(Press-News.org) Consistently exercising 2-3 times a week over the long term is linked to a lower current risk of insomnia as well as the ability to clock up the recommended 6-9 hours of shut eye every night, suggests an international 10-year study published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Regular exercise is associated with better overall health, and several studies have suggested that physical activity promotes better quality sleep and may improve symptoms of chronic insomnia, note the researchers.
But it’s not entirely clear how much gender, age, weight (BMI), overall fitness, general health and exercise type contribute to this association, they add.
To explore this further, the researchers assessed the frequency, duration, and intensity of weekly physical activity and symptoms of insomnia, nightly sleep clocked up, and daytime sleepiness among middle-aged adults from 21 centres in nine European countries.
The 4399 study participants (2085 men; 2254 women) were drawn from the European Community Respiratory Health Survey.
They had answered questions on the frequency and duration of physical activity at baseline (ECRHS II;1998-2002) and on physical activity, insomnia symptoms (Basic Nordic Sleep Questionnaire; scale 1-5), sleep duration and daytime sleepiness (Epworth Sleepiness Scale) 10 years later (ECRHS III; 2011-14).
Participants who reported that they exercised at least two or more times a week, for 1 hour/week or more, were classified as being physically active.
Over the 10 year period, 37% (1601) of participants were persistently inactive; 18% (775) became physically active; 20% (881) became inactive; and 25% (1082) were persistently active.
Participants in Norway were most likely to be persistently active, while participants in Spain, followed by Estonia, were most likely to be persistently inactive.
Persistently active participants were more likely to be men, younger, and to weigh slightly less. They were also less likely to be current smokers and more likely to be currently working.
After adjusting for age, sex, weight (BMI), smoking history, and study centre, those who were persistently active were significantly (42%) less likely to find it difficult to fall asleep, 22% less likely to have any symptom of insomnia, and 40% less likely to report 2 or 3 (37% less likely) insomnia symptoms.
Insomnia symptoms were also independently associated with age, female gender, and weight.
As for total nightly hours of sleep and daytime sleepiness, after adjusting for age, sex, weight, smoking history, and study centre, persistently active participants were most likely to be normal sleepers while the persistently inactive were least likely to be in that category.
The persistently active were significantly (55%) more likely to be normal sleepers and significantly less likely (29%) to be short (6 hours or less), and 52% less likely to be long, sleepers (9 hours or more). And those who became active were 21% more likely to be normal sleepers than those who were persistently inactive.
The researchers acknowledge that they weren’t able to objectively assess changes in physical activity levels between the two time points and that all the elements relied on subjective assessment via questionnaire.
But they nevertheless conclude: “Our results are in line with previous studies that have shown the beneficial effect of [physical activity] on symptoms of insomnia, but the current study additionally shows the importance of consistency in exercising over time, because the association was lost for initially active subjects who became inactive.”
END
Consistently exercising 2-3 times a week over the long term linked to lower current insomnia risk
And ability to clock up recommended 6-9 hours of shut eye every night, 10-year study shows
2024-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Handing out vapes in A&E helps smokers quit
2024-03-27
Peer reviewed – randomised controlled trial - humans
Giving out free e-cigarette starter packs in hospital emergency departments to people who smoke helps more people quit – according to research from the University of East Anglia.
The trial, funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), offered advice, an e-cigarette starter pack and referral to stop smoking services to people attending A&E for any reason, to help them to stop smoking.
Six months later, almost one in four people given the starter packs said they had quit smoking. And those who received ...
Shared digital NHS prescribing record could avoid nearly 1 million annual drug errors
2024-03-27
Implementing a single shared digital prescribing record across the NHS in England could avoid nearly 1 million drug errors every year, stopping up to 16,000 fewer patients from being harmed, and saving up to 22 lives every year, suggests a modelling study, published online in BMJ Quality & Safety.
The figures, which are based on the assumption that such a system could reduce medication errors by at least 10%, and by as much as 50%, could also save £millions for the NHS, say the researchers.
Previously published research suggests that drug errors cost the NHS £98 ...
Stanford Medicine-designed AI tools tackle soft tissue sarcomas, identify new treatment strategies
2024-03-26
Using novel machine learning tools developed at Stanford Medicine, researchers have mapped three distinct cellular configurations that correspond to clinical outcomes for patients with a rare, difficult-to-treat cancer called soft tissue sarcoma.
In particular, the technique identified a cellular neighborhood that correlated with a positive response to immunotherapy, which may help physicians make treatment decisions.
“These cancers are challenging,” said Everett Moding, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of radiation oncology. “Up to half of patients diagnosed with a primary tumor will develop distant metastases, but we don’t have a good way to predict ...
ARPA-H awards Columbia researchers nearly $39M to develop a living knee replacement
2024-03-26
A team of researchers from Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC) and Columbia Engineering has been awarded up to a $38.95 million contract from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) to build a living knee replacement from biomaterials and human stem cells, including a patient’s own cells. ARPA-H is a federal funding agency that funds transformative biomedical and health research breakthroughs, rapidly translating research from the lab to applications in the marketplace.
The Award
The award, part of the ARPA-H’s Novel Innovations for Tissue Regeneration ...
How genes work together to shape how much you smoke
2024-03-26
Take a puff of nicotine for the first time, and your DNA plays an important role, alongside social and environmental factors, in shaping what happens next.
In recent years, scientists have identified thousands of genetic variants believed to influence everything from when people first try smoking to how good that first cigarette feels to how often they light up and how hard it is to quit. Some variants influence how quickly we metabolize nicotine, while others underlie how sensitive we are to it. But little is known about how they interact with each other and with other genetic differences.
A new University of Colorado Boulder study sheds unprecedented ...
University of Oklahoma engineer receives NSF CAREER Award to advance gas sensing technologies
2024-03-26
NORMAN, OKLA. – Binbin Weng, Ph.D., an engineering professor at the University of Oklahoma, has been awarded a National Science Foundation CAREER Award presented to early-career faculty with the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education. The $497,370 grant will fund his project “Enabling New States of Light in Mid-Wave Infrared Photonics for Gas Sensing Applications.”
Weng says there is a growing demand for distributed gas sensing networks capable of continuously monitoring gas threats on a broad scale. However, current technologies face significant challenges in size, power consumption ...
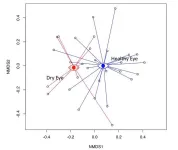
More than meets the eye: Researchers uncover the microbial secrets of dry eye
2024-03-26
Researchers have used advanced sequencing technology to determine how the mix of microbes present in patients with healthy eyes differs from the mix found in patients with dry eye. The new work could lead to improved treatments for various eye problems and for diseases affecting other parts of the body.
Microbial communities in and on our body — collectively referred to as the human microbiota — play an essential role in keeping us healthy. Although many studies have focused on microbial communities in our gut, understanding the microbiota present in other body sites is critical for advancing our knowledge of human health and developing targeted interventions ...
Researchers identify microbes that help plants thwart parasite
2024-03-26
Bacteria that could help one of Africa’s staple crops resist a major pest have been identified by researchers at the University of California, Davis. Their findings, published March 26 in Cell Reports, could improve yields of sorghum, a mainstay of food and drink in West and East African countries.
About 20 percent of Africa’s sorghum crop is lost due to witchweed (Striga hermonthica), a parasitic plant that steals nutrients and water by latching onto the plant’s roots.
In the new study, UC Davis researchers show that soil microbes induce changes in sorghum roots that make the plant more resistant to infection by witchweed. They ...
Late surgical repair for preterm babies born with inguinal hernia shows better results compared to early repair, study finds
2024-03-26
Delaying surgical inguinal hernia repair in preterm infants until after discharge from the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) appears to reduce the likelihood of serious adverse events, according to researchers at UTHealth Houston.
A study led by first and corresponding author Martin L. Blakely, MD, MS, MMHC, professor of surgery and pediatrics with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, analyzed the safety of early versus late surgical repair for preterm infants born with an inguinal hernia. The findings were published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
“The biggest question we wanted ...
Two plant extracts with potential as GLP-1 agonist weight loss pills are identified by AI-based analysis
2024-03-26
*Note - This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Two plant compounds with potential as GLP-1 agonist weight loss pills have been identified in an AI (artificial intelligence)-based study, the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) (Venice 12-15 May), will hear.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists such as semaglutide and tirzepatide are highly effective at helping people lose weight. By mimicking the action of a hormone ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Consistently exercising 2-3 times a week over the long term linked to lower current insomnia riskAnd ability to clock up recommended 6-9 hours of shut eye every night, 10-year study shows