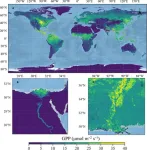
In the field of environmental and climate science, researchers have developed the Comprehensive Mechanistic Light Response (CMLR) gross primary production (GPP) dataset. Derived from the TROPOMI satellite's solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) observations, this global dataset offers unprecedented insights into Earth's GPP, the process through which plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into essential resources.
Gross Primary Production (GPP), the process through which plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into glucose and oxygen, is the Earth's largest carbon flux. Accurate quantification of GPP is crucial for understanding carbon budgets and their implications on climate change and land management policies. However, traditional methods for estimating global GPP are challenged by the complexity of integrating biophysical and biochemical processes at various scales. This challenge has led to the development of the Comprehensive Mechanistic Light Response (CMLR) GPP dataset, and the details are in the article (DOI: 10.34133/remotesensing.0127) published in the Journal of Remote Sensing on 13 Feb 2024.
This dataset, for the first time, harnesses solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF), a direct signal emitted by plants during photosynthesis, offering a more accurate and direct measurement of plant productivity on a global scale. The researchers employed a sophisticated light response model adjusted for the canopy scale to transform TROPOMI's SIF observations into a global GPP dataset. This method represents a substantial leap from previous models by integrating direct physiological signals from plants, thus reducing uncertainties and enhancing the dataset's reliability across diverse environmental conditions and vegetation types. Through rigorous validation against tower-based GPP measurements, the CMLR GPP dataset demonstrated strong correlation and consistency, proving its efficacy in accurately capturing the spatial and temporal patterns of global photosynthesis.
Liangyun Liu, a senior researcher involved in the study, emphasized the significance of this advancement: "The CMLR GPP dataset not only enhances our understanding of global photosynthesis but also serves as a crucial tool for monitoring the Earth's carbon cycle. This dataset is a testament to the power of combining satellite technology with ecological research to address pressing environmental challenges."
The creation of the CMLR GPP dataset marks a pivotal moment in environmental research, offering unprecedented insights into the Earth's carbon cycle, informing climate change models, and aiding policy decisions on land management and climate mitigation.
###
References
DOI
10.34133/remotesensing.0127
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.34133/remotesensing.0127
Funding information
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 41825002 and 42071310). This work has been supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) under Germany’s Excellence Strategy - EXC 2070 - 390732324.
About Journal of Remote Sensing
The Journal of Remote Sensing, an online-only Open Access journal published in association with AIR-CAS, promotes the theory, science, and technology of remote sensing, as well as interdisciplinary research within earth and information science.
END
New satellite dataset sheds light on Earth's plant growth
2024-04-01
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Machine learning provides a new picture of the great gray owl
2024-04-01
The great gray owl has long been thought of as a sentinel of the Alaska wilderness, keeping watch over snow-laden forests as far north as the Brooks Range, well away from human populations.
In a study published last week with Nature Scientific Reports, a team of University of Alaska Fairbanks researchers upends the notion that the iconic bird — known as the phantom of the North — lives far from cities, towns and other markers of human density.
“We like to think of our wildlife, especially in Alaska, as existing in pristine wilderness untouched by humans,” said Falk Huettmann, professor ...
Pilot study shows ketogenic diet improves severe mental illness
2024-04-01
For people living with serious mental illness like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, standard treatment with antipsychotic medications can be a double-edged sword. While these drugs help regulate brain chemistry, they often cause metabolic side effects such as insulin resistance and obesity, which are distressing enough that many patients stop taking the medications.
Now, a pilot study led by Stanford Medicine researchers has found that a ketogenic diet not only restores metabolic health in these patients as they continue their medications, but it further improves their psychiatric conditions. The results, published March 27 in Psychiatry Research, suggest that a dietary intervention ...
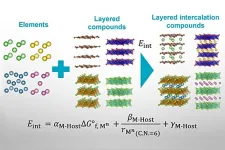
Physics-based predictive tool will speed up battery and superconductor research
2024-04-01
Tokyo, Japan – From lithium-ion batteries to next-generation superconductors, the functionality of many modern, advanced technologies depends on the physical property known as intercalation. Unfortunately, it's difficult to identify in advance which of the many possible intercalated materials are stable, which necessitates a lot of trial-and-error lab work in product development.
Now, in a study recently published in ACS Physical Chemistry Au, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, ...
New advance against a form of heart failure prevalent in men
2024-04-01
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a gene on the Y chromosome that contributes to the greater incidence of heart failure in men.
Y chromosome loss in men occurs progressively throughout life and can be detected in approximately 40% of 70-year-old men. UVA’s Kenneth Walsh, PhD, discovered in 2022 that this loss can contribute to heart muscle scarring and lead to deadly heart failure. (That finding was the first to directly link Y chromosome loss to a specific harm to men’s health; Y chromosome loss is increasingly thought ...
Canton wins Wayne Bardin International Travel Award
2024-04-01
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society selected Ana Canton, M.D., Ph.D., as the recipient of its 2024 C. Wayne Bardin, MD, International Travel Award for her outstanding ENDO abstract and her research contributions to the care of patients with pediatric endocrine disorders.
The C. Wayne Bardin, MD, International Travel Award was created in honor of Past President Wayne Bardin, who made remarkable research contributions to both reproductive physiology and contraception throughout his long career. As the winner, ...
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center experts to present leading-edge research at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2024
2024-04-01
Physicians and scientists from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) will join oncology experts and members of the global cancer research community to present the latest advances in cancer discovery during the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting on April 5-10 in San Diego, California.
MSK experts will present significant research and will be available to comment on topics including cancer metastasis, immunology, molecular biology and genetics, and early drug development.
Vinod Balachandran, MD, will present updates on personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines in pancreatic cancer ...
Kennedy Krieger publishes major national research and guidance on pediatric autism
2024-04-01
BALTIMORE, April 1, 2024— Researchers at Kennedy Krieger Institute are sharing their expertise on autism spectrum disorder in a medical journal reaching thousands of pediatric professionals worldwide. The journal, Pediatric Clinics, provides the latest clinical information on health and related issues for children and adolescents.
The newly released volume is titled "Pediatric Management of Autism." This issue features five original articles written by 10 faculty members from the Institute. Each contribution investigates crucial aspects of caring for children with autism, offering actionable insights.
Dr. Paul ...
Canada lynx historic range in US likely wider than previously thought
2024-04-01
PULLMAN, Wash. – A broader past could mean a brighter future for Canada lynx in the U.S., according to recent research.
The study, published in the journal Biological Conservation, indicates that lynx might do well in the future in parts of Utah, central Idaho and the Yellowstone National Park region, even considering climate change and the lack of lynx in those areas now.
Using a model validated by historic records, researchers first found that in 1900, Canada lynx had more suitable habitat in the U.S. than the few northern corners of the country where they are found currently. The study showed ...
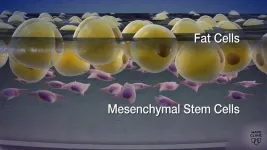
Study documents safety, improvements from stem cell therapy after spinal cord injury
2024-04-01
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A Mayo Clinic study shows stem cells derived from patients' own fat are safe and may improve sensation and movement after traumatic spinal cord injuries. The findings from the phase 1 clinical trial appear in Nature Communications. The results of this early research offer insights on the potential of cell therapy for people living with spinal cord injuries and paralysis for whom options to improve function are extremely limited.
In the study of 10 adults, the research team noted seven participants demonstrated ...
Simple equations clarify cloud climate conundrum
2024-04-01
New analysis based on simple equations has reduced uncertainty about how clouds will affect future climate change.
Clouds have two main effects on global temperature – cooling the planet by reflecting sunlight, and warming it by acting as insulation for Earth’s radiation.
The impact of clouds is the largest area of uncertainty in global warming predictions.
In the new study, researchers from the University of Exeter and the Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique in Paris created a model that predicts how ...