(Press-News.org) Researchers have incorporated a swept illumination source into an open-top light-sheet microscope to enable improved optical sectioning over a larger area of view. The advance makes the technique more practical for nondestructive 3D pathology.
3D pathology is being explored as an alternative to traditional slide-based histology because it can provide detailed 3D insights into pathological structures and cellular interactions without altering the tissue. This approach makes it possible to analyze complex 3D tissue structures and to image thick tissues, which is not possible with slide-based methods.
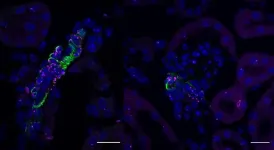
The researchers used their improved open-top light-sheet microscope to capture images of densely labeled clinical specimens, showing its potential for nondestructive 3D pathology. Kevin W. Bishop from the University of Washington will detail the work at Optica’s Biophotonics Congress being held in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, 07 – 10 April 2024. Bishop’s presentation is scheduled for Tuesday, 09 April at 13:45 - 14:00 EDT.
For certain diseases, like prostate cancer, it can be challenging to determine which patients need aggressive treatment and which patients do not. 3D information could ultimately help clinicians better determine the best course of treatment for each patient.
Open-top light-sheet microscopy is used to rapidly acquire 3D images of fluorescently labeled tissues that have been treated in a way that makes them transparent or translucent. The typical setup uses a fixed thin sheet of light to illuminate and image the sample from below, much like a flatbed document scanner. This enables high-resolution imaging of large areas at much faster speeds than are possible with other 3D imaging approaches (e.g. confocal microscopy).
Although many types of labels can be used with this microscopy technique, 3D pathology samples typically use dyes that mimic the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining used in traditional histology slides. Because this type of staining is much denser than highly targeted stains, the microscope’s optical-sectioning capability — its ability to visualize a thin slice within a 3D sample — becomes key to achieving good image quality.
Although better sectioning is possible by using a higher illumination numerical aperture, this creates a shorter depth of focus that reduces the system’s usable field of view. To overcome this challenge, the researchers developed a new open-top light-sheet microscope that incorporates an axially swept illumination arm.
Compared to their previous microscope design with a fixed light sheet, the new system quadrupled the field of view and doubled the optical sectioning ability without compromising volumetric imaging speed. The researchers demonstrated its usefulness by imaging a densely labeled cleared mouse kidney. They also acquired other datasets from clinical tissues to further show that the optimized system can deliver the image quality and field of view necessary for 3D pathology studies.
“We plan to use this platform to run large-scale clinical studies that will help us understand where 3D pathology can have the greatest clinical impact,” said Bishop.
About Optica Biophotonics Congress
Optica Biophotonics Congress is an annual meeting that focuses on biomedical optics and optics in the life sciences in alternating years. The 2024 meeting, Optica Biophotonics Congress: Biomedical Optics, Biomedical Optics focuses on technological solutions to medical challenges and medical applications. The meeting will be held as an in-person event with on-demand content. More information at https://www.optica.org/events/congress/biophotonics_congress_biomedical_optics/.
About Optica
Optica, Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide, is the society dedicated to promoting the generation, application, archiving and dissemination of knowledge in the field. Founded in 1916, it is the leading organization for scientists, engineers, business professionals, students and others interested in the science of light. Optica's renowned publications, meetings, online resources and in-person activities fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate scientific, technical and educational achievement. Discover more at: Optica.org
Media Contact
mediarelations@optica.org
END
Researchers add swept illumination to open-top light-sheet microscope
Advance improves field of view and optical sectioning, laying groundwork for 3D pathology applications
2024-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-quality microwave signals generated from tiny photonic chip
2024-03-20
In a new Nature study, Columbia Engineering researchers have built a photonic chip that is able to produce high-quality, ultra-low-noise microwave signals using only a single laser. The compact device — a chip so small, it could fit on a sharp pencil point — results in the lowest microwave noise ever observed in an integrated photonics platform.
The achievement provides a promising pathway towards small-footprint ultra-low-noise microwave generation for applications such as high-speed communication, atomic clocks, and autonomous vehicles.
The challenge
Electronic devices for global navigation, wireless communications, radar, and ...
OFC 2024 brings innovations from leading global organizations and cutting-edge tech demonstrations to California
2024-03-20
SAN DIEGO—A wave of innovation is hitting California as the Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC) gears up to showcase the latest breakthroughs in optical communications and networking.
OFC will take place at the San Diego Convention Center from 24 to 28 March 2024 drawing industry leaders, experts, academia, media, analysts and students from around the world to explore the latest in optical technology.
Innovative advancements in industrial technologies, as well as research in 800ZR, Coherent PON, Linear Pluggable Optics (LPO), multicore fiber, AI and ...
Killer whales use specialized hunting techniques to catch marine mammals in the open ocean
2024-03-20
Killer whales foraging in deep submarine canyons off the coast of California represent a distinct subpopulation that uses specialized hunting techniques to catch marine mammals, Josh McInnes at the University of British Columbia and colleagues report March 20 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Killer whales (Orcinus orca) are found in oceans around the world, but they form separate populations, or ‘ecotypes’, that have their own social structure, food preferences and hunting behaviors. One ecotype, known as transient killer whales, specialize in hunting marine ...
The first Neolithic boats in the Mediterranean
2024-03-20
More than 7,000 years ago, people navigated the Mediterranean Sea using technologically sophisticated boats, according to a study published March 20, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Juan F. Gibaja of the Spanish National Research Council, Barcelona and colleagues.
Many of the most important civilizations in Europe originated on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. During the Neolithic, communities clearly traveled and traded across the water, as evidenced by watercraft in the archeological record and the presence ...
Universal controller could push robotic prostheses, exoskeletons into real-world use
2024-03-20
Robotic exoskeletons designed to help humans with walking or physically demanding work have been the stuff of sci-fi lore for decades. Remember Ellen Ripley in that Power Loader in Alien? Or the crazy mobile platform George McFly wore in 2015 in Back to the Future, Part II because he threw his back out?
Researchers are working on real-life robotic assistance that could protect workers from painful injuries and help stroke patients regain their mobility. So far, they have required extensive calibration and context-specific tuning, which keeps them largely limited to research labs.
Mechanical engineers at Georgia Tech ...
Autism acceptance varies across countries – where should we target support?
2024-03-20
Societal acceptance of autism varies considerably across different countries, with lowest levels of acceptance found in Japan and Belgium, new research shows.
A survey of 306 autistic individuals from eight countries revealed that around three quarters of respondents do not feel accepted, or only sometimes feel accepted, as an autistic person. Among these countries, participants in Japan and Belgium reported the lowest levels of acceptance, while those in Canada, the UK, and South Africa reported comparatively higher levels.
The study, published in PLOS ONE, is the ...
A replacement for traditional motors could enhance next-gen robots
2024-03-20
Whether it’s a powered prosthesis to assist a person who has lost a limb or an independent robot navigating the outside world, we are asking machines to perform increasingly complex, dynamic tasks. But the standard electric motor was designed for steady, ongoing activities like running a compressor or spinning a conveyor belt – even updated designs waste a lot of energy when making more complicated movements.
Researchers at Stanford University have invented a way to augment electric motors to make them much more efficient at performing dynamic ...
Icy impacts: Planetary scientists use physics and images of impact craters to gauge the thickness of ice on Europa
2024-03-20
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Sometimes planetary physics is like being in a snowball fight. Most people, if handed an already-formed snowball, can use their experience and the feel of the ball to guess what kind of snow it is comprised of: packable and fluffy, or wet and icy.
Using nearly the same principles, planetary scientists have been able to study the structure of Europa, Jupiter’s icy moon.
Additional Information
When worlds collide: Studying impact craters to uncover the secrets of the solar system
Breaking in a new planet
Purdue scientists and engineers push the boundaries of space knowledge, studying the ...
Ancient giant dolphin discovered in the Amazon
2024-03-20
Measuring between 3 to 3.5 meters, 16 million years old: Paleontologists from the University of Zurich have announced the discovery of a new species of freshwater dolphin in the Peruvian Amazon region. Surprisingly, its closest living relatives can be found in the river dolphins of South Asia.
River dolphins are among the rarest modern cetaceans, with most extant species critically endangered. Despite their similar appearance, however, these animals are not directly related, but represent the late survivors of different cetacean groups that once inhabited our planet.
An international ...
Study suggests an ‘odor sensor’ may explain male and female differences in blood pressure
2024-03-20
Using data from both mice and humans, a Johns Hopkins Medicine research team has found that a cell surface protein that senses odors and chemicals may be responsible for — and help explain — sex differences in mammalian blood pressure. The unusual connection between such protein receptors and sex differences in blood pressure, reported in the March 20 issue of Science Advances, may lead to a better understanding of long known differences in blood pressure between females and males.
Blood ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Researchers add swept illumination to open-top light-sheet microscopeAdvance improves field of view and optical sectioning, laying groundwork for 3D pathology applications