(Press-News.org) People who use e-cigarettes are significantly more likely to develop heart failure compared with those who have never used them, according to one of the largest prospective studies to date investigating possible links between vaping and heart failure. The findings are being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session.
Heart failure is a condition affecting more than 6 million U.S. adults in which the heart becomes too stiff or too weak to pump blood as effectively as it should. It can often lead to debilitating symptoms and frequent hospitalizations as people age. Electronic nicotine products, which include e-cigarettes, vape pens, hookah pens, personal vaporizers and mods, e-cigars, e-pipes and e-hookahs, deliver nicotine in aerosol form without combustion. Since they were first introduced in the U.S. in the late 2000s, electronic nicotine products have often been portrayed as a safer alternative to smoking, but a growing body of research has led to increased concern about potential negative health effects.
“More and more studies are linking e-cigarettes to harmful effects and finding that it might not be as safe as previously thought,” said Yakubu Bene-Alhasan, MD, a resident physician at MedStar Health in Baltimore and the study’s lead author. “The difference we saw was substantial. It’s worth considering the consequences to your health, especially with regard to heart health.”
For the study, researchers used data from surveys and electronic health records in All of Us, a large national study of U.S. adults run by the National Institutes of Health, to analyze associations between e-cigarette use and new diagnoses of heart failure in 175,667 study participants (an average age of 52 years and 60.5% female). Of this sample, 3,242 participants developed heart failure within a median follow-up time of 45 months.
The results showed that people who used e-cigarettes at any point were 19% more likely to develop heart failure compared with people who had never used e-cigarettes. In calculating this difference, researchers accounted for a variety of demographic and socioeconomic factors, other heart disease risk factors and participants’ past and current use of other substances, including alcohol and tobacco products. The researchers also found no evidence that participants’ age, sex or smoking status modified the relationship between e-cigarettes and heart failure.
Breaking the data down by type of heart failure, the increased risk associated with e-cigarette use was statistically significant for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)—in which the heart muscle becomes stiff and does not properly fill with blood between contractions. However, this association was not significant for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)—in which the heart muscle becomes weak and the left ventricle does not squeeze as hard as it should during contractions. Rates of HFpEF have risen in recent decades, which has led to an increased focus on determining risk factors and improving treatment options for this type of heart failure.
The findings align with previous studies conducted in animals, which signaled e-cigarette use can affect the heart in ways that are relevant to the heart changes involved in heart failure. Other studies in humans have also shown links between e-cigarette use and some risk factors associated with developing heart failure. However, previous studies attempting to assess the direct connection between e-cigarette use and heart failure have been inconclusive, which Bene-Alhasan said is due to the inherent limitations of the cross-sectional study designs, smaller sample sizes and the smaller number of heart failure events seen in previous research.
Researchers said the new study findings point to a need for additional investigations of the potential impacts of vaping on heart health, especially considering the prevalence of e-cigarette use among younger people. Surveys indicate that about 5% to 10% of U.S. teens and adults use e-cigarettes. In 2018, the U.S. Surgeon General called youth e-cigarette use an epidemic and warned about the health risks associated with nicotine addiction.
“I think this research is long overdue, especially considering how much e-cigarettes have gained traction,” Bene-Alhasan said. “We don’t want to wait too long to find out eventually that it might be harmful, and by that time a lot of harm might already have been done. With more research, we will get to uncover a lot more about the potential health consequences and improve the information out to the public.”
Bene-Alhasan also said e-cigarettes are not recommended as a tool to quit smoking, since many people may continue vaping long after they quit smoking. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a combination of counseling and medications as the best strategy for quitting smoking.
Researchers said that the study’s prospective observational design allows them to infer, but not conclusively determine, a causal relationship between e-cigarette use and heart failure. However, with its large sample size and detailed data on substance use and health information, Bene-Alhasan said the study is one of the most comprehensive studies to assess this relationship to date.
For more information about the health effects of e-cigarettes, visit CardioSmart.org/StopSmoking.
Bene-Alhasan will present the study, “Electronic Nicotine Product Use Is Associated with Incident Heart Failure - The All of Us Research Program,” on Sunday, April 7, 2024, at 3:15 p.m. ET / 19:15 UTC in Hall B4-5.
ACC.24 will take place April 6-8, 2024, in Atlanta, bringing together cardiologists and cardiovascular specialists from around the world to share the newest discoveries in treatment and prevention. Follow @ACCinTouch, @ACCMediaCenter and #ACC24 for the latest news from the meeting.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at ACC.org.
###
END
Is the view from your doorstep mostly trees and sky or buildings and grass? The answer could influence your cardiovascular health, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session. Using an analysis of Google Street View images powered by machine learning, researchers found people living in surroundings rich in sidewalks, trees and clear sky saw a significantly lower risk of major adverse cardiac events.
“A lot of research has shown that environmental factors strongly affect our health. If we can find a way to stratify this risk and provide interventions before cardiovascular events happen, then ...
Chestnut Hill, Mass (4/2/2024) – Dual topological phases have been discovered in an intrinsic monolayer crystal, a finding that reveals new and unique rule-bending properties in a quantum material, an international team of scientists led by Boston College physicists reported recently in the online version of the journal Nature.
The discovery of a dual topological insulator introduces a new method for creating topological flat minibands through electron interactions, which offer a promising platform for exploring exotic quantum phases and electromagnetism, ...
Brussels, Belgium, and San Francisco, United States - The Public Library of Science (PLOS) and the European Council of Doctoral Candidates and Junior Researchers (“Eurodoc”), today announced a strategic partnership between the organizations to increase awareness of Open Science, its principles, and its implementation into research practices.
“In addition to supporting researchers, we also strive to support the implementation of Open Science principles and increase the adoption of ...
Investments in mitigating climate change in many cases benefit future generations more than those alive today. However, initial costs must be borne by those living now, so many climate mitigation policies rely on some level of intergenerational altruism for support. To investigate the strength and shape of intergenerational altruism, Gustav Agneman and colleagues asked Swedish study participants to engage in an experimental task in which they allocated fictional resources across generations, after being told how many descendants they might be expected to have in the next 250 years. On average, participants allocated most of the resources to the present generation, and fewer and ...
The pursuit of carbon neutrality drives the exploration of clean energy sources, with hydrogen fuel cells emerging as a promising avenue. In these cells, hydrogen undergoes an electrochemical reaction with oxygen to produce electricity and water. Also, the reverse of this process, called electrolysis, can be used to split the abundantly available water to produce hydrogen and oxygen. These two technologies can work in tandem to provide a clean and renewable source of energy. A pivotal element in these two technologies is the platinum (Pt) electrode.
Hydrogen fuel cells consist of two electrodes: an anode and a cathode, with an ...
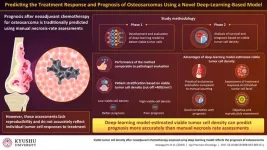
Fukuoka, Japan - Researchers at Kyushu University have developed and validated a machine-learning model that can accurately evaluate the density of surviving tumor cells after treatment in pathological images of osteosarcoma—the most prevalent malignant bone tumor. The model can assess how individual tumor cells respond to treatment and can predict overall patient prognosis more reliably than conventional methods.
Surgery and chemotherapy have significantly improved the outcomes of patients with localized osteosarcoma. However, patients with advanced metastatic disease (the stage where cancerous cells have spread to distant tissues) have a low survival rate. ...
All-solid-state lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries with solid electrolytes are non-flammable and have higher energy density and transference numbers than those with liquid electrolytes. They are expected to take a share of the market for conventional liquid electrolyte Li-ion batteries, such as electric vehicles. However, despite these advantages, solid electrolytes have lower Li-ion conductivity and pose challenges in achieving adequate electrode-solid electrolyte contact. While sulfide-based solid electrolytes are conductive, they react with moisture to form toxic hydrogen disulfide. Therefore, there's ...
A new study found that during the pandemic pediatric emergency departments (EDs) saw more children and adolescents who needed a psychiatric admission, as well as an increase in severe conditions, such as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and substance use disorders. The higher demand for a psychiatric inpatient bed often exceeded availability, resulting in over 12-hour stays in the ED awaiting admission for nearly 20 percent of children with mental health emergencies in 2022, up from 7 percent before the pandemic. Findings were published in Academic Emergency Medicine.
“Our data shows that pediatric emergency departments saw more severe mental health presentations during the pandemic, ...
We’ve all been there: staring at a math test with a problem that seems impossible to solve. What if finding the solution to a problem took almost a century? For mathematicians who dabble in Ramsey theory, this is very much the case. In fact, little progress had been made in solving Ramsey problems since the 1930s.
Now, University of California San Diego researchers Jacques Verstraete and Sam Mattheus have found the answer to r(4,t), a longstanding Ramsey problem that has perplexed ...
Chickens are one of the most economically important animals in the world today. However, the story of their origins and dispersal across the ancient world is still poorly understood. In fact, new archaeological techniques have recently led to the recognition that many finds of bones previously thought to represent early chickens in fact belonged to wild birds. Now, in a new publication, an international team of archaeologists, historians, and biomolecular scientists present the earliest clear evidence for the raising of chickens for egg production, and argue that the loss of seasonal egg laying was the main driver for the dispersal of domestic chickens across Eurasia and northeast Africa.
Using ...