(Press-News.org) Today, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) announced several key appointments and a new AI residency program to advance the organization’s AI strategy for science, which is focused on building predictive models of healthy and diseased cells. Several AI experts from academia and industry have joined a newly established AI Advisory Group, which will provide guidance to leaders at CZI and across the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub Network as these organizations work to enable AI at scale for nonprofit life science research. In addition, CZI is launching an AI residency program to develop foundational AI/ML models and tools that will enable new scientific breakthroughs. Theofanis Karaletsos, a technology leader in AI/ML research and science, has also been hired as CZI’s Head of Artificial Intelligence for Science.
The organization’s newly-formed AI Advisory Group, which is composed of several members from CZI’s Scientific Advisory Board and the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub Board of Directors, will provide guidance and cross-disciplinary feedback to senior leadership teams at CZI and across the CZ Biohub Network. These advisors have deep expertise in leveraging AI/ML models and methods to advance scientific research:
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI. Altman was also recently named to the CZ Biohub Board.
Regina Barzilay, Distinguished Professor for AI and Health and AI Faculty Lead at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Barzilay was also recently named to CZI’s Scientific Advisory Board.
Reid Hoffman, Partner at Greylock and the Co-Founder of Linkedin. Hoffman joined the CZ Biohub Board in 2016.
Emma Lundberg, Associate Professor of Bioengineering at Stanford University and Co-Director of the Human Protein Atlas.
Joelle Pineau, Associate Professor of Computer Science at McGill University and Vice President of AI Research at Meta. Pineau was also recently named to CZI’s Scientific Advisory Board.
Mike Schroepfer, Founder and Partner of Gigascale Capital, Former CTO of Meta. Schroepfer was also recently named to the CZ Biohub Board.
“Bringing these AI leaders and residents on board is an important milestone for our team as we work towards enabling AI/ML at scale to accelerate the pace of scientific research,” said Stephen Quake, Head of Science at CZI. “Their participation will help us build a strong foundation for our AI work as an organization — and accelerate the progress we're making towards deepening the scientific community’s understanding of human biology at a cellular level.”
Karaletsos will lead CZI’s AI strategy for science, including the organization’s vision to develop virtual cell models, utilizing one of the largest high-performance AI computing systems for nonprofit life science research. He will collaborate with scientific leaders at CZI including Emma Lundberg, a member of CZI’s AI Advisory Group and an Associate Professor of Bioengineering at Stanford University, to launch an in-house AI Residency Program. The new program coalesces AI/ML leaders from academia to develop AI models and applications that will be openly and widely available to the scientific research community. In collaboration with CZI scientists and engineers, the projects spearheaded by these residents will lay the foundation for virtual cell models that will allow researchers to explore the molecular underpinnings of human health and disease.
“Enabling AI at scale for life science research will pave the way for new biomedical discoveries,” said Theofanis Karaletsos, Head of Artificial Intelligence for Science at CZI. “I’m excited to collaborate with different teams across CZI and the Biohub Network to expand our AI capabilities.”
CZI’s work in science includes grantmaking programs, open-source software development, and close collaboration with its partner institutes at the CZ Biohub Network. The CZ Biohub Network includes the San Francisco, Chicago, and New York Biohubs as well as the Chan Zuckerberg Imaging Institute. CZI also collaborates with institutional partners such as the Kempner Institute for the Study of Natural & Artificial Intelligence at Harvard University. For more information, please visit www.chanzuckerberg.com/science.
END
CZI launches AI Advisory Group and residency program to accelerate development of virtual cell models
Advisors, key hires, and in-house AI residents will inform the organization’s AI strategy, including the development of virtual cell models to advance scientific research
2024-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Natural molecule found in coffee and human body increases NAD+ levels, improves muscle function during ageing
2024-03-21
A research consortium led by Nestlé Research in Switzerland and the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine) made a recent discovery that the natural molecule trigonelline present in coffee, fenugreek, and also in the human body, can help to improve muscle health and function. In an international collaboration among the University of Southampton, University of Melbourne, University of Tehran, University of South Alabama, University of Toyama and University of Copenhagen, the work builds on a previous collaborative ...
As we age, our cells are less likely to express longer genes
2024-03-21
Aging may be less about specific “aging genes” and more about how long a gene is. Many of the changes associated with aging could be occurring due to decreased expression of long genes, say researchers in an opinion piece publishing March 21 in the journal Trends in Genetics. A decline in the expression of long genes with age has been observed in a wide range of animals, from worms to humans, in various human cell and tissue types, and also in individuals with neurodegenerative disease. Mouse experiments show that the phenomenon can be mitigated via known anti-aging factors, including dietary restriction.
“If you ask me, this ...
Researchers name prehistoric amphibian ancestor discovered in Smithsonian collection after Kermit the Frog
2024-03-21
Scientists have uncovered the fossilized skull of a 270-million-year-old ancient amphibian ancestor in the collection of the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History. In a paper published today, March 21, in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, the team of researchers described the fossil as a new species of proto-amphibian, which they named Kermitops gratus in honor of the iconic Muppet, Kermit the Frog.
According to Calvin So, a doctoral student at the George Washington University and the lead author on the new paper, naming the new creature after the beloved frog character, who was created ...
Better cancer trials could be around the corner
2024-03-21
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Associate Professor and Cancer Center member Tobias Janowitz led a COVID-19 clinical trial with Northwell Health in 2021. When he and Clinical Fellow Hassal Lee reviewed the data, a surprising trend emerged. “The patient roster was very diverse,” Janowitz explains. “We’d made no deliberate effort toward that other than conducting the trial remotely.”
When it comes to cancer trials, many variables impact patient participation. One measurable factor is distance. On average, people are less likely to ...
Long-term body mass index variability and adverse cardiovascular outcomes
2024-03-21
About The Study: This analysis including 157,000 individuals from two large study cohorts found that among U.S. veterans, higher body mass index (BMI) variability was a significant risk marker associated with adverse cardiovascular events independent of mean BMI across major racial and ethnic groups. Results were consistent in the UK Biobank for the cardiovascular death end point. Further studies should investigate the phenotype of high BMI variability.
Authors: Yan V. Sun, Ph.D., M.S., ...
Postconcussive symptoms after early childhood concussion
2024-03-21
About The Study: In this early childhood study including 303 children, concussion was associated with more postconcussive symptoms than orthopedic injuries or typical development up to three months after injury. Given the limited verbal and cognitive abilities typical of early childhood, using developmentally appropriate manifestations and behaviors is a valuable way of tracking postconcussive symptoms and could aid in concussion diagnosis in young children.
Authors: Miriam Beauchamp, Ph.D., of the Universite de Montreal, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
Entanglements of humpback whales in fish farms rare – and naivety could be to blame
2024-03-21
The first study of humpback whale entanglements in B.C. aquaculture facilities in PLOS One found eight over 13 years, with the curiosity of young whales a potential contributing factor.
A rare occurrence
Entanglements are one of several threats to humpbacks. The eight occurred from 2008 to 2021 at seven fish farms, with five animals successfully released and three deaths. The entanglements accounted for less than six per cent of all entanglements in B.C. Approximately 7,000 animals return to B.C. waters annually.
Most whales became entangled between the predator and containment nets on fish farms. In five cases, experienced ...
Opto-RANK: A light switch for osteoclasts
2024-03-21
Tokyo, Japan – Drinking milk helps your bones grow big and strong; but what if direct exposure to light could help too? Now, researchers from Japan report that lighting up bone tissue could help treat bone disease.
In a study published last month in Scientific Reports, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that a treatment approach based on light could help activate bones to repair themselves.
Bones are constantly being remodeled through the action of osteoclasts, which break down bone tissue, and osteoblasts, which create new bone tissue. ...
Connecting computers so they can think faster
2024-03-21
We are used to computers getting faster and faster, but complicated calculations involving lots of data can take a very long time, even today.
This applies to calculations of chemical reactions, how proteins assume different three-dimensional forms and so-called phase transitions, where one chemical substance transitions from one state to another, such as from solid to liquid form.
These types of results are often very important – for example, in the chemical industry.
Down from one year to ten days
These complicated calculations can take years to perform, and access to the most ...
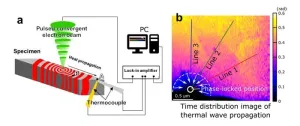
In-situ observation of nanoscale heat propagation
2024-03-21
1. A NIMS research team has developed a technique that enables the nanoscale observation of heat propagation paths and behavior within material specimens. This was achieved using a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) capable of emitting a pulsed electron beam and a nanosized thermocouple—a high-precision temperature measurement device developed by NIMS.
2. Public interest in energy conservation and recycling has grown considerably in recent years. This change has inspired scientists to develop next-generation materials/devices capable of controlling and utilizing heat with a high degree of precision, including thermoelectric devices able to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] CZI launches AI Advisory Group and residency program to accelerate development of virtual cell modelsAdvisors, key hires, and in-house AI residents will inform the organization’s AI strategy, including the development of virtual cell models to advance scientific research