How the brain senses body position and movement
2024-03-21
(Press-News.org)
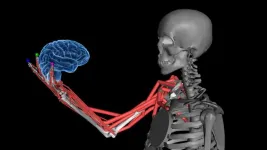
How does your brain know the position and movement of your different body parts? The sense is known as proprioception, and it is something like a “sixth sense”, allowing us to move freely without constantly watching our limbs.
Proprioception involves a complex network of sensors embedded in our muscles that relay information about limb position and movement back to our brain. However, little is known about how the brain puts together the different signals it receives from muscles.
A new study led by Alexander Mathis at EPFL now sheds light on the question by exploring how our brains create a cohesive sense of body position and movement. Published in Cell, the study was carried out by PhD students Alessandro Marin Vargas, Axel Bisi, and Alberto Chiappa, with experimental data from Chris Versteeg and Lee Miller at Northwestern University.
“It is widely believed that sensory systems should exploit the statistics of the world and this theory could explain many properties of the visual and auditory system,” says Mathis. “To generalize this theory to proprioception, we used musculoskeletal simulators to compute the statistics of the distributed sensors.”
The researchers used this musculoskeletal modeling to generate muscle spindle signals in the upper limb to generate a collection of “large-scale, naturalistic movement repertoire”. They then used this repertoire to train thousands of “task-driven” neural network models on sixteen computational tasks, each of which reflects a scientific hypothesis about the computations carried out by the proprioceptive pathway, which includes parts of the brainstem and somatosensory cortex.
The approach allowed the team to comprehensively analyse how different neural network architectures and computational tasks influence the development of “brain-like” representations of proprioceptive information. They found that neural network models trained on tasks that predict limb position and velocity were most effective, suggesting that our brains prioritize integrating the distributed muscle spindle input to understand body movement and position.
The research highlights the potential of task-driven modeling in neuroscience. Unlike traditional methods that focus on predicting neural activity directly, task-driven models can offer insights into the underlying computational principles of sensory processing.
The research also paves the way for new experimental avenues in neuroscience, since a better understanding of proprioceptive processing could lead to significant advancements in neuroprosthetics, with more natural and intuitive control of artificial limbs.
Reference
Alessandro Marin Vargas, Axel Bisi, Alberto Chiappa, Chris Versteeg, Lee Miller, Alexander Mathis. Task-driven neural network models predict neural dynamics of proprioception. Cell 21 March 2024. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.02.036
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-21
Species diversity promotes ecosystem stability
Biodiversity loss may accelerate ecosystem destabilization
What maintains stability within an ecosystem and prevents a single best competitor from displacing other species from a community? Does ecosystem stability depend upon the presence of a wide variety of species, as early ecologists believed, or does diversity do the exact opposite, and lead to instability, as modern theory predicts?
Resolving a long-standing debate among ecologists
A new study from McGill University and ...
2024-03-21
University of Calgary researchers have discovered the lungs communicate directly with the brain when there is an infection. Findings show the brain plays a critical role in triggering the symptoms of sickness, which may change the way we treat respiratory infections and chronic conditions.
“The lungs are using the same sensors and neurons in the pain pathway to let the brain know there’s an infection,” says Dr. Bryan Yipp, MD '05, MSc'05, clinician researcher at the Cumming School of Medicine and ...
2024-03-21
A team led by Dr. Samie Jaffrey, the Greenberg-Starr Professor of Pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been awarded a three-year, $1.65 million grant for RNA research under a biotechnology-development program run by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
The competitive Molecular Foundations for Biotechnology program funds cutting-edge research that lays the groundwork for future clinical and industrial biotechnologies. The new award is one of nine that have been given to research teams across the United States this year, with funding assistance from the National Institutes of Health, to advance the promise of RNA-based therapeutics and ...
2024-03-21
NEW YORK, NY / TORONTO, ON – March, 21, 2024 – Artificial intelligence may make it difficult for even the most discerning ears to detect deepfake voices – as recently evidenced in the fake Joe Biden robocall and the bogus Taylor Swift cookware ad on Meta – but scientists at Klick Labs say the best approach might actually come down to using AI to look for what makes us human.
Inspired by their clinical studies using vocal biomarkers to help enhance health outcomes, and their fascination with sci-fi films like “Blade Runner,” the Klick ...
2024-03-21
Although there are many differences between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes, there are also similarities, such as inflammation of the insulin-producing cells. Researchers at Lund University have studied a protein called C3, which plays a central role in the body’s immune system. The protein is secreted from cells and is found in large quantities in the blood. Previous studies by the same researchers have shown that C3 is also present inside cells and plays an important role there. Now, their latest study in PNAS shows that the protein C3 protects insulin-producing cells from damage and death when it is present ...
2024-03-21
1. A NIMS research team has developed the world’s first n-channel diamond MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). The developed n-channel diamond MOSFET provides a key step toward CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor: one of the most popular technologies in the computer chip) integrated circuits for harsh-environment- applications as well as the development of diamond power electronics.
2. Semiconductor diamond has outstanding physical properties such as ultra wide-bandgap energy of 5.5 eV, high carriers mobilities, ...
2024-03-21
Research Highlights:
A study of nearly 4 million young adults under age 40 in South Korea found that those who had ideal cardiovascular health were nearly two-thirds less likely to develop heart disease, stroke and/or kidney disease during a 12-year follow-up period.
Adults who had low heart health scores at study baseline in 2009-2010 but improved their cardiovascular health thereafter also had a reduced risk of heart disease, stroke or kidney disease compared to people with persistent low heart health scores.
Embargoed until 10:30 a.m. CT/11:30 a.m. ET, Thursday, March 21, 2024
CHICAGO, March 21, 2024 — An ...
2024-03-21
Today, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) announced several key appointments and a new AI residency program to advance the organization’s AI strategy for science, which is focused on building predictive models of healthy and diseased cells. Several AI experts from academia and industry have joined a newly established AI Advisory Group, which will provide guidance to leaders at CZI and across the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub Network as these organizations work to enable AI at scale for nonprofit life science research. In addition, CZI is launching an AI residency program to develop foundational AI/ML models and tools that will enable ...
2024-03-21
A research consortium led by Nestlé Research in Switzerland and the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine) made a recent discovery that the natural molecule trigonelline present in coffee, fenugreek, and also in the human body, can help to improve muscle health and function. In an international collaboration among the University of Southampton, University of Melbourne, University of Tehran, University of South Alabama, University of Toyama and University of Copenhagen, the work builds on a previous collaborative ...
2024-03-21
Aging may be less about specific “aging genes” and more about how long a gene is. Many of the changes associated with aging could be occurring due to decreased expression of long genes, say researchers in an opinion piece publishing March 21 in the journal Trends in Genetics. A decline in the expression of long genes with age has been observed in a wide range of animals, from worms to humans, in various human cell and tissue types, and also in individuals with neurodegenerative disease. Mouse experiments show that the phenomenon can be mitigated via known anti-aging factors, including dietary restriction.
“If you ask me, this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How the brain senses body position and movement