(Press-News.org) Bethesda, MD (March 26, 2024) – Modeling studies and expert consensus published today in the journals Gastroenterology and Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology shed new light on the promise and peril of liquid biopsy (blood tests) for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening that are currently in development.
“Based on their current characteristics, blood tests should not be recommended to replace established colorectal cancer screening tests, since blood tests are neither as effective or cost-effective, and would worsen outcomes,” said David Lieberman, MD, chair, AGA CRC Workshop chair and lead author of an expert commentary on liquid biopsy for CRC screening.
An AGA expert panel employed previously validated decision models to estimate the effects of a new blood-based CRC screening test on an average-risk population aged 45-75, assuming the test met minimal Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) criteria for CRC sensitivity (74%) and specificity (90%). The aim was to define properties of successful CRC screening blood test and compare possible outcomes with the established strategies of annual fecal immunochemical tests (FIT), triennial multitarget stool DNA (MT-sDNA) tests (Cologuard) and every-10-year colonoscopies.
Key conclusions in the expert commentary, published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology:
A blood test for CRC that meets minimal CMS criteria for sensitivity and performed every three years would likely result in better outcomes than no screening.
A blood test for CRC offers a simple process that could encourage more people to participate in screening. Patients who may have declined colonoscopy should understand the need for a colonoscopy if findings are abnormal.
Because blood tests for CRC are predicted to be less effective and more costly than currently established screening programs, they cannot be recommended to replace established effective screening methods.
Although blood tests would improve outcomes in currently unscreened people, substituting blood tests for a currently effective test would worsen patient outcomes and increase cost.
Potential benchmarks that industry might use to assess an effective blood test for CRC going forward would be sensitivity for stage I-III CRC of >90%, with sensitivity for advanced adenomas of > 40-50%.
“Unless we have the expectation of high sensitivity and specificity, blood-based colorectal cancer tests could lead to false positive and false negative results, which are both bad for patient outcomes,” noted John Carethers, MD, AGAF, AGA past president and vice chancellor for health sciences at the University of California San Diego.
An expert panel convened in September 2023 for the AGA CRC Workshop and considered modeling performed by two independent groups, including a team from the Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) Colorectal Cancer consortium and a team from Stanford University. These modeling studies are published today in Gastroenterology:
Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening With a Blood Test That Meets the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Coverage Decision
https://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(24)00174-4/fulltext
DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.012
Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening With Blood-Based Biomarkers (Liquid Biopsy) vs Fecal Tests or Colonoscopy
https://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(24)00293-2/fulltext
DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.03.011
Blood tests detect circulating nucleotides such as cell-free DNA and/or metabolic products associated with CRC and its precursors. Tests are currently in development by Guardant and Freenome.
Panelists:
David Lieberman, Oregon Health and Science University
Aasma Shaukat, NYU Grossman School of Medicine
Folasade P. May, University of California Los Angeles
John M. Carethers, University of California San Diego
Iris Lansdorp-Vogelaar, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center, Rotterdam
Uri Ladabaum, Stanford University School of Medicine
Timothy R. Church, University of Minnesota
Anjelica Davis, Fight Colorectal Cancer
Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, The Ohio State University
John M. Inadomi, University of Utah Health
Pedro Nascimento de Lima, RAND Corporation
Rosita van den Puttelaar, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center, Rotterdam
###
Contact for media: Mara Shapiro, media@gastro.org, 301-329-5709
About the AGA Institute
The American Gastroenterological Association is the trusted voice of the GI community. Founded in 1897, the AGA has grown to more than 16,000 members from around the globe who are involved in all aspects of the science, practice and advancement of gastroenterology. The AGA Institute administers the practice, research and educational programs of the organization. www.gastro.org
AGA is on Instagram.
Like AGA on Facebook.
Follow us on X @AmerGastroAssn
Check out our videos on YouTube.
Join AGA on LinkedIn.
END
New data offer reality check on blood-based colorectal cancer screening
A blood test will be better than nothing, but may lead to more colorectal cancer cases and deaths than established screening tests.
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Virginia Tech study considers ways to increase accessibility for all wildlife enthusiasts
2024-03-26
One in three birders experiences accessibility challenges to participation in birding, according to Virginia Tech researchers Emily Sinkular and Ashley Dayer.
“I like to think of our research as blending together two previously unconnected fields: disability studies and wildlife recreation,” said Sinkular, a Ph.D. student and lead author of the study published March 26 in the journal Human Dimensions and Wildlife. “There’s been quite a lot of research on disability and lots of research on birding, but very few researchers have combined these two topics together.”
The ...
From autism to Alzheimer’s: A large-scale animal study links brain pH changes to wide-ranging cognitive issues
2024-03-26
A global collaborative research group comprising 131 researchers from 105 laboratories across seven countries announces a groundbreaking research paper submitted to eLife. Titled "Large-scale Animal Model Study Uncovers Altered Brain pH and Lactate Levels as a Transdiagnostic Endophenotype of Neuropsychiatric Disorders Involving Cognitive Impairment," the study identifies brain energy metabolism dysfunction leading to altered pH and lactate levels as common hallmarks in numerous animal models of neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders, such as intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depressive disorders, and Alzheimer’s ...
Tiniest ‘starquake’ ever detected – new study
2024-03-26
An orange dwarf star has yielded the tiniest ‘starquakes’ ever recorded, measured by an international team of scientists.
Named Epsilon Indi, the star is the smallest and coolest dwarf star yet observed with solar-like oscillations – “starquakes” like those shown by the Sun. These oscillations provide indirect glimpses of stellar interiors – just as earthquakes tell us about Earth's interior – and so are important sources of information about the makeup of the star.
The measurements ...
Italians’ and Swedes’ gestures vary when they tell stories, which may show cultures think differently about narratives
2024-03-26
When we talk, we often use our hands in addition to words. Gesturing is a phenomenon that has been observed across languages and cultures. Some cultures are typically thought to use more gestures than others.
To find out if the deeply rooted stereotype of Italians gesturing more than other cultures is true, researchers in Sweden have examined the differences in gesture rate and function between Italians and Swedes who were telling a story to a friend.
“We show that Italians do gesture more than Swedes, which was expected,” ...
New treatment target identified for Alzheimer's disease
2024-03-26
Researchers at the University of Leeds and Lancaster University in the UK have identified a new potential target for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease – PDE4B.
Alzheimer's disease is the leading cause of dementia and disability in old age. As the number of people diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease is on the increase, new treatments are urgently needed to improve the quality of life for people living with the disease.
PDE4B is an enzyme inside cells that breaks down a molecule known as cyclic AMP, which regulates a range of cellular processes. Based on an Australian study that identified the ...
Discovery of amino acid unveils how light makes plants open
2024-03-26
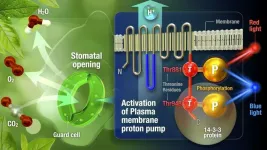
Scientists from Nagoya University have discovered a novel regulatory mechanism that controls the opening of stomata in plants, which is crucial for harnessing solar energy through photosynthesis. The team uncovered the role of phosphorylation at the 881st threonine residue (Thr881) of the plasma membrane proton pump in response to red and blue light in this process. This research opens up possibilities for manipulating plant physiology in specific ways, benefiting agriculture and the environment. The researchers reported their findings in Nature Communications.
“This phosphorylation event, ...
Crackdown on illicit drugs detects rise in ‘designer’ drug substitutes
2024-03-26
As authorities crack down on illicit drugs, University of South Australia experts have issued an alert on the use of the synthetic stimulant pentylone, as new research finds a 75% increase in detections across Australia.
In a new study as part of the Australian Criminal Intelligence Commission’s National Wastewater Drug Monitoring Program, researchers identified 20 different novel psychoactive substances (NPS) in wastewater treatment plants across Australia (between Feb 22-23) with pentylone detected at every collection site. Other NPS, eutylone and phenibut were also commonly detected.
Pentylone, (street name ‘bath salts’), ...
Treatment for blindness-causing retinal detachment using viscous seaweed
2024-03-26
It’s taboo to consume seaweed soup before exams in Korea since it can lead to failing the exam. The belief is rooted in the idea that the slippery nature of seaweed may cause people to slip and falter during the test. The slick surface of seaweeds such as seaweed and kelp is attributed to alginate, a mucilaginous substance. Notably, an intriguing study exploring the use of alginate for the treatment of retinal detachment has been recently published.
A collaborative effort between Professor Hyung Joon Cha from the Department of Chemical Engineering and the School of Convergence Science and Technology and Dr. Geunho Choi from ...
More needs to be done for depressed stroke survivors as incidence climbs
2024-03-26
Researchers say more needs to be done for depressed stroke survivors as new findings show 60% of stroke survivors would experience depression within 18 years, a much higher estimation than previous studies.
This compares to 22% of the general population experiencing depression in the same time frame.
The King’s College London study, published today in The Lancet Regional Health – Europe, also found 90% of cases of depression occurred within five years of surviving a stroke, indicating a key time for healthcare intervention.
The findings, funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research, looks at incidence of mild ...
Research lights up process for turning CO2 into sustainable fuel
2024-03-26
Researchers have successfully transformed CO2 into methanol by shining sunlight on single atoms of copper deposited on a light-activated material, a discovery that paves the way for creating new green fuels.
An international team of researchers from the University of Nottingham's School of Chemistry, University of Birmingham, University of Queensland and University of Ulm have designed a material, made up of copper anchored on nanocrystalline carbon nitride. The copper atoms are nested ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] New data offer reality check on blood-based colorectal cancer screeningA blood test will be better than nothing, but may lead to more colorectal cancer cases and deaths than established screening tests.