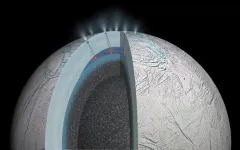
(Press-News.org) The ice-encrusted oceans of some of the moons orbiting Saturn and Jupiter are leading candidates in the search for extraterrestrial life. A new lab-based study led by the University of Washington in Seattle and the Freie Universität Berlin shows that individual ice grains ejected from these planetary bodies may contain enough material for instruments headed there in the fall to detect signs of life, if such life exists.
“For the first time we have shown that even a tiny fraction of cellular material could be identified by a mass spectrometer onboard a spacecraft,” said lead author Fabian Klenner, a UW postdoctoral researcher in Earth and space sciences. “Our results give us more confidence that using upcoming instruments, we will be able to detect lifeforms similar to those on Earth, which we increasingly believe could be present on ocean-bearing moons.”
The open-access study was published March 22 in Science Advances. Other authors in the international team are from The Open University in the U.K.; NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; the University of Colorado, Boulder; and the University of Leipzig.
The Cassini mission that ended in 2017 discovered parallel cracks near the south pole of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. Emanating from these cracks are plumes containing gas and ice grains. NASA’s Europa Clipper mission, scheduled to launch in October, will carry more instruments to explore in even more detail an icy moon of Jupiter, Europa.
To prepare for that mission, researchers are studying what this new generation of instruments might find. It is technically prohibitive to directly simulate grains of ice flying through space at 4 to 6 kilometers per second to hit an observational instrument, as the actual collision speed will be. Instead, the authors used an experimental setup that sends a thin beam of liquid water into a vacuum, where it disintegrates into droplets. They then used a laser beam to excite the droplets and mass spectral analysis to mimic what instruments on the space probe will detect.
Newly published results show that instruments slated to go on future missions, like the SUrface Dust Analyzer onboard Europa Clipper, can detect cellular material in one out of hundreds of thousands of ice grains.
The study focused on Sphingopyxis alaskensis, a common bacterium in waters off Alaska. While many studies use the bacterium Escherichia coli as a model organism, this single-celled organism is much smaller, lives in cold environments, and can survive with few nutrients. All these things make it a better candidate for potential life on the icy moons of Saturn or Jupiter.
“They are extremely small, so they are in theory capable of fitting into ice grains that are emitted from an ocean world like Enceladus or Europa,” Klenner said.
Results show that the instruments can detect this bacterium, or portions of it, in a single ice grain. Different molecules end up in different ice grains. The new research shows that analyzing single ice grains, where biomaterial may be concentrated, is more successful than averaging across a larger sample containing billions of individual grains.
A recent study led by the same researchers showed evidence of phosphate on Enceladus. This planetary body now appears to contain energy, water, phosphate, other salts and carbon-based organic material, making it increasingly likely to support lifeforms similar to those found on Earth.
The authors hypothesize that if bacterial cells are encased in a lipid membrane, like those on Earth, then they would also form a skin on the ocean’s surface. On Earth, ocean scum is a key part of sea spray that contributes to the smell of the ocean. On an icy moon where the ocean is connected to the surface (e.g., through cracks in the ice shell), the vacuum of outer space would cause this subsurface ocean to boil. Gas bubbles rise through the ocean and burst at the surface, where cellular material gets incorporated into ice grains within the plume.
“We here describe a plausible scenario for how bacterial cells can, in theory, be incorporated into icy material that is formed from liquid water on Enceladus or Europa and then gets emitted into space,” Klenner said.
The SUrface Dust Analyzer onboard Europa Clipper will be higher-powered than instruments on past missions. This and future instruments also will for the first time be able to detect ions with negative charges, making them better suited to detecting fatty acids and lipids.
“For me, it is even more exciting to look for lipids, or for fatty acids, than to look for building blocks of DNA, and the reason is because fatty acids appear to be more stable,” Klenner said.
“With suitable instrumentation, such as the SUrface Dust Analyzer on NASA’s Europa Clipper space probe, it might be easier than we thought to find life, or traces of it, on icy moons,” said senior author Frank Postberg, a professor of planetary sciences at the Freie Universität Berlin. “If life is present there, of course, and cares to be enclosed in ice grains originating from an environment such as a subsurface water reservoir.”
The study was funded by the European Research Council, NASA and the German Research Foundation (DFG). Other co-authors are Janine Bönigk, Maryse Napoleoni, Jon Hillier and Nozair Khawaja at the Freie Universität Berlin; Karen Olsson-Francis at The Open University in the U.K.; Morgan Cable and Michael Malaska at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Sascha Kempf at the University of Colorado, Boulder; and Bernd Abel at the University of Leipzig.
END
Signs of life detectable in single ice grain emitted from extraterrestrial moons
2024-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tudor era horse cemetery in Westminster revealed as likely resting place for elite imported animals
2024-03-22
Archaeological analysis of a near unique animal cemetery discovered in London nearly 30 years ago has revealed the international scale of horse trading by the elites of late medieval and Tudor England.
Using advanced archaeological science techniques, including studying chemical composition, researchers have been able to identify the likely origins of several physically elite horses and the routes they took to reach British shores during the formative years of their life.
These animals – akin to modern supercars – were sourced from a variety of locations across ...
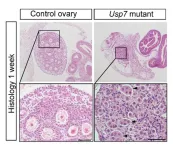
Researchers uncover protein interactions controlling fertility in female mice
2024-03-22
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 18:00hrs GMT Friday 22 March 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Researchers uncover protein interactions controlling fertility in female mice
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have shed light on the proteins controlling the development of ovaries in mice before and after birth. This could lead to a better understanding of how female infertility develops.
Following their research identifying the gene responsible for initiating the development ...
Scientists explore complex pattern of tipping points in the Atlantic’s current system
2024-03-22
An international team of scientists have warned against relying on nature providing straightforward ‘early warning’ indicators of a climate disaster, as new mathematical modelling shows new fascinating aspects of the complexity of the dynamics of climate.
It suggests that the climate system could be more unpredictable than previously thought.
By modelling the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation, one of the main ocean current systems, the team which included mathematicians from the University of Leicester have found that the stability of ...
University College Dublin seeking to appoint a Full Professor of Data Science for Weather and Climate
2024-03-22
As part of a new multi-million-euro academic research programme at University College Dublin (UCD) funded by Met Éireann (the Irish National Meteorological Service) to support the further development of weather and climate services for Ireland using data science and Artificial Intelligence (AI), UCD is seeking to appoint a Full Professor of Data Science for Weather and Climate.
This exciting new senior academic post is a permanent position in the UCD School of Mathematics and Statistics arising from a funding award of €5 million over five years from Met Éireann, ...
Scientists uncover evidence that microplastics are contaminating archaeological remains
2024-03-22
Researchers have for the first time discovered evidence of microplastic contamination in archaeological soil samples.
The team discovered tiny microplastic particles in deposits located more than seven metres deep, in samples dating back to the first or early second century and excavated in the late 1980s.
Preserving archaeology in situ has been the preferred approach to managing historical sites for a generation. However, the research team say the findings could prompt a rethink, with the tiny particles potentially compromising the preserved remains.
Microplastics are small plastic particles, ranging from 1μm (one thousandth of a millimetre) ...
Toronto researchers devise new way to find proteins for targeted treatment of disease
2024-03-22
Researchers at the University of Toronto and Sinai Health have created a new platform to identify proteins that can be co-opted to control the stability of other proteins — a new but largely unrealized approach to the treatment of disease.
The researchers developed a method to interrogate the entire human proteome for ‘effector’ proteins, which can influence the stability of other proteins via induced proximity. The study marks the first time researchers have searched for effector proteins on this scale, and has identified many new effectors that could be used therapeutically.
“We found more than 600 new effector proteins in 14,000 ...
Researchers invent artificial intelligence model to design new superbug-fighting antibiotics
2024-03-22
Attention editors: Under embargo by the journal Nature Machine Intelligence until Friday, March 22, 12 p.m. eastern
Hamilton, ON, Mar. 22, 2024 – Researchers at McMaster University and Stanford University have invented a new generative artificial intelligence model which can design billions of new antibiotic molecules that are inexpensive and easy to build in the laboratory.
The worldwide spread of drug-resistant bacteria has created an urgent need for new antibiotics, but even modern AI methods are limited ...
An avocado a day may improve overall diet quality, researchers report
2024-03-22
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Eating one avocado per day may improve overall diet quality, according to a team led by researchers in Penn State’s Department of Nutritional Sciences. Poor diet quality is a risk factor for many diseases, including heart disease, and many American adults have poor diet quality and do not meet key dietary recommendations provided by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
This study was led by Kristina Petersen, associate professor of nutritional sciences, and Penny ...
CU researchers describe tools to better understand CaMKII, a protein involved in brain and heart disease
2024-03-22
AURORA, Colo. (March 22, 2024) – The health impacts of a complex protein that plays a major role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease and heart conditions can be lessened by three kinds of drug inhibitors, according to scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
In an overview of the protein and the inhibitors published today in the journal Cell Reports, the CU researchers discussed the best ways to use the interventions.
The protein, CaMKII, is ubiquitous in cells throughout the body but is perhaps best known for its prominent role in the brain and the heart. It is critical in learning and memory but if misregulated can ...
Theoretical physicist Carlo Rovelli to receive 2024 Lewis Thomas Prize
2024-03-22
From photons to atheism to Churchill’s extraterrestrial musings, the stunning breadth of Carlo Rovelli’s work has spurred readers to think deeply about the intersection of science and culture, transforming staggering complexity into widely accessible writing along the way.
For this artful ability to educate and engage, Rovelli will be presented with the 2024 Lewis Thomas Prize for Writing about Science at The Rockefeller University on April 9. Named after its first recipient, noted physician-scientist and essayist Lewis Thomas, the prize was ...