(Press-News.org) Tropical Heliconius butterflies are well known for the bright colour patterns on their wings. These striking colour patterns not only scare off predators – the butterflies are poisonous and are distasteful to birds – but are also important signals during mate selection. A team led by evolutionary biologist Richard Merrill from LMU Munich, in cooperation with researchers from the Universidad del Rosario in Bogotá (Colombia) and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (Panama), has now exploited the diversity of warning patterns of various Heliconius species to investigate the genetic foundations of these preferences. In the process, the scientists identified a gene that is directly linked to evolutionary changes in a visually guided behaviour, the first time such a connection has been demonstrated in an animal, as they report in the journal Science.
For their study, the researchers carried out hundreds of behavioural experiments to investigate the mating preferences of three Heliconius species in Colombia: Heliconius melpomene and Heliconius timareta, both of which have a bright red band on their forewing, and Heliconius cydno, which has a white forewing band. They discovered that males of all three species prefer partners that look like themselves, with no differences in the preferences of the two more distantly related red species.
Using genomic analyses, the researchers demonstrated that the preference for red females is associated with a genomic region where hybridization between these two red species has resulted in sharing of genetic material. “We managed to identify regucalcin1 as a key gene controlling visual preference, in these butterflies,” says Matteo Rossi, who carried out research on the butterflies in Merrill’s lab alongside fellow PhD candidate Alexander Hausmann. “If regucalcin1 is silenced, it impairs courtship toward conspecific females, proving a direct link between gene and behaviour,” explains Rossi.
Genetic exchange through hybridization
Further analyses by the scientists showed that regucalcin1 was transferred from H. melpomene to H. timareta sometime in their evolutionary past. “We’ve known for quite a while that the red colour pattern gene was introduced from one species to the other through hybridization, and suspected that the same might be true for the corresponding preference. To finally show it, and identify the specific gene is really exciting,” says Carolina Pardo-Diaz, Dean of Biology at the Universidad del Rosario, and one of the lead authors on the paper. Thanks to regucalcin1, the attractiveness of red females and thus the reproductive success of H. timareta was increased.
“We see differences in visual preferences all around us in nature when animals choose who to mate with. With our results, we were able to establish a direct link between a particular visual preference and a specific gene for the first time, and also demonstrate that hybridization can play an important role in the evolution of these behaviours,” emphasises Merrill.
END
How butterflies choose mates: gene controls preferences
In a first, LMU evolutionary biologists have identified a gene that influences visual preferences in tropical butterflies.
2024-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mysterious exporter for brassinosteroid first identified
2024-03-21
When you are reading this article, there are multiple hormones working diligently inside your body to stabilize your health status. Same as human beings, it is impossible for plants to grow and reproduce without being regulated by phytohormones. One of the phytohormones is the Brassinosteroid (BR) hormones, also named as the sixth phytohormone.
According to a study published in Science on March 22, 2024, researchers led by Prof. SUN Linfeng from the Division of Life Sciences and Medicine of the University of Science and Technology ...
New reactor could save millions when making ingredients for plastics and rubber from natural gas
2024-03-21
Images
A new way to make an important ingredient for plastics, adhesives, carpet fibers, household cleaners and more from natural gas could reduce manufacturing costs in a post-petroleum economy by millions of dollars, thanks to a new chemical reactor designed by University of Michigan engineers.
The reactor creates propylene, a workhorse chemical that is also used to make a long list of industrial chemicals, including ingredients for nitrile rubber found in automotive hoses and seals as well as blue protective gloves. ...
How the brain senses body position and movement
2024-03-21
How does your brain know the position and movement of your different body parts? The sense is known as proprioception, and it is something like a “sixth sense”, allowing us to move freely without constantly watching our limbs.
Proprioception involves a complex network of sensors embedded in our muscles that relay information about limb position and movement back to our brain. However, little is known about how the brain puts together the different signals it receives from muscles.
A new study led by Alexander Mathis at EPFL now sheds light on the question by exploring how our brains create a cohesive sense of body position and movement. Published in Cell, ...
Species diversity promotes ecosystem stability
2024-03-21
Species diversity promotes ecosystem stability
Biodiversity loss may accelerate ecosystem destabilization
What maintains stability within an ecosystem and prevents a single best competitor from displacing other species from a community? Does ecosystem stability depend upon the presence of a wide variety of species, as early ecologists believed, or does diversity do the exact opposite, and lead to instability, as modern theory predicts?
Resolving a long-standing debate among ecologists
A new study from McGill University and ...
University of Calgary research finds a direct communication path between the lungs and the brain
2024-03-21
University of Calgary researchers have discovered the lungs communicate directly with the brain when there is an infection. Findings show the brain plays a critical role in triggering the symptoms of sickness, which may change the way we treat respiratory infections and chronic conditions.
“The lungs are using the same sensors and neurons in the pain pathway to let the brain know there’s an infection,” says Dr. Bryan Yipp, MD '05, MSc'05, clinician researcher at the Cumming School of Medicine and ...
NSF awards grant for evolution-inspired design of therapeutic RNAs
2024-03-21
A team led by Dr. Samie Jaffrey, the Greenberg-Starr Professor of Pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been awarded a three-year, $1.65 million grant for RNA research under a biotechnology-development program run by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
The competitive Molecular Foundations for Biotechnology program funds cutting-edge research that lays the groundwork for future clinical and industrial biotechnologies. The new award is one of nine that have been given to research teams across the United States this year, with funding assistance from the National Institutes of Health, to advance the promise of RNA-based therapeutics and ...
Best way to bust deepfakes? Use AI to find real signs of life, say Klick Labs scientists
2024-03-21
NEW YORK, NY / TORONTO, ON – March, 21, 2024 – Artificial intelligence may make it difficult for even the most discerning ears to detect deepfake voices – as recently evidenced in the fake Joe Biden robocall and the bogus Taylor Swift cookware ad on Meta – but scientists at Klick Labs say the best approach might actually come down to using AI to look for what makes us human.
Inspired by their clinical studies using vocal biomarkers to help enhance health outcomes, and their fascination with sci-fi films like “Blade Runner,” the Klick ...
The protein that protects insulin-producing cells
2024-03-21
Although there are many differences between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes, there are also similarities, such as inflammation of the insulin-producing cells. Researchers at Lund University have studied a protein called C3, which plays a central role in the body’s immune system. The protein is secreted from cells and is found in large quantities in the blood. Previous studies by the same researchers have shown that C3 is also present inside cells and plays an important role there. Now, their latest study in PNAS shows that the protein C3 protects insulin-producing cells from damage and death when it is present ...
World’s first N-channel diamond field-effect transistor
2024-03-21
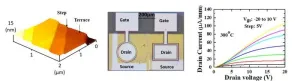
1. A NIMS research team has developed the world’s first n-channel diamond MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). The developed n-channel diamond MOSFET provides a key step toward CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor: one of the most popular technologies in the computer chip) integrated circuits for harsh-environment- applications as well as the development of diamond power electronics.
2. Semiconductor diamond has outstanding physical properties such as ultra wide-bandgap energy of 5.5 eV, high carriers mobilities, ...
Adults younger than 40 with ideal heart health had lower heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease risk
2024-03-21
Research Highlights:
A study of nearly 4 million young adults under age 40 in South Korea found that those who had ideal cardiovascular health were nearly two-thirds less likely to develop heart disease, stroke and/or kidney disease during a 12-year follow-up period.
Adults who had low heart health scores at study baseline in 2009-2010 but improved their cardiovascular health thereafter also had a reduced risk of heart disease, stroke or kidney disease compared to people with persistent low heart health scores.
Embargoed until 10:30 a.m. CT/11:30 a.m. ET, Thursday, March 21, 2024
CHICAGO, March 21, 2024 — An ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] How butterflies choose mates: gene controls preferencesIn a first, LMU evolutionary biologists have identified a gene that influences visual preferences in tropical butterflies.