Bendable energy storage materials by cool science
2024-03-19
(Press-News.org)
Imaging being able to wear your smartphone on your wrist, not as a watch, but literally as a flexible band that surrounds around your arm. How about clothes that charge your gadgets just by wearing them? Recently, a collaborative team led by Professor Jin Kon Kim and Dr. Keon-Woo Kim of Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Professor Taesung Kim and M.S./Ph.D. student Hyunho Seok of Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU), and Professor Hong Chul Moon of University of Seoul (UOS) has brought a step closer to making this realty. This research work was published in Advanced Materials.
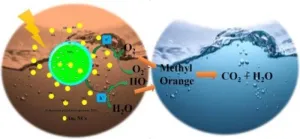
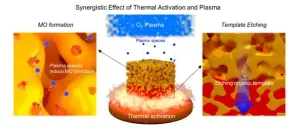
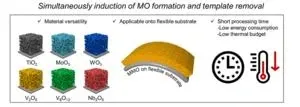
Mesoporous metal oxides (MMOs) are characterized by pores ranging from 2 to 50 nanometers (nm) in size. Due to their extensive surface area, MMOs have various applications, such as high-performance energy storage and efficient catalysis, semiconductors, and sensors. However, the integration of MMOs on wearable and flexible devices remains a great challenge, because plastic substrates could not maintain their integrity at elevated temperatures (350°C or above) where MMOs could be synthesized.
The research team tackled this problem by using synergetic effect of heat and plasma to synthesize various MMOs including vanadium oxide (V2O5), renowned high-performance energy storage materials, V6O13, TiO2, Nb2O5, and WO3, on flexible materials at much lower temperatures (150 ~ 200 oC). The high reactive plasma chemical moieties provide enough energy that could be compensated by high temperature. The fabricated devices could be bent thousands of times without losing the energy storage performance.
Professor Jin Kon Kim, the leading researcher, expressed his opinion, stating: “We’re on the brink of a revolution in wearable tech”. “Our breakthrough could lead to gadgets that are not only more flexible but also much more adaptable to our daily needs”
This research was supported by National Creative Initiative Research Program, the Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program, and the Nano & Material Technology Development Program.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-19
A five-day course of once-daily inorganic nitrate reduces the risk of a serious complication following a coronary angiogram, in which the dye used causes damage to the kidneys. The clinical trial, led by Queen Mary University of London and funded by Heart Research UK, also showed that the five-day course improves renal outcomes at three months and major adverse cardiac events (MACE) at one year compared to placebo.
Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN), also known as contrast associated acute kidney injury (CA-AKI), is an uncommon but serious complication following ...
2024-03-19
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
6 p.m. PT / 9 p.m. ET, March 18, 2024
To coincide with publication in The Gerontologist
Media Contact: Suzanne Leigh (415) 680-5133
Suzanne.Leigh@UCSF.edu
Subscribe to UCSF News
People with dementia and those who care for them should be screened for loneliness, so providers can find ways to keep them socially connected, according to experts at UC San Francisco and Harvard, who made the recommendations after finding that both groups experienced declines in social well-being as the disease progressed.
The patients, whose ...
2024-03-19
Since the 1970s, the federal government has listed the active ingredients in mushrooms—psilocybin and psilocin—as illegal and having no accepted medical use.
However, in recent years, medical professionals have found that these substances are safe and effective for treating stubborn conditions such as treatment-resistant depression and post-traumatic stress disorder. Some jurisdictions now allow for the medical use of mushrooms, while others are considering permitting or at least decriminalizing their recreational use.
Clinicians now find themselves needing to carefully ...
2024-03-19
Irvine, Calif., March 18, 2024 — A research team led by the University of California, Irvine has discovered the key role that the APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B enzymes play in driving cancer mutations by modifying the DNA in tumor genomes, offering potential new targets for intervention strategies.
The study, published today online in the journal Nature Communications, describes how the researchers identified the process by which APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B detect specific DNA structures, resulting in mutations at distinct positions within the tumor genome.
“It’s critical to understand how cancer cells accumulate mutations leading to ...
2024-03-18
The blue whale genome was published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, and the Etruscan shrew genome was published in the journal Scientific Data.
Research models using animal cell cultures can help navigate big biological questions, but these tools are only useful when following the right map.
“The genome is a blueprint of an organism,” says Yury Bukhman, first author of the published research and a computational biologist in the Ron Stewart Computational Group at the Morgridge Institute, an independent research organization that works in affiliation with the University of Wisconsin–Madison in emerging fields ...
2024-03-18
Water pollution from dyes used in textile, food, cosmetic and other manufacturing is a major ecological concern with industry and scientists seeking biocompatible and more sustainable alternatives to protect the environment.
A new study led by Flinders University has discovered a novel way to degrade and potentially remove toxic organic chemicals including azo dyes from wastewater, using a chemical photocatalysis process powered by ultraviolet light.
Professor Gunther Andersson, from the Flinders Institute for NanoScale Science and Technology, says the process involves creating metallic ‘clusters’ of just nine gold (Au) atoms chemically ‘anchored’ ...
2024-03-18
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Food companies’ sponsorship of children’s sports may encourage children to buy their products, new research to be presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) (Venice 12-15 May), has found.
The Canadian research also found that many children view food companies that sponsor or give money to children’s sports as being “generous” ...
2024-03-18
To democratize access to lab-grown organ-like structures known as organoids and other advanced stem cell and transcriptomic technologies, USC will launch the CIRM ASCEND Center, dedicated to “Advancing Stem Cell Education and Novel Discoveries.” Funded by a $3.95 million grant from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), the voter-created state agency charged with distributing public funding to support stem cell research and education, ASCEND joins a network of shared resources laboratories ...
2024-03-18
MADISON –– Scientists have been measuring global methane emissions for decades, but the boreal arctic —with a wide range of biomes including wetlands that extend across the northern parts of North America, Europe and Asia — is a key region where accurately estimating highly potent greenhouse gas emissions has been challenging.
Wetlands are great at storing carbon, but as global temperatures increase, they are warming up. That causes the carbon they store to be released into the atmosphere in the form of methane, which contributes to more global warming.
Now, researchers — including the University ...
2024-03-18
The Lundquist Institute is proud to announce that Wei Yan, MD, PhD, a distinguished professor at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and Lundquist investigator, has been appointed by the American Society of Andrology and the European Academy of Andrology as the new Editor-in-Chief of Andrology, the highly-respected journal in the field of reproductive medicine.
Dr. Yan's appointment to Andrology is a testament to his dedication to reproductive medicine. With extensive editorial experience, including his previous roles as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Bendable energy storage materials by cool science