(Press-News.org) BALTIMORE, April 1, 2024— Researchers at Kennedy Krieger Institute are sharing their expertise on autism spectrum disorder in a medical journal reaching thousands of pediatric professionals worldwide. The journal, Pediatric Clinics, provides the latest clinical information on health and related issues for children and adolescents.
The newly released volume is titled "Pediatric Management of Autism." This issue features five original articles written by 10 faculty members from the Institute. Each contribution investigates crucial aspects of caring for children with autism, offering actionable insights.
Dr. Paul Lipkin, a neurodevelopmental pediatrician and professor of pediatrics in the Center for Development and Learning at Kennedy Krieger Institute, is one of the guest editors of this issue. He is thrilled to play a role in educating clinicians worldwide about the latest and much-needed information on the care needs of children with autism.
“Up to now, limited information has been available to pediatric clinicians and researchers for the longer-term care for autism spectrum disorder throughout childhood,” Dr. Lipkin said. “This addresses a significant gap in resources for those providing critical care to children and youth with autism and pediatricians globally.”
The articles Kennedy Krieger researcher contributed to are the following:
Profound Autism: An Imperative Diagnosis
Autism Spectrum Disorder at Home and in School
Psychopharmacology Management in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Mental Health Crises in Autistic Children: A Framework for Prevention and Intervention in Primary Care
Mortality and Autism: Suicide and Elopement
Each article contributed by Kennedy Krieger faculty provides in-depth reviews on autism spectrum disorder, offering actionable insights. Dr. Lipkin says while many pediatricians now have adopted screening and early identification of autism spectrum disorder into their practices, Kennedy Krieger has been leading the charge for ongoing care of children beyond screening.
“Our care for patients at Kennedy Krieger has always been interdisciplinary and multifaceted,” Dr. Lipkin said. “When a child arrives to our Center for Autism Services, Science and Innovation (CASSI™) or one of our other programs that service children with autism, they receive highly tailored treatment from a team of neurologists, pediatricians, psychiatrists, and more.”
One of the contributors to the volume includes Dr. Mary L. O'Connor Leppert, a neurodevelopmental pediatrician at Kennedy Krieger Institute. Much of her research in this journal involves the evaluation of teaching strategies and early identification of autism spectrum disorder.
“School can be a challenging environment due to factors like academic, communication and social demands, new rules, social expectations, and more,” Dr. Leppert said. “This then translates to behaviors at home. Parents and educators overall need support in better curriculum development as well as training on identifying autism spectrum disorder in early childhood.”
Looking ahead, Dr. Lipkin and Dr. Leppert are continuing their work by teaching physicians-in-training and future medical specialists how to evaluate and treat complex-care patients. They say the journal will be a roadmap for the path ahead.
“We anticipate pediatric clinicians using the journal as a reference tool for the next five to 10 years,” Dr. Leppert said. “It’s exciting knowing our institute is really championing innovation and educating the pediatric community about caring for children with autism.”
About Kennedy Krieger Institute
Kennedy Krieger Institute, an internationally known, non-profit organization located in the greater Baltimore/Washington, D.C. region, transforms the lives of more than 27,000 individuals a year through inpatient and outpatient medical, behavioral health and wellness therapies, home and community services, school-based programs, training and education for professionals and advocacy. Kennedy Krieger provides a wide range of services for children, adolescents and adults with diseases, disorders or injuries that impact the nervous system, ranging from mild to severe. The Institute is home to a team of investigators who contribute to the understanding of how disorders develop, while at the same time pioneer new interventions and methods of early diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Visit KennedyKrieger.org for more information about Kennedy Krieger.
###
END
PULLMAN, Wash. – A broader past could mean a brighter future for Canada lynx in the U.S., according to recent research.
The study, published in the journal Biological Conservation, indicates that lynx might do well in the future in parts of Utah, central Idaho and the Yellowstone National Park region, even considering climate change and the lack of lynx in those areas now.
Using a model validated by historic records, researchers first found that in 1900, Canada lynx had more suitable habitat in the U.S. than the few northern corners of the country where they are found currently. The study showed ...
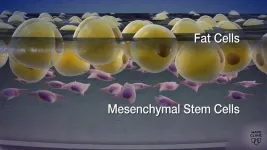
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A Mayo Clinic study shows stem cells derived from patients' own fat are safe and may improve sensation and movement after traumatic spinal cord injuries. The findings from the phase 1 clinical trial appear in Nature Communications. The results of this early research offer insights on the potential of cell therapy for people living with spinal cord injuries and paralysis for whom options to improve function are extremely limited.
In the study of 10 adults, the research team noted seven participants demonstrated ...
New analysis based on simple equations has reduced uncertainty about how clouds will affect future climate change.
Clouds have two main effects on global temperature – cooling the planet by reflecting sunlight, and warming it by acting as insulation for Earth’s radiation.
The impact of clouds is the largest area of uncertainty in global warming predictions.
In the new study, researchers from the University of Exeter and the Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique in Paris created a model that predicts how ...
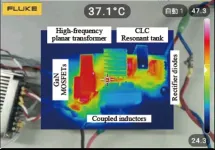
A new electrical power converter design achieves a much higher efficiency at lower cost and maintenance than before. The direct current voltage boost converter developed by Kobe University is poised to be a significant contribution to the further development of electric and electronic components across power generation, health care, mobility and information technology.
Devices that harvest energy from sunlight or vibrations, or power medical devices or hydrogen-fueled cars have one key component in common. This so-called “boost converter” converts low-voltage direct current input into high-voltage direct current output. Because it is such a ubiquitous ...
Study suggests high blood pressure may originate early in life and that preventing overweight and obesity during the developmental years could help reduce the substantial disease burden associated with high blood pressure in later life.
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Children and teenagers living with overweight or obesity are more likely to have high blood pressure as adults (aged 50-64 years), suggesting the processes behind the condition could begin as early as childhood, suggests new research being ...
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
A population-wide observational study to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) shows an association between tuberculosis (TB) and cancer, with those with current or previous TB more likely ...
Previous smallpox vaccination contributes significantly to higher neutralising antibodies following first MVA-BN dose
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 ...
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) shows that the antibodies produced by Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara - Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) vaccination against mpox wane significantly within a year of receiving the vaccination – but in people with pre-existing immunity due to childhood smallpox vaccination in childhood, antibody levels remain high in almost all cases. The study is presented by PhD student Dr. Marc Shamier, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Netherlands, from a research team led by Dr Rory de Vries.
During the 2022-2023 ...
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) details the case of a man who had received two doses of the monkey pox vaccine in Autumn, 2022 yet experienced a ‘breakthrough’ mpox infection in January 2024. The authors believe breakthrough should be considered in fully vaccinated individuals engaging in high-risk behaviors. They also call for further research on the need for booster ...
Researchers from Lund University in Sweden have identified distinct molecular signatures associated with the clinical signs of sepsis that could provide more accurate diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis, as well as help to target specific therapies at patients who would benefit most, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April).
“A simple blood test when combined with a personalised risk model has the potential to save lives by providing more accurate sepsis diagnosis and determining who may go on to develop more severe clinical ...