(Press-News.org) ROCHESTER, Minn. — A new multicenter, international study suggests that people who have early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and high levels of immune cells within their tumors may have a lower risk of recurrence and better survival rates even when not treated with chemotherapy. The study was published in the Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA).
TNBC is a breast cancer subtype that does not respond to drugs that target the estrogen receptor or the HER2 protein. It grows rapidly, is more likely to spread beyond the breast before diagnosis and is more likely to recur than other breast cancers. TNBC represents about 15% of all breast cancers and is more common in younger people and in women of African American, Hispanic and Indian descent. Immune cells, also known as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, or TILs, are naturally existing immune system cells that can move from the bloodstream into a tumor and can recognize and destroy cancer cells.
"This is an important finding because it highlights that the abundance of TILs in breast tissue is a prognostic biomarker in people with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer, even when chemotherapy is not administered," says Roberto Leon-Ferre, M.D., a breast medical oncologist at Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center and first author of the study. "The study's findings may inspire future clinical trials to explore whether patients with a favorable prognosis (high TILs) can avoid intensive chemotherapy regimens."
"This meta-analysis confirms robustly the prognostic value of TILs that we have previously reported in TNBC patients treated with chemotherapy and expands it to patients treated without chemotherapy," says Sarah Flora Jonas, Ph.D., a statistician at Gustave Roussy and co-first author of the study. "Future studies may allow the use of this biomarker along with standard clinicopathological factors to inform treatment decisions in TNBC patients."
"Of interest, the first report suggesting that an increased number of immune cells being associated with better prognosis in breast cancer patients was described by doctors at Mayo Clinic more than 100 years ago," says Roberto Salgado, M.D., co-chair of the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group and co-lead of the study. "It took a global effort and a century later to reexamine this biomarker and bring it closer to application in patient care."
"TILs are not currently measured or reported in the routine examination of tissue samples of breast cancer," says co-senior author, Matthew Goetz, M.D., a medical oncologist at Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center and the Erivan K. Haub Family Professor of Cancer Research Honoring Richard F. Emslander, M.D. "While prior studies have focused on measuring TILs in people treated with chemotherapy, this is the largest study to comprehensively demonstrate that the presence of TILs influences the natural behavior of breast cancer in people who have surgery and/or radiation with no additional medical treatment."
For this study, Mayo Clinic and Gustave Roussy researchers, in collaboration with the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group, led 11 additional groups to collect data on 1,966 participants with early-stage TNBC who only underwent surgery with or without radiation therapy but did not receive chemotherapy. The participants had been followed for a median of 18 years. The results showed that higher levels of TILs in breast cancer tissue were associated with lower recurrence rates among participants with early-stage TNBC.
"Five years after surgery, 95% of participants with small tumors, stage 1 TNBC, and whose tumors had high TILs were alive, compared to 82% of patients whose tumors had low TILs. Importantly, the breast cancer recurrence rate was significantly lower among patients whose tumors had high TILs," says co-senior author, Stefan Michiels, Ph.D., head of Oncostat team, Gustave Roussy, Inserm U1018, University Paris-Saclay. "With nearly 2,000 participants involved in the study, we have now assembled the largest international cohort across three continents of people with TNBC in which the primary treatment was surgery without chemotherapy."
"The results of this study could lead to a recommendation to include TILs in the pathology reports of early-stage TNBC worldwide, as it has the potential to inform clinicians and patients when they discuss treatment options," says Dr. Salgado.
Furthermore, this biomarker would only require a visual evaluation by a pathologist looking through a microscope, meaning there are no additional costs associated with identifying the presence of immune cells. This could be particularly beneficial to regions with limited resources, adds Dr. Leon-Ferre.
Most people with early-stage TNBC undergo chemotherapy either before or after surgery, including people with stage 1 breast cancer. Most people receive multiple chemotherapy drugs in combination, which can cause significant side effects. Currently, the main factors taken into consideration to determine the course of chemotherapy treatment for each person are the tumor size and the presence of lymph node metastases. However, the authors identified that the number of TILs further influences the risk of future recurrence.
The researchers plan to evaluate TILs as biomarkers in prospective clinical trials evaluating chemotherapy selection based on TIL levels. Ongoing efforts to conduct additional research with other potential biomarkers are underway.
For a complete list of authors, disclosures and funding, see the full paper.
###
About Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center
Designated as a comprehensive cancer center by the National Cancer Institute, Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center is defining new boundaries in possibility, focusing on patient-centered care, developing novel treatments, training future generations of cancer experts and bringing cancer research to communities. At Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center, a culture of innovation and collaboration is driving research breakthroughs that are changing approaches to cancer prevention, screening and treatment, and improving the lives of cancer survivors.
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization committed to innovation in clinical practice, education and research, and providing compassion, expertise and answers to everyone who needs healing. Visit the Mayo Clinic News Network for additional Mayo Clinic news.
About Gustave Roussy
Ranked as the leading French and European Cancer Centre and fourth in the world, Gustave Roussy is a centre with comprehensive expertise and is devoted entirely to patients suffering with cancer. The Institute is a founding member of the Paris Saclay Cancer Cluster. It is a source of diagnostic and therapeutic advances. It caters for almost 50,000 patients per year and its approach is one that integrates research, patient care and teaching. It is specialized in the treatment of rare cancers and complex tumors and it treats all cancers in patients of any age. Its care is personalized and combines the most advanced medical methods with an appreciation of the patient’s human requirements. In addition to the quality of treatment offered, the physical, psychological and social aspects of the patient’s life are respected. 4,100 professionals work on its two campuses: Villejuif and Chevilly-Larue. Gustave Roussy brings together the skills, which are essential for the highest quality research in oncology: 40% of patients treated are included in clinical studies. For further information: www.gustaveroussy.fr/en, Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram
END
New study finds triple-negative breast cancer tumors with an increase in immune cells have lower risk of recurrence after surgery
2024-04-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights into how tumors on adrenal glands develop
2024-04-02
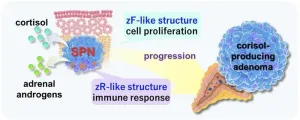
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Kyushu University's Faculty of Medical Sciences report on new insights into the mechanisms of how adrenal gland tumors are formed. The team identified a new type of tumor cell population that they termed 'steroids-producing nodules' or SPNs, that exhibits the unique characteristic of producing two different hormones. Specific structures in SPNs were found to lead to cortisol-producing adenomas, or CPAs, noncancerous tumors that produce excessive cortisol.
Their findings, published in eBioMedicine, ...
Ask Chat GPT about your radiation oncology treatment
2024-04-02
· AI responses to common patient questions were on par or exceeded answers from professional societies
· Goal also to reduce clinician workload and burnout
· More than 60% of cancer patients require radiation oncology treatment
CHICAGO --- Cancer patients about to undergo radiation oncology treatment have lots of questions. Could ChatGPT be the best way to get answers?
A new Northwestern Medicine study tested a specially designed ChatGPT to see if it could successfully provide answers to patients’ common questions about radiation oncology. Patients may be too overwhelmed to address all their concerns during a clinical visit ...
Surveillance colonoscopy findings in older adults with a history of colorectal adenomas
2024-04-02
About The Study: In this study of 9,740 surveillance colonoscopies among 9,601 adults ages 70 to 85 with prior colorectal adenoma, colorectal cancer detection was rare regardless of prior adenoma finding, whereas the advanced neoplasia yield was 12% overall. Yields were higher among those with a prior advanced adenoma than among those with prior nonadvanced adenoma and did not increase significantly with age. These findings can help inform whether to continue surveillance colonoscopy in older adults.
Authors: Jeffrey K. Lee, M.D., M.P.H., of Kaiser Permanente Northern California in Oakland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Metabolic profile and long-term risk of depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders
2024-04-02
About The Study: High levels of glucose and triglycerides and low levels of high-density lipoprotein were associated with future risk of depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders in this study of more than 200,000 participants. These findings may support closer follow-up of individuals with metabolic dysregulations for the prevention and diagnosis of psychiatric disorders.
Authors: Charilaos Chourpiliadis, M.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding ...
Wound treatment gel fights the battle against antibacterial resistance
2024-04-02
WASHINGTON, April 2, 2024 – Hydrogels are popular for use in skin ailments and tissue engineering. These polymer-based biocompatible materials are useful for their abilities to retain water, deliver drugs into wounds, and biodegrade. However, they are complicated to manufacture and not very resilient to external forces like rubbing against clothing, sheets, or wound dressings. They are also not inherently able to battle bacterial infections, so they are often infused with antimicrobial drugs or metal ions, which can ...
Finding the connective tissue of soft materials
2024-04-02
The human body uses adhesion to hold itself together. For example, a tendon attaches muscle to bone, while connective tissue attaches muscle to skin.
Hydrogel-based soft materials are based on these biomimetic mechanical behaviors, which makes them a revolutionary design of biomedical implants, human-machine interfaces, and bio-inspired soft robots. However, there are limitations to overcome before they are able to fully replace commonly used hard materials.
Qihan Liu, assistant professor of mechanical and materials ...
Scientists link certain gut bacteria to lower heart disease risk
2024-04-02
Changes in the gut microbiome have been implicated in a range of diseases including type 2 diabetes, obesity, and inflammatory bowel disease. Now, a team of researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard along with Massachusetts General Hospital has found that microbes in the gut may affect cardiovascular disease as well. In a study published in Cell, the team has identified specific species of bacteria that consume cholesterol in the gut and may help lower cholesterol and heart disease risk in people.
Members of Ramnik Xavier’s lab, Broad’s Metabolomics Platform, and ...
Gene analysis generates spatial map of intestinal cells and traces their trajectories during gut inflammation
2024-04-02
Cells within the intestines perform various roles including nutrient absorption, sensing, and maintaining homeostasis. Certain chronic disorders are distinctly characterized by gut inflammation, which disrupts intestinal cells and can lead to a remodeling of the gut and the introduction of new immune cells. To better understand the types of cells and their positioning within the intestines, researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, in collaboration with investigators ...
Gloom and doom warnings about climate change do not work
2024-04-02
If you want to spread a message about climate change and global warming, you need to adapt the message according to your intended audience and what you want to achieve.
Researchers have now developed an app to help people who want to spread their message on climate issues to ensure they generate the most support possible – be they researchers, politicians, various decision makers or legislators.
Huge survey involving 63 countries
59,000 people participated in surveys as part of the work on creating the app, and Norway was among ...
The 2024 Career Optimism Index® study highlights shift from the great resignation to a great talent stagnation – and how employers can break through
2024-04-02
Today the University of Phoenix Career Institute® released its 2024 Career Optimism Index®, a comprehensive study examining the state of American workers' career trajectories and sentiments about the future of their job and career opportunities. This year's Index, the fourth consecutive year it has been fielded, reveals that workers and employers are facing a critical moment of talent stagnation in the workplace.
More than half (53%) of Americans report feeling easily replaceable in their job position and 64% of workers say their company does not offer opportunities ...