(Press-News.org) Bacteria in cancer unmasked - a closer look at our microscopic co-inhabitants
Researchers at the Netherlands Cancer Institute have compiled a detailed catalogue of bacteria living in cancer metastases. Having analyzed over 4000 tumors, they shed light on the diversity of these co-inhabitants and how they might interact with cancer cells and their surroundings. For example, certain bacteria were linked to a worse response to immunotherapy. This study paves the way to a better understanding of how bacteria help or hinder cancer (therapy), and how we can use this for patients’ advantage. The researchers publish their findings today in the scientific journal Cell.
On and in our bodies live billions of microorganisms: bacteria, viruses and yeasts - our microbiome. We need them, and they need us. Bacteria help us digest our food, for example, and cooperate with our immune system in the fight against pathogens. Gut bacteria in particular have been extensively studied, including in the context of cancer. For example, they can influence the effectiveness of immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
Metastases
But these tiny co-inhabitants also house outside the gut. Bacteria are found in tumors, for example. With new techniques, researchers are getting better at finding out which microbes they are. But how bacteria get to a tumor and what exactly they do there remains largely unknown, making it unclear how important they are to disease and the effect of treatments.
26 cancer types
Because many patients eventually die from metastases, and many treatments target them, the research groups of Emile Voest and Lodewyk Wessels took a closer look at those metastases. After all, little was known about bacteria in these tumors. Together with their colleagues at, among others, the Netherlands Cancer Institute and Oncode Institute they have now mapped which bacteria are present in cancer metastases. Both groups are
In tissue from more than 4,000 metastases of 26 types of cancer, the researchers analyzed the code of the DNA present. From that genetic material you can see not only which human cells are there, but also which bacteria - because these also have DNA. For this purpose they used clinical information and DNA data generated by Hartwig Medical Foundation.
Terabytes
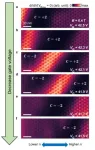
With that unimaginably large mountain of information (400 terabytes), they used computer power to figure out which bacteria congregate in which places (see figure). This required a lot of clever programming, because there is relatively little bacterial DNA in such a piece of tissue.
"Surprisingly, it’s not just metastases from colon cancer that contain a lot of bacteria," says researcher Thomas Battaglia. One might expect that because most of our bacteria reside in the colon, from where they could possibly travel along during metastasis to elsewhere in the body. “Also, which bacteria are present in a metastasis is strongly related to the location in the body, the conditions there, and the cancer type.”
Therapy response
They also discovered a link between bacteria and therapy efficacy. Patients with lung cancer and Fusobacterium in their metastasis, for example, responded worse to immunotherapy than peers without that bacteria. Thomas: "We also noted that the more diverse the bacterial community, the more active the adjacent tumor cells."
"Our work opens doors for exploring new forms of treatments, for example against bacteria that might help the tumor," co-author Iris Mimpen says. "It helps us understand how the complex environment of tumors works, an environment in which all kinds of cells - including bacteria - live together and influence each other."
This research was financially supported by the AVL Foundation, KWF Dutch Cancer Society and Oncode Institute.
END
Bacteria in cancer unmasked
Researchers at the Netherlands Cancer Institute have compiled a detailed catalogue of bacteria living in cancer metastases.
2024-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Top factors in nurses ending health care employment between 2018 and 2021
2024-04-09
About The Study: The top contributing factors for leaving health care employment were planned retirement, burnout, insufficient staffing, and family obligations in this cross-sectional study of 7,887 nurses. The leading reasons signal opportunities for employers to reattract an existing nurse workforce and retain currently employed nurses.
Authors: K. Jane Muir, Ph.D., R.N., F.N.P.-B.C., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Firearm ownership and support for political violence in the United States
2024-04-09
About The Study: In this survey study with 12,000 participants, firearm owners were only moderately more supportive of political violence than nonowners. Recent purchasers and owners who always or nearly always carried firearms in public were more supportive of and willing to engage in political violence than other subsets of firearm owners. These findings can guide risk-based prevention efforts.
Authors: Garen J. Wintemute, M.D., M.P.H., of the UC Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Nurses cite employer failures as their top reason for leaving
2024-04-09
PHILADELPHIA (EMBARGOED UNTIL APRIL 9, 2024 at 11:00 AM EST) – A new study from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing’s Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research (CHOPR) – published in JAMA Network Open today – showed that, aside from retirements, poor working conditions are the leading reasons nurses leave healthcare employment. These study findings come at a time when hospital executives cite staffing problems as their most pressing concern.
“Prior studies evaluate nurses’ ...
New technique lets scientists create resistance-free electron channels
2024-04-09
An international research team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has taken the first atomic-resolution images and demonstrated electrical control of a chiral interface state – an exotic quantum phenomenon that could help researchers advance quantum computing and energy-efficient electronics.
The chiral interface state is a conducting channel that allows electrons to travel in only one direction, preventing them from being scattered backwards and causing energy-wasting electrical resistance. Researchers are working to better understand the properties of chiral interface states in real materials ...
Study uncovers multiple lineages of stem cells contributing to neuron production
2024-04-09
The development of the cerebral cortex largely depends on the stem cells responsible for generating neurons, known as Radial Glial Cells. Until now, it was considered that these stem cells generated neurons following a simple process, that is, a single cell lineage. However, a study led by the Neurogenesis and cortical expansion laboratory, headed by researcher Víctor Borrell at the Institute for Neurosciences (IN), a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the Miguel Hernández University (UMH) of Elche, has discovered not only that there are many more types of Radial Glial Cells than previously thought, but ...
More synchrony between parents and children not always better
2024-04-09
More synchrony between parents and children may not always be better, new research has revealed.
For the first time a new University of Essex study looked at behavioural and brain-to-brain synchrony in 140 families with a special focus on attachment.
It looked at how they feel and think about emotional bonds whilst measuring brain activity as mums and dads solved puzzles with their kids.
The study – published in Developmental Science - discovered that mums with insecure attachment traits showed more brain-to-brain synchrony with their children.
Dr Pascal Vrticka, ...
New consensus statement aims to improve endometriosis evaluation
2024-04-09
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound (SRU) expert consensus statement to improve endometriosis evaluation was published today in the journal Radiology.
Endometriosis is a common condition with substantial diagnostic delay, leading patients to experience pain, infertility, lost wages and interrupted relationships.
The consensus provides recommendations for augmenting routine pelvic ultrasounds through additional maneuvers and imaging to improve diagnosis of deep endometriosis.
Endometriosis, the presence of endometrium-like tissue outside the uterus, is a prevalent and potentially debilitating ...
Blood protein could help detect delayed concussion recovery in children
2024-04-09
Researchers have discovered a blood protein that could help detect which children will experience ongoing concussion symptoms more than two weeks after an injury.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the Journal of Neurotrauma, found the protein was a potential biomarker for delayed recovery from concussion in children.
For the study, blood samples were collected from children, aged five-18 years, who presented to the emergency department at The Royal Children’s Hospital less than 48 hours after a concussion.
Levels ...
Experimental collaboration between archaeologists and MeatEater highlights the prevalence of equifinality in archaeological interpretation
2024-04-09
Kent State University’s experimental archaeologists, along with those from several other universities, joined forces with the popular hunting, outdoors, and conservation media platform, MeatEater, Inc., for a unique animal processing experiment, shedding new light on ancient stone knives and showcasing the importance of testing and looking for equifinality. ‘Equifinality’ is when two or more distinct processes can lead to the same outcome or result.
The Kent State archaeologists included Professor Metin I. Eren, Ph.D.; Assistant Professor Michelle ...
People with hypothyroidism and type D personality may be more likely to experience poor treatment outcomes
2024-04-09
WASHINGTON—New research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism finds a high prevalence of type D personality among people with hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Between 10-15% of people with treated hypothyroidism experience persistent symptoms despite achieving normal thyroid hormone levels, and the underlying causes are unclear.
Type D personality, which is characterized by pessimism, worry, stress, negative emotions and social withdrawal, is sometimes associated with poor health status and symptom burden, but this association has not previously ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Bacteria in cancer unmaskedResearchers at the Netherlands Cancer Institute have compiled a detailed catalogue of bacteria living in cancer metastases.