(Press-News.org)
A paper proposing a hybrid data driven framework considering feature extraction for battery state of health estimation and remaining useful life prediction was published in the journal Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation on 29 March 2024.
VMD is used for completely non-recursive modal variation to deal with signals. The optimal solution of the variational problem is obtained finally by effective decomposition component of the given signal. By iteration, the VMD algorithm can decompose the signals into some intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) and a relevant residual value containing multiple different frequency scales.
SVM algorithm based on statistical learning theory was proposed by Vapnik, mainly used for pattern recognition and classification. Based on the VC dimension theory, SVM obtains the global optimal solution. To reduce the parameter dimension, the optimization process is simplified by introducing the kernel function. When used as a regression tool, SVM implements a variant of the algorithm called SVR.
The SSA algorithm is a new type of swarm intelligence optimization algorithm, and its basic structure is similar to ABC algorithm except the search operator. In this paper, it is used to optimize penalty constant C and Kernel function parameter σ to realize the accurate prediction of MKSVM model.
Elite chaotic opposition-learning method is adopted to generate an initial population to enhance its quality and diversity. By selecting elite individuals on a larger scale, the algorithm can improve the local escape ability and convergence performance, then lead to a more accurate solution. In this paper, the chaotic skew tent map is chosen to generate the initial population to enhance the stability of the initial individuals due to its characteristic of randomness and ergodicity.
Since the update weight is large and not changed much during iteration, it may miss the global optimum. Adaptive weights are introduced to improve the performance of SSA algorithm to find the global optimum.
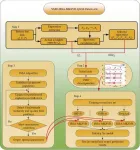
In this study, researchers present a hybrid framework considering feature extraction for a better performance of battery SOH estimation and RUL prediction. The hybrid framework combining VMD, improved sparrow search algorithm (ISSA) and multi-kernel support vector regression (MKSVR) model. The contributions are summarized. First, eight features are obtained to fed into the life prediction model by feature extraction. Secondly, VMD method is applied to decompose the original data to make the capacity data more stable. Then, elite chaotic opposition-learning strategy and adaptive weights are adopted to optimize the traditional sparrow search algorithm (SSA) to obtain more accurate parameters of the prediction model. Finally, MKSVR is used to solve the low prediction accuracy problem caused by large sample data and uneven distribution of high-dimensional feature space.
Dataset from National Aeronautics and Space Administration are applied for experimental verification. The RUL predictions with different start points are conducted to verify the stability of the VMD-ISSA-MKSVR framework. By comparison with IPSO-SVR, ISSA-SVR, BL-ELM and VMD-ISSA-SVR, it can be verified that the errors of SOH estimation and RUL prediction obtained by the VMD-ISSA-MKSVR framework are the smallest. It has relatively high prediction accuracy and stability.
###
Reference
Authors: Yuan Chen a, Wenxian Duan b, Yigang He c, Shunli Wang d, Carlos Fernandez e
Title of original paper: A Hybrid Data Driven Framework Considering Feature Extraction for Battery State of Health Estimation and Remaining Useful Life Prediction
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geits.2024.100160
Affiliations:
aSchool of Artificial Intelligence, Anhui University, Hefei 230009, China
bState Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
cSchool of Electrical Engineering and Automation, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, China
dSchool of Information Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China
eSchool of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen, AB10-7GJ, UK
END
Complimentary press passes are now available for NUTRITION 2024, the annual flagship meeting of the American Society for Nutrition. Join us June 29–July 2 in Chicago for the latest developments in nutrition research, practice and policy.
As the pre-eminent meeting in nutrition science, NUTRITION attracts thousands of scientists, practitioners, policymakers, advocacy leaders and industry professionals each year. Reporters are invited to attend in person to connect with the field’s leaders and learn about exciting scientific ...
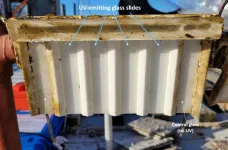
AMHERST, Mass. – A group of researchers led by University of Massachusetts Amherst engineers have created ultraviolet (UV) rays-emitting glass that can reduce 98% of biofilm from growing on surfaces in underwater environments, as reported in the journal Biofilm.
Biofilm is a slimy layer of various types of microorganisms that grows on wet surfaces. “If you look down your sink and touch the inner side of it—that slimy substance is biofilm,” describes Mariana Lanzarini-Lopes, ...
A woman’s cardiovascular risk can rise sharply after she goes through menopause, quickly catching up to men of a similar age and health profile, according to new findings presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session. Researchers said the study underscores the importance of recognizing and addressing early warning signs of heart disease risk in women as they lose the protective effects of estrogen after menopause.
“This is a unique study cohort of only post-menopausal ...
Individuals with heart disease stand to gain the most from a low-sodium diet but, on average, consume over twice the recommended daily sodium intake, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session.
Sodium is an essential nutrient, but consuming too much can raise blood pressure, which damages blood vessels and forces the heart to work harder. Excess sodium can also cause the body to retain fluid, exacerbating conditions like heart failure. The current U.S. Dietary Guidelines put out by the U.S. Department of Agriculture ...
People who use e-cigarettes are significantly more likely to develop heart failure compared with those who have never used them, according to one of the largest prospective studies to date investigating possible links between vaping and heart failure. The findings are being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session.
Heart failure is a condition affecting more than 6 million U.S. adults in which the heart becomes too stiff or too weak to pump blood as effectively as it should. It can often lead to debilitating symptoms and frequent hospitalizations as people age. Electronic nicotine products, which include ...
Is the view from your doorstep mostly trees and sky or buildings and grass? The answer could influence your cardiovascular health, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session. Using an analysis of Google Street View images powered by machine learning, researchers found people living in surroundings rich in sidewalks, trees and clear sky saw a significantly lower risk of major adverse cardiac events.
“A lot of research has shown that environmental factors strongly affect our health. If we can find a way to stratify this risk and provide interventions before cardiovascular events happen, then ...
Chestnut Hill, Mass (4/2/2024) – Dual topological phases have been discovered in an intrinsic monolayer crystal, a finding that reveals new and unique rule-bending properties in a quantum material, an international team of scientists led by Boston College physicists reported recently in the online version of the journal Nature.
The discovery of a dual topological insulator introduces a new method for creating topological flat minibands through electron interactions, which offer a promising platform for exploring exotic quantum phases and electromagnetism, ...
Brussels, Belgium, and San Francisco, United States - The Public Library of Science (PLOS) and the European Council of Doctoral Candidates and Junior Researchers (“Eurodoc”), today announced a strategic partnership between the organizations to increase awareness of Open Science, its principles, and its implementation into research practices.
“In addition to supporting researchers, we also strive to support the implementation of Open Science principles and increase the adoption of ...
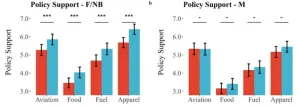
Investments in mitigating climate change in many cases benefit future generations more than those alive today. However, initial costs must be borne by those living now, so many climate mitigation policies rely on some level of intergenerational altruism for support. To investigate the strength and shape of intergenerational altruism, Gustav Agneman and colleagues asked Swedish study participants to engage in an experimental task in which they allocated fictional resources across generations, after being told how many descendants they might be expected to have in the next 250 years. On average, participants allocated most of the resources to the present generation, and fewer and ...
The pursuit of carbon neutrality drives the exploration of clean energy sources, with hydrogen fuel cells emerging as a promising avenue. In these cells, hydrogen undergoes an electrochemical reaction with oxygen to produce electricity and water. Also, the reverse of this process, called electrolysis, can be used to split the abundantly available water to produce hydrogen and oxygen. These two technologies can work in tandem to provide a clean and renewable source of energy. A pivotal element in these two technologies is the platinum (Pt) electrode.
Hydrogen fuel cells consist of two electrodes: an anode and a cathode, with an ...