(Press-News.org) Scientists have uncovered a key step in the wound healing process that becomes disabled in diseases like diabetes and ageing, contributing to a global healthcare cost of managing poorly healing wounds exceeding $250 billion a year. Importantly, the research published in Nature reveals a molecule involved in the healing of tissues that – when injected into animal models – leads to a drastic acceleration of wound closure, up to 2.5 times faster, and 1.6 times more muscle regeneration.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Mikaël Martino, from Monash University’s Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute (ARMI) in Melbourne, Australia, said the discovery “could transform regenerative medicine, because it sheds light on the crucial role of sensory neurons in orchestrating the repair and regeneration of tissues, offering promising implications for improving patient outcomes.”
The cost of managing poorly healing wounds costs around $250 billion a year. “In adults with diabetes alone – where poor blood flow can lead to quickly worsening wounds that are often very slow or impossible to heal – the lifetime risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU), the most common diabetes-related wound, is 20 to 35 per cent and this number is rising with increased longevity and medical complexity of people with diabetes,” co-lead author, ARMI’s Dr Yen-Zhen Lu said.
Nociceptive sensory neurons, also called nociceptors, are the nerves in our body that sense pain. These neurons alert us to potentially damaging stimuli in tissues by detecting dangers like tissue damage, inflammation, extremes in temperature, and pressure.
The researchers discovered that – during the healing process – sensory neuron endings grow into injured skin and muscle tissues, communicating with immune cells through a neuropeptide called calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP).
“Remarkably, this neuropeptide acts on immune cells to control them, facilitating tissue healing after injury,” Associate Professor Martino said.
Importantly they found that sensory neurons are crucial to the dissemination of CGRP because they showed that the selective removal of sensory neurons in mice reduce CGRP and significantly impairs skin wound healing and muscle regeneration following injury.
When the scientists administered an engineered version of CGRP to mice with neuropathy similar to that seen in diabetic patients, it led to rapid wound healing and muscle regeneration.
According to Associate Professor Martino, these findings hold significant promise for regenerative medicine, particularly for the treatment of poorly-healing tissues and chronic wounds.
“By harnessing neuro-immune interactions, the team aims to develop innovative therapies that address one of the root causes of impaired tissue healing, offering hope to millions,” he said.
“This study has uncovered significant implications for advancing our understanding of the tissue healing process after acute injury. Harnessing the potential of this neuro-immuno-regenerative axis opens new avenues for effective therapies, whether as standalone treatments or in combination with existing therapeutic approaches. “
END
Discovery has potential to solve the billion-dollar global cost of poorly managed wound healing
Scientists uncover key step in the wound healing process that is disabled in diseases like diabetes and ageing - finding a protein promoting wound healing and muscle regeneration
2024-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newly uncovered history of a key ocean current carries a warning on climate
2024-03-27
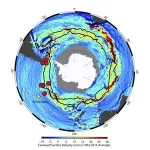
It carries more than 100 times as much water as all the world's rivers combined. It reaches from the ocean's surface to its bottom, and measures as much as 2,000 kilometers across. It connects the Indian, Atlantic and Pacific oceans, and plays a key role in regulating global climate. Continuously swirling around the southernmost continent, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current is by far the world's most powerful and consequential mover of water. In recent decades it has been speeding up, but scientists have been unsure whether ...
Evolution of the most powerful ocean current on Earth
2024-03-27
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current plays an important part in global overturning circulation, the exchange of heat and CO2 between the ocean and atmosphere, and the stability of Antarctica’s ice sheets. An international research team led by the Alfred Wegener Institute and the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory have now used sediments taken from the South Pacific to reconstruct the flow speed in the last 5.3 million years. Their data show that during glacial periods, the current slowed; during interglacials, it accelerated. Consequently, if ...
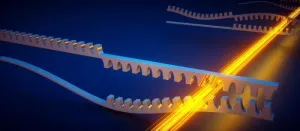
New topological metamaterial amplifies sound waves exponentially
2024-03-27
Researchers at AMOLF, in collaboration with partners from Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, have realized a new type of metamaterial through which sound waves flow in an unprecedented fashion. It provides a novel form of amplification of mechanical vibrations, which has the potential to improve sensor technology and information processing devices. This metamaterial is the first instance of a so-called ‘bosonic Kitaev chain’, which gets its special properties from its nature as a topological material. It was realized by making nanomechanical resonators interact with laser light through radiation pressure forces. The discovery, which is published on March ...
Making long-term memories requires nerve-cell damage
2024-03-27
March 27, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Just as you can’t make an omelet without breaking eggs, scientists at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found that you can’t make long-term memories without DNA damage and brain inflammation. Their surprising findings were published online today in the journal Nature.
“Inflammation of brain neurons is usually considered to be a bad thing, since it can lead to neurological problems such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease,” said study leader Jelena Radulovic, M.D., Ph.D., professor in the Dominick P. Purpura Department of Neuroscience, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, and the Sylvia ...
Anastasopoulos studying machine translation for Austronesian languages
2024-03-27
Anastasopoulos Studying Machine Translation For Austronesian Languages
Antonios Anastasopoulos, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding for: "Machine Translation for Austronesian Languages."
He is helping to develop a solution that can automatically translate languages of the southeast Asia and Pacific regions, with a particular focus on languages of lndonesia and the Philippines.
Anastasopoulos received $63,680 from Barron Associates, Inc., on a subaward from the U.S. Department of the Army for this project. Funding began ...
Complete sugarcane genome sequence opens up new era in breeding
2024-03-27
The first comprehensive reference genome for ‘R570’, a widely cultivated modern sugarcane hybrid, has been completed in a landmark advancement for agricultural biotechnology.
Sugarcane contributes $2.2 billion to the Australian economy and accounts for 80 per cent of global sugar supply. The mapping of its genetic blueprint opens opportunities for new tools to enhance breeding programs around the world for this valuable bioenergy and food crop.
It is one of the last major crops to be fully sequenced, due to the fact its genome is almost three times the size of humans’ and far more ...
Super permeable wearable electronics developed for stable, long-term biosignal monitoring by scientists at City University of Hong Kong
2024-03-27
Super wearable electronics that are lightweight, stretchable and increase sweat permeability by 400-fold have been developed by scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK), enabling reliable long-term monitoring of biosignals for biomedical devices.
Led by Professor Yu Xinge in CityUHK’s Department of Biomedical Engineering (BME), the research team has recently developed a universal method to creating these super wearable electronics that allow gas and sweat permeability, solving the most critical issue facing wearable biomedical devices.
Wearable ...
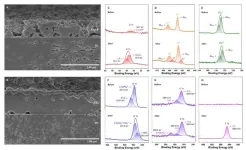
Improving the safety of HED LIBs by co-coating separators with ceramics and solid-state electrolytes
2024-03-27
They published their work on Mar. 20, 2024, in Energy Material Advances.
"TR poses a critical safety concern for HED LIBs," said paper author Jiantao Wang, the general manager of National Power Battery Innovation Center, the general manager of China Automotive Battery Research Institute Co., Ltd, professor in General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals. "It hinders HED LIBs wide application in electric vehicles."
Wang explained that TR can occur during various ...
A decade of aphantasia research: what we’ve learned about people who can’t visualize
2024-03-27
People who can’t visualise an image in their mind’s eye are less likely to remember the details of important past personal events or to recognise faces, according to a review of nearly ten years of research.
People who cannot bring to mind visual imagery are also less likely to experience imagery of other kinds, like imagining music, according to new research by the academic who first discovered the phenomenon.
Professor Adam Zeman, of the University of Exeter, first coined the term aphantasia in 2015, to describe those who can’t visualise. ...
Implantable batteries can run on the body’s own oxygen
2024-03-27
From pacemakers to neurostimulators, implantable medical devices rely on batteries to keep the heart on beat and dampen pain. But batteries eventually run low and require invasive surgeries to replace. To address these challenges, researchers in China devised an implantable battery that runs on oxygen in the body. The study, published March 27 in the journal Chem, shows in rats that the proof-of-concept design can deliver stable power and is compatible with the biological system.
“When you think about it, oxygen is the source of our life,” says corresponding author Xizheng Liu, who specializes in energy materials and devices at Tianjin University of Technology. “If ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Discovery has potential to solve the billion-dollar global cost of poorly managed wound healingScientists uncover key step in the wound healing process that is disabled in diseases like diabetes and ageing - finding a protein promoting wound healing and muscle regeneration