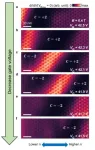
(Press-News.org) An international research team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has taken the first atomic-resolution images and demonstrated electrical control of a chiral interface state – an exotic quantum phenomenon that could help researchers advance quantum computing and energy-efficient electronics.
The chiral interface state is a conducting channel that allows electrons to travel in only one direction, preventing them from being scattered backwards and causing energy-wasting electrical resistance. Researchers are working to better understand the properties of chiral interface states in real materials but visualizing their spatial characteristics has proved to be exceptionally difficult.
But now, for the first time, atomic-resolution images captured by a research team at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley have directly visualized a chiral interface state. The researchers also demonstrated on-demand creation of these resistance-free conducting channels in a 2D insulator.
Their work, which was reported in the journal Nature Physics, is part of Berkeley Lab’s broader push to advance quantum computing and other quantum information system applications, including the design and synthesis of quantum materials to address pressing technological needs.
“Previous experiments have demonstrated that chiral interface states exist, but no one has ever visualized them with such high resolution. Our work shows for the first time what these 1D states look like at the atomic scale, including how we can alter them – and even create them,” said first author Canxun Zhang, a former graduate student researcher in Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division and the Department of Physics at UC Berkeley. He is now a postdoctoral researcher at UC Santa Barbara.
Chiral interface states can occur in certain types of 2D materials known as quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulators that are insulators in bulk but conduct electrons without resistance at one-dimensional “edges” – the physical boundaries of the material and interfaces with other materials.
To prepare chiral interface states, the team worked at Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry to fabricate a device called twisted monolayer-bilayer graphene, which is a stack of two atomically thin layers of graphene rotated precisely relative to one another, creating a moiré superlattice that exhibits the QAH effect.
In subsequent experiments at the UC Berkeley Department of Physics, the researchers used a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) to detect different electronic states in the sample, allowing them to visualize the wavefunction of the chiral interface state. Other experiments showed that the chiral interface state can be moved across the sample by modulating the voltage on a gate electrode placed underneath the graphene layers. In a final demonstration of control, the researchers showed that a voltage pulse from the tip of an STM probe can “write” a chiral interface state into the sample, erase it, and even rewrite a new one where electrons flow in the opposite direction.
The findings may help researchers build tunable networks of electron channels with promise for energy-efficient microelectronics and low-power magnetic memory devices in the future, and for quantum computation making use of the exotic electron behaviors in QAH insulators.
The researchers intend to use their technique to study more exotic physics in related materials, such as anyons, a new type of quasiparticle that could enable a route to quantum computation.
“Our results provide information that wasn’t possible before. There is still a long way to go, but this is a good first step,” Zhang said.
The work was led by Michael Crommie, a senior faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division and physics professor at UC Berkeley.
Tiancong Zhu, a former postdoctoral researcher in the Crommie group at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley, contributed as co-corresponding author and is now a physics professor at Purdue University.
The Molecular Foundry is a DOE Office of Science user facility at Berkeley Lab.
This work was supported by the DOE Office of Science. Additional funding was provided by the National Science Foundation.
###
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) is committed to delivering solutions for humankind through research in clean energy, a healthy planet, and discovery science. Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest problems are best addressed by teams, Berkeley Lab and its scientists have been recognized with 16 Nobel Prizes. Researchers from around the world rely on the Lab’s world-class scientific facilities for their own pioneering research. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
END
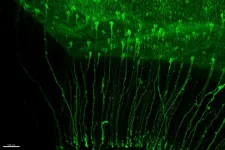
The development of the cerebral cortex largely depends on the stem cells responsible for generating neurons, known as Radial Glial Cells. Until now, it was considered that these stem cells generated neurons following a simple process, that is, a single cell lineage. However, a study led by the Neurogenesis and cortical expansion laboratory, headed by researcher Víctor Borrell at the Institute for Neurosciences (IN), a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the Miguel Hernández University (UMH) of Elche, has discovered not only that there are many more types of Radial Glial Cells than previously thought, but ...
More synchrony between parents and children may not always be better, new research has revealed.
For the first time a new University of Essex study looked at behavioural and brain-to-brain synchrony in 140 families with a special focus on attachment.
It looked at how they feel and think about emotional bonds whilst measuring brain activity as mums and dads solved puzzles with their kids.
The study – published in Developmental Science - discovered that mums with insecure attachment traits showed more brain-to-brain synchrony with their children.
Dr Pascal Vrticka, ...
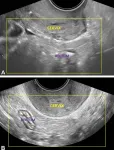
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound (SRU) expert consensus statement to improve endometriosis evaluation was published today in the journal Radiology.
Endometriosis is a common condition with substantial diagnostic delay, leading patients to experience pain, infertility, lost wages and interrupted relationships.
The consensus provides recommendations for augmenting routine pelvic ultrasounds through additional maneuvers and imaging to improve diagnosis of deep endometriosis.
Endometriosis, the presence of endometrium-like tissue outside the uterus, is a prevalent and potentially debilitating ...
Researchers have discovered a blood protein that could help detect which children will experience ongoing concussion symptoms more than two weeks after an injury.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the Journal of Neurotrauma, found the protein was a potential biomarker for delayed recovery from concussion in children.
For the study, blood samples were collected from children, aged five-18 years, who presented to the emergency department at The Royal Children’s Hospital less than 48 hours after a concussion.
Levels ...
Kent State University’s experimental archaeologists, along with those from several other universities, joined forces with the popular hunting, outdoors, and conservation media platform, MeatEater, Inc., for a unique animal processing experiment, shedding new light on ancient stone knives and showcasing the importance of testing and looking for equifinality. ‘Equifinality’ is when two or more distinct processes can lead to the same outcome or result.
The Kent State archaeologists included Professor Metin I. Eren, Ph.D.; Assistant Professor Michelle ...
WASHINGTON—New research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism finds a high prevalence of type D personality among people with hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Between 10-15% of people with treated hypothyroidism experience persistent symptoms despite achieving normal thyroid hormone levels, and the underlying causes are unclear.
Type D personality, which is characterized by pessimism, worry, stress, negative emotions and social withdrawal, is sometimes associated with poor health status and symptom burden, but this association has not previously ...
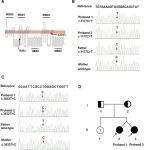
Researchers in China and Italy have made a significant breakthrough in understanding Dubin-Johnson syndrome (DJS), a rare inherited liver disorder. The team identified specific genetic mutations responsible for DJS in a pair of dizygotic twins, offering valuable insights into the cause of the disease and potentially improving diagnosis for patients with unclear symptoms.
DJS disrupts the liver's ability to eliminate waste products, leading to a buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment in the blood. This ...
Background and objectives
Sinonasal mucosal melanoma (SNMM) is a rare aggressive malignancy that presents with dismal outcomes and a high metastatic propensity. The prognostic factors as well as therapeutic regimens remain largely unknown due to the rarity of SNMM. This study aimed to assess the characteristics of SNMM patients associated with a better prognosis.
Methods
We performed an observational cross-sectional study to investigate the prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) therapy in 12 SNNM patients who were diagnosed at our institution and treated with anti-PD-L1 ...
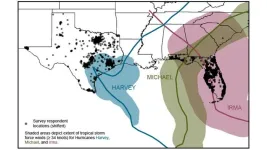
Rapid climate change is prompting adaptation to threats such as tropical cyclones, wildfires, and droughts—but relatively trivial adaptation actions may lull people into inaccurate perceptions of their personal risk. Researchers from the University of California, Irvine; Stanford University; and the University of California, Los Angeles surveyed 2,774 Texas and Florida residents about tropical cyclones—also known in North America as hurricanes—five times between 2017 and 2022. The survey ...
Virtue is a normative concept comprising a set of moral and social codes acceptable to society. Historically, in the West, especially in ancient Greek and Christian belief systems, virtue was viewed as "excellence" aspirational to all human beings. In contrast, the East, especially in a Confucian belief system, viewed it similarly but being aspirational to only select individuals, such as rulers. However, the rise of modern values and sociopolitical overhauls almost pushed the concept of ...