had a 91% higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
People with heart disease or cancer also had an increased risk of cardiovascular death.
Compared with a standard schedule of eating across 12-16 hours per day, limiting food intake to less than 8 hours per day was not associated with living longer.
Embargoed until 3 p.m. CT/4 p.m. ET, Monday, March 18, 2024
CHICAGO, March 18, 2024 — An analysis ...
Alternative tidal wetlands in plain sight overlooked Blue Carbon superstars
2024-03-18
Blue Carbon projects are expanding globally; however, demand for credits outweighs the available credits for purchase.
Currently, only three types of wetlands are considered Blue Carbon ecosystems: mangroves, saltmarsh and seagrass.
However, other tidal wetlands also comply with the characteristics of what is considered Blue Carbon, such as tidal freshwater wetlands, transitional forests and brackish marshes.
In a new study, scientists from Australia, Indonesia, Singapore, South Africa, Vietnam, the US and Mexico have highlighted the increasing opportunities for Blue Carbon projects for the conservation, restoration and improved management of highly threatened ...
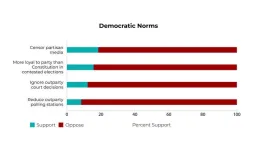
The majority of Americans do not support anti-democratic behavior, even when elected officials do
2024-03-18
EMBARGOED UNTIL MARCH 18 AT 3 P.M. EST
Recently, fundamental tenets of democracy have come under threat, from attempts to overturn the 2020 election to mass closures of polling places.
A new study from the Polarization Research Lab, a collaboration among researchers at the Annenberg School for Communication at the University of Pennsylvania, Dartmouth College, and Stanford University, has found that despite this surge in anti-democratic behavior by U.S. politicians, the majority of Americans oppose anti-democratic attitudes and reject partisan violence.
From September 2022 to October 2023, a period which included the 2022 midterm ...
Genes identified that allow bacteria to thrive despite toxic heavy metal in soil
2024-03-18
VANCOUVER, Wash. -- Some soil bacteria can acquire sets of genes that enable them to pump the heavy metal nickel out of their systems, a study has found. This enables the bacteria to not only thrive in otherwise toxic soils but help plants grow there as well.
A Washington State University-led research team pinpointed a set of genes in wild soil bacteria that allows them to do this in serpentine soils which have naturally high concentrations of toxic nickel. The genetic discovery, detailed in the journal Proceedings of the National Academies ...
Scientists’ discovery could reduce dependence on animals for vital anti-blood clot drug
2024-03-18
Heparin, the world’s most widely used blood thinner, is used during procedures ranging from kidney dialysis to open heart surgery. Currently, heparin is derived from pig intestines, but scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have discovered how to make it in the lab. They have also developed a path to a biomanufacturing process that could potentially revolutionize how the world gets its supply of this crucial medicine.
“In recent years, with disease and contamination issues disrupting the global supply chain of pig heparin and potentially putting millions of patients at risk, it’s clear we need to diversify ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] New study reveals insights into COVID-19 antibody response durabilityResearchers at the Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine published a new study in the Journal of Infectious Diseases investigating the antibody response following SARS-CoV-2 infection